|
Hajdúnánás District
Hajdúnánás () is a district in north-western part of Hajdú-Bihar County. ''Hajdúnánás'' is also the name of the town where the district seat is found. The district is located in the Northern Great Plain, Northern Great Plain Statistical Region. This district is a part of Hajdúság historical and geographical region. Geography Hajdúnánás District borders with Tiszavasvári District ''(Szabolcs-Szatmár-Bereg County)'' to the north, Hajdúböszörmény District to the southeast, Balmazújváros District to the south, Mezőcsát District and Tiszaújváros District ''(Borsod-Abaúj-Zemplén County)'' to the west. The number of the inhabited places in Hajdúnánás District is 6. Municipalities The district has 2 List of cities and towns of Hungary, towns and 4 villages. (ordered by population, as of 1 January 2012) The bolded municipalities are cities. Demographics In 2011, it had a population of 29,614 and the population density was 54/km². Ethnicity Besides the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Districts Of Hungary
Districts of Hungary are the second-level divisions of Hungary after counties. They replaced the 175 subregions of Hungary in 2013. There are 174 districts in the 19 counties, and there are 23 districts in Budapest. Districts of the 19 counties are numbered by Arabic numerals and named after the district seat, while districts of Budapest are numbered by Roman numerals and named after the historical towns and neighbourhoods. In Hungarian, the districts of the capital and the rest of the country hold different titles. The districts of Budapest are called ''kerületek'' (lit. district, pl.) and the districts of the country are called ''járások.'' By county Baranya County Bács-Kiskun County Békés County Borsod-Abaúj-Zemplén County Csongrád-Csanád County Fejér County Győr-Moson-Sopron County Hajdú-Bihar County Heves County Jász-Nagykun-Szolnok County Komárom-Esztergom County Nógrád County Pest County Somogy C ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polgár, Hungary
Polgár is a city in the administrative county of Hajdú-Bihar in eastern Hungary. This is a town with 8,598 inhabitants at the tri–point of 3 counties at the temporary end of the No. 3 motorway. Its natural vegetation is part of the Tiszántúl district, and the birds are the most valuable of its fauna. It is rich in fish and game (pheasant, wild duck, partridge, boar, hare, deer). In the vicinity of Polgár, various Bronze Age items were excavated. The Blessed Virgin church was built from 1852 to 1856 in a neo-Classical style according to plans by József Hild. In 1944, it was blown up, then it was re–constructed from 1948 to 1958. The Kálvária group of buildings from 1769 is a listed monument including the Polonkai House. The town is picturesque as the streets of this market town preserve the characteristics of the folk architecture of Matyóland. Health and spa facilities include a medicinal and open-air bath and water sport facilities. A boating lake and a 20 hectare par ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reformed Church In Hungary
The Reformed Church in Hungary (, MRE, ) is the largest Protestant church in Hungary, with parishes also among the Hungarian diaspora abroad. It is made up of 1,249 congregations in 27 presbyteries and four church districts and has a membership of over 1.6 million, making it the second largest church in Hungary, behind the Catholic Church. As a Continental Reformed church, its doctrines and practices reflect a Calvinist theology, for which the Hungarian term is ' (). The Hungarian Reformed Church became the symbol of national Hungarian culture, since it led to the translation of the Bible into the Hungarian language by Hussite pastors, and contributed to the education of the population through its school system. History The Reformation spread to Hungary during the 16th century. In Geneva, Switzerland, the French reformer John Calvin formulated the doctrines of the Reformed Church, and his followers spread the Reformed (Calvinist) gospel across Europe. As a result of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hungarian Greek Catholic Church
