|
Grosvenor Challenge Cup
The Grosvenor Challenge Cup, commonly known as the Grosvenor Cup, was a trophy presented by Lord Edward Grosvenor in 1923 to the winner of a light aircraft time trial competition.Dorman 1951, p. 188. Entries were initially restricted to British designs using aero engines of less than 150 horsepower. The first competitions were held at Lympne Aerodrome in Kent. The contest continued until 1935 with a break to 1949 when the Royal Aero Club resumed the races at Elmdon where the entry was opened to British and international designs with a weight less than 1,000 kilograms. For the 1949 event the contest had been briefly renamed to The Grosvenor Challenge Trophy Race, the 1950 event reverted to the former title. Grosvenor Lord Edward Grosvenor the former Royal Naval Air Service (RNAS) aviator and the youngest son of the Duke of Westminster presented the cup, his objective in offering the cup "is to give a chance to the low-power machine, one comparable to the average motor c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Edward Arthur Grosvenor
Lord Edward Arthur Grosvenor, MC (27 October 1892 – 26 August 1929) was a British aviator. Early life Grosvenor, also known as Ned, was born on 27 October 1892 to Hugh Grosvenor, 1st Duke of Westminster, and Katherine Caroline Cavendish, daughter of William Cavendish, 2nd Baron Chesham. Grosvenor was educated at Eton College before embarking on a career in the military. Military service After completing his education, Grosvenor joined the French Foreign Legion. In 1912, he left the legion and went on to be commissioned in the Royal Horse Guards. Joining the Royal Horse Guards from the Cheshire Yeomanry (with whom he served between 1910 and 1912), he began his service as a second lieutenant on probation. After the outbreak of the First World War, Grosvenor transferred to the Royal Flying Corps and served in France and Italy. His wartime service saw him awarded the Military Cross as well as Italy's Order of Saints Maurice and Lazarus. The report of the award of the Itali ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Francis McClean
Lieutenant-Colonel Sir Francis Kennedy McClean, (1 February 1876 – 11 August 1955) was a British civil engineer and pioneer aviator. Sir Francis was one of the founding members of the Royal Aero Club and one of the founders of naval aviation and amateur flying. Early life McClean was born on 1 February 1876, the son of astronomer Frank McClean, and was educated at Charterhouse before the Royal Indian Engineering College at Cooper's Hill. His grandfather John Robinson McClean, also a civil engineer, came from Belfast. McClean worked as a civil engineer in the Indian Public Works Department from 1898 to 1902 when he left to focus on aviation matters. Interest in astronomy Through is father's influence, McClean was an enthusiastic amateur astronomer and especially interested in solar eclipses. He was a volunteer assistant on the 30 August 1905 solar eclipse expedition to Palma, Majorca. McClean organized 2 astronomical expeditions: one to Flint Island for the 3 January 1908 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hucknall Aerodrome
Hucknall Aerodrome was a former general aviation and RAF aerodrome located north northwest of Nottingham, Nottinghamshire, England and west of Hucknall town. The aerodrome had been operated by the Merlin Flying Club since 1971, and then by Rolls-Royce Group plc. Before its closure, it was owned and operated by ITP Aero. Hucknall Aerodrome had a CAA Ordinary Licence (Number P507) that allowed daytime flights for the public transport of passengers or for flying instruction as authorised by the licensee and was not available for public transport passenger flights required to use a licensed aerodrome. It was a C.1916 grass aerodrome of significant historical importance. On 1 March 2015 the aerodrome closed indefinitely to be turned into a housing and industrial estate. History The Great War Hucknall Aerodrome dates to 1916 when it opened under No. 12 (Training) Group, 27th Wing, housing No. 15 Training Depot of the Royal Flying Corps (RFC) operating the Curtiss Jenny JN-4. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Armstrong Siddeley Genet
The Armstrong Siddeley Genet was a five-cylinder, air-cooled, radial engine for aircraft use built in the UK, first run in 1926. It developed 80 hp at 2,200 rpm in its final form and was a popular light aircraft powerplant. Following the company tradition with a slight deviation the engine was named after the Genet, a catlike animal of the same order but different family. Variants and applications Genet I Genet I producing 65 hp. * Avro 618 Ten * Avro Avian prototype * Blackburn Bluebird I * BFW M.23 * Cierva autogyros. C.9 and C.10 * Drzewiecki JD-2 * Fleet Fawn * Junkers A50 Junior * Medwecki and Nowakowski M.N.5 * Saro Cutty Sark * Southern Martlet * Westland-Hill Pterodactyl Genet II The Genet II produced 80 hp due to an increased compression ratio of 5.25:1. * ANEC IV * Avro Avian * Blackburn Bluebird II * Cierva C.19 autogyro * Darmstadt D-18 * de Havilland DH.60 Moth * Fairchild 21 * Klemm Kl 25 * Nicholas-Beazley NB-8G * Par ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
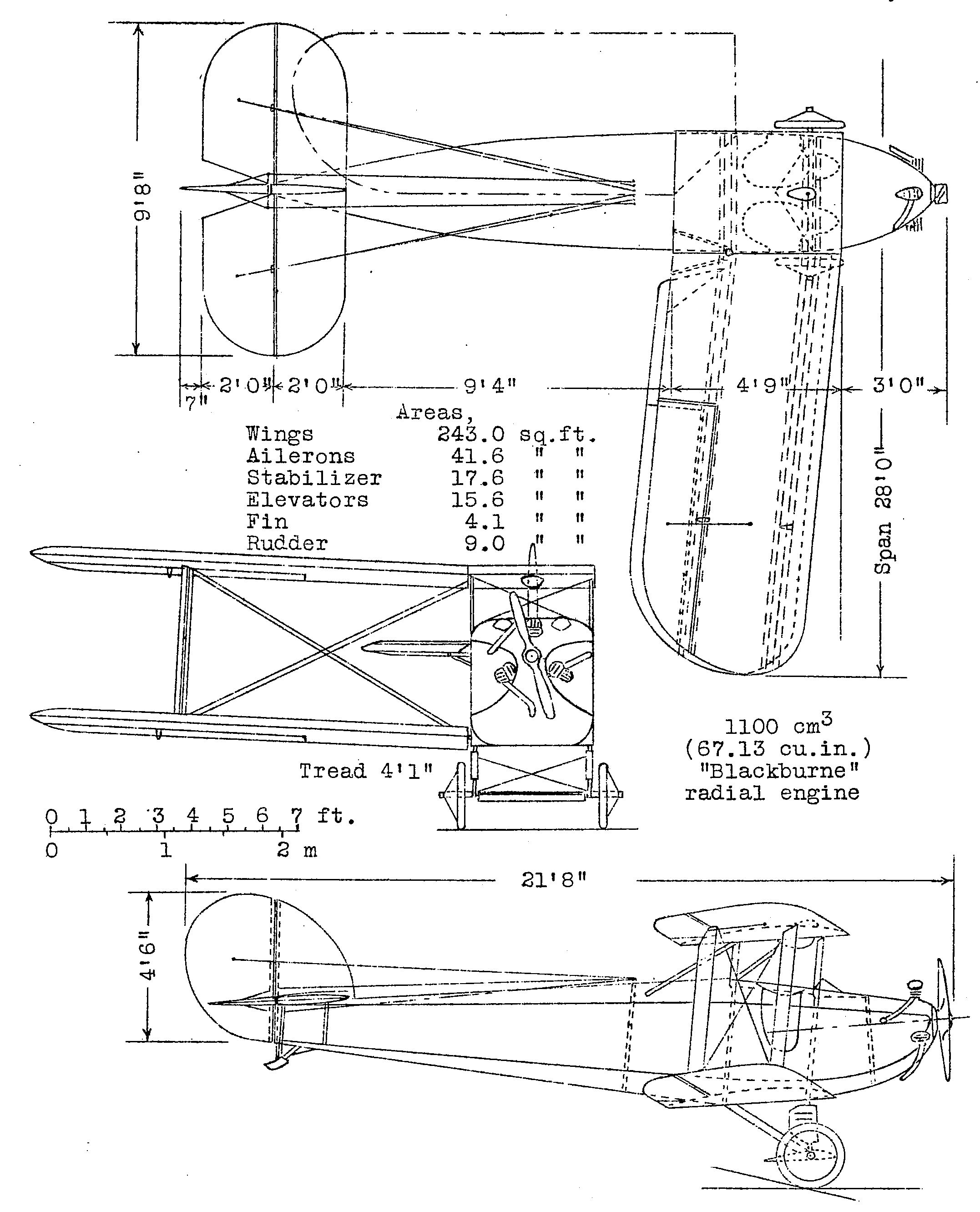
Blackburn Bluebird
The Blackburn L.1 Bluebird was a British single-engine biplane light trainer/tourer with side-by-side seating, built in small numbers by Blackburn Aircraft in the 1920s. Design and development The Bluebird L.1 was initially designed as a competitor in the Lympne light aircraft trials to be held in September 1924 for a low-powered two-seater, fitted with a 67 in³ (1,100 cc) Blackburne Thrush three-cylinder radial engine. The Bluebird was a wooden single-bay biplane, with folding wings and was fitted with a single side-by-side cockpit.Jackson 1974, p. 208. Although first flying in 1924,Taylor 1989, p. 157 problems with the engine, which failed to give the expected power, meant that it could not compete in the 1924 competition.Jackson 1968, pp. 190–191. It was realised that the machines that resulted from the 1923 and 1924 light aircraft trials were too low-powered for serious use. The Daily Mail sponsored a similar competition in September 1926, this time allowin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Robert Blackburn (aviation Pioneer)
Robert Blackburn, OBE, FRAeS (26 March 1885 – 10 September 1955) was an English aviation pioneer and the founder of Blackburn Aircraft. Early life and education Blackburn was born in Kirkstall, Leeds, Yorkshire, England to Kate (''née'' Naylor) and George William Blackburn, an engineer and works manager of William Green & Sons, lawnmower and steamroller manufacturers. He was the eldest of three brothers and attended Leeds Modern School and graduated in engineering at the University of Leeds, and built his first aircraft, a monoplane, in 1909. He made his first short flight on the sandy beach at Filey in the spring of 1909. The aircraft was badly damaged in 1910 when he attempted to make a turn. Career He moved to Filey and built a second monoplane which established his reputation as an aviation pioneer and in 1911 founded the Blackburn Aeroplane Company. In 1914 he married Tryphena Jessica Thompson, known as Jessy Blackburn and with her help and inheritance created t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John Stanley Chick
Air Commodore John Stanley Chick, (22 December 1897 – 21 January 1960), was a Welsh officer of the Royal Air Force, who began his aviation career as a World War I flying ace credited with 16 aerial victories. World War I service John Stanley Chick began his military career as a pioneer in the Royal Engineers in 1914. He transferred to the Royal Flying Corps in February 1917 as a Cadet at Denham. He was commissioned a probationary second lieutenant on 3 May 1917. Chick was granted his pilots certificate, No. 4735, on 27 May 1917. In November 1917, he was assigned to No. 11 Squadron. Piloting a two-seater Bristol F.2 Fighter, he scored all his triumphs in the first four and half months of 1918. On 12 March 1918, he drove down out of control a German observation plane and four Fokker Dr.I fighters. All five triumphs were scored on a single sortie. On 1 April 1918, he was promoted to lieutenant. On 15 May, he ended his victory string by setting a German observation plane afire ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bristol Cherub
The Bristol Cherub is a British two-cylinder, air-cooled, aircraft engine designed and built by the Bristol Aeroplane Company. Introduced in 1923 it was a popular engine for ultralight and small aircraft in the 1930s. Variants ;Cherub I :Initial direct drive version introduced in 1923. Bore and stroke of for a displacement of 67 cu in (1.095 L). at 2,500 rpm. ;Cherub II :Geared down (2:1) version of the Cherub I. ;Cherub III :An improved and slightly larger (1.228 L) direct drive version introduced in 1925. Applications Survivors An airworthy Messerschmitt M17 replica is owned and operated by the EADS Heritage Flight at Manching and is powered by an original Bristol Cherub III. Retrieved: 9 August 2009 Engines on display A preserved Bristol Cherub ...[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