The Hungarian Greek Catholic Church or the Byzantine Catholic Church in Hungary is a '' sui iuris'' (autonomous) Eastern Catholic church based in Hungary. As a particular church of the Catholic Church, it is in full communion with the Holy See. Its liturgical usage is that of the Byzantine Rite in the Hungarian language. History Hungary's Greek Catholics were originally concentrated in what is now northeastern Hungary. This region was historically inhabited by Byzantine Rite Christians from the Carpathian Mountains (Ruthenians and Romanians). Serbs fleeing the Turkish advance arrived later in what was then Hungary, but most stayed in the area that is now part of Serbia. Later still, when the Turks were driven back from Vienna in 1683 and from Buda and central Hungary in 1686, Ruthenians and Slovaks settled in the abandoned lands of Hungary. They were cared for by the Ruthenian Eparchy of Mukacheve (Hungarian: ''Munkács''). In the 17-18th centuries, during the conflict wit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Roman Catholicism In Hungary
Hungarian Catholics, like elsewhere, are part of the worldwide Catholic Church under the spiritual leadership of the Pope in Rome. According to a 2019 survey by Eurobarometer, 62% of Hungarians consider themselves Catholics. The Latin Church in the country is divided into 12 dioceses, including 4 archdioceses. In addition, there is a Latin territorial abbey and a separate '' sui juris'' particular Church for those who adhere to the Byzantine Rite known as the Hungarian Greek Catholic Church. Caritas Hungary is the social and humanitarian relief arm of the Church. Cardinal Péter Erdő was seen as a leading candidate in the 2025 papal conclave. He gained significant support and was the favored choice of conservative Catholic networks in the United States, Erdő participated in the papal conclave 2005 and the papal conclave 2013, which elected Benedict XVI and Francis. Latin hierarchy * Archdiocese of Esztergom-Budapest with its suffragan dioceses: ** Diocese of Győr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Romani People In Hungary
Romani people in Hungary (also known as roma or Romani Hungarians; ) are Hungary, Hungarian citizens of Romani people, Romani descent. According to the 2011 census, they comprise 3.18% of the total population, which alone makes them the largest minority in the country, although various estimations have put the number of Romani people as high as 8.8% of the total population. They are sometimes referred as Hungarian Gypsies, but that is sometimes considered to be a list of ethnic slurs, racial slur. History and language Origin The Romani people originate from North India, Northern India, from the northwestern Indian regions of Rajasthan and Punjab. The linguistic evidence has indisputably shown that roots of Romani language lie in India: the language has grammatical characteristics of Indo-Aryan languages and shares with them a big part of the basic lexicon, for example, body parts or daily routines. More exactly, Romani shares the basic lexicon with Hindi and Punjabi language, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
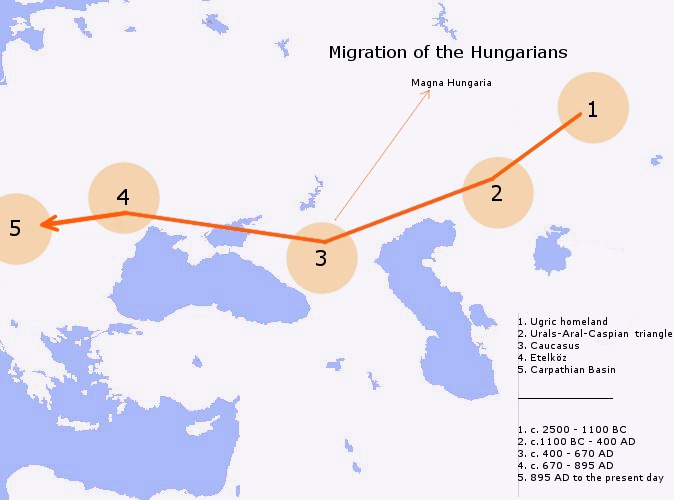
Hungarians
Hungarians, also known as Magyars, are an Ethnicity, ethnic group native to Hungary (), who share a common Culture of Hungary, culture, Hungarian language, language and History of Hungary, history. They also have a notable presence in former parts of the Kingdom of Hungary. The Hungarian language belongs to the Ugric languages, Ugric branch of the Uralic languages, Uralic language family, alongside the Khanty languages, Khanty and Mansi languages, Mansi languages. There are an estimated 14.5 million ethnic Hungarians and their descendants worldwide, of whom 9.6 million live in today's Hungary. About 2 million Hungarians live in areas that were part of the Kingdom of Hungary before the Treaty of Trianon in 1920 and are now parts of Hungary's seven neighbouring countries, Hungarians in Slovakia, Slovakia, Hungarians in Ukraine, Ukraine, Hungarians in Romania, Romania, Hungarians in Serbia, Serbia, Hungarians of Croatia, Croatia, Prekmurje, Slovenia, and Hungarians in Austria, Aust ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Population Density
Population density (in agriculture: Standing stock (other), standing stock or plant density) is a measurement of population per unit land area. It is mostly applied to humans, but sometimes to other living organisms too. It is a key geographical term.Matt RosenberPopulation Density Geography.about.com. March 2, 2011. Retrieved on December 10, 2011. Biological population densities Population density is population divided by total land area, sometimes including seas and oceans, as appropriate. Low densities may cause an extinction vortex and further reduce fertility. This is called the Allee effect after the scientist who identified it. Examples of the causes of reduced fertility in low population densities are: * Increased problems with locating sexual mates * Increased inbreeding Human densities Population density is the number of people per unit of area, usually transcribed as "per square kilometre" or square mile, and which may include or exclude, for example, ar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Atheism
Atheism, in the broadest sense, is an absence of belief in the Existence of God, existence of Deity, deities. Less broadly, atheism is a rejection of the belief that any deities exist. In an even narrower sense, atheism is specifically the position that there no deities. Atheism is contrasted with theism, which is the belief that at least one deity exists. Historically, evidence of atheistic viewpoints can be traced back to classical antiquity and Nāstika, early Indian philosophy. In the Western world, atheism declined after Christianity gained prominence. The 16th century and the Age of Enlightenment marked the resurgence of atheistic thought in Europe. Atheism achieved a significant position worldwide in the 20th century. Estimates of those who have an absence of belief in a god range from 500 million to 1.1 billion people. Atheist organizations have defended the autonomy of science, freedom of thought, secularism, and secular ethics. Arguments for atheism range from p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Irreligion
Irreligion is the absence or rejection of religious beliefs or practices. It encompasses a wide range of viewpoints drawn from various philosophical and intellectual perspectives, including atheism, agnosticism, religious skepticism, rationalism, secularism, and non-religious spirituality. These perspectives can vary, with individuals who identify as irreligious holding diverse beliefs about religion and its role in their lives. Relatively little scholarly research was published on irreligion until around the year 2010. Overview Over the past several decades, the number of secular persons has increased, with a rapid rise in the early 21st century, in many countries. In virtually every high-income country and many poor countries, religion has declined. Highly secular societies tend to be societally healthy and successful. Social scientists have predicted declines in religious beliefs and their replacement with more scientific/naturalistic outlooks (secularizati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Calvinism
Reformed Christianity, also called Calvinism, is a major branch of Protestantism that began during the 16th-century Protestant Reformation. In the modern day, it is largely represented by the Continental Reformed Christian, Presbyterian, Congregational, and Waldensians traditions, as well as parts of the Methodist, Anglican (known as "Episcopal" in some regions) and Baptist traditions. Reformed theology emphasizes the authority of the Bible and the sovereignty of God, as well as covenant theology, a framework for understanding the Bible based on God's covenants with people. Reformed churches emphasize simplicity in worship. Several forms of ecclesiastical polity are exercised by Reformed churches, including presbyterian, congregational, and some episcopal. Articulated by John Calvin, the Reformed faith holds to a spiritual (pneumatic) presence of Christ in the Lord's Supper. Emerging in the 16th century, the Reformed tradition developed over several genera ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Greek Catholicism
Greek Catholic Church or Byzantine-Catholic Church may refer to: * The Catholic Church in Greece * The Eastern Catholic Churches that use the Byzantine Rite, also known as the Greek Rite: ** The Albanian Greek Catholic Church ** The Belarusian Greek Catholic Church ** The Bulgarian Greek Catholic Church ** The Greek Catholic Church of Croatia and Serbia ** The Greek Byzantine Catholic Church ** The Hungarian Greek Catholic Church ** The Italo-Albanian Catholic Church ** The Macedonian Greek Catholic Church ** The Malta Greek Catholic Church ** The Melkite Greek Catholic Church ** The Romanian Greek Catholic Church ** The Russian Greek Catholic Church ** The Ruthenian Greek Catholic Church ** The Slovak Greek Catholic Church ** The Ukrainian Greek Catholic Church The Ukrainian Greek Catholic Church (UGCC) is a Major archiepiscopal church, major archiepiscopal ''sui iuris'' ("autonomous") Eastern Catholic Churches, Eastern Catholic church that is based in Ukraine. As a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |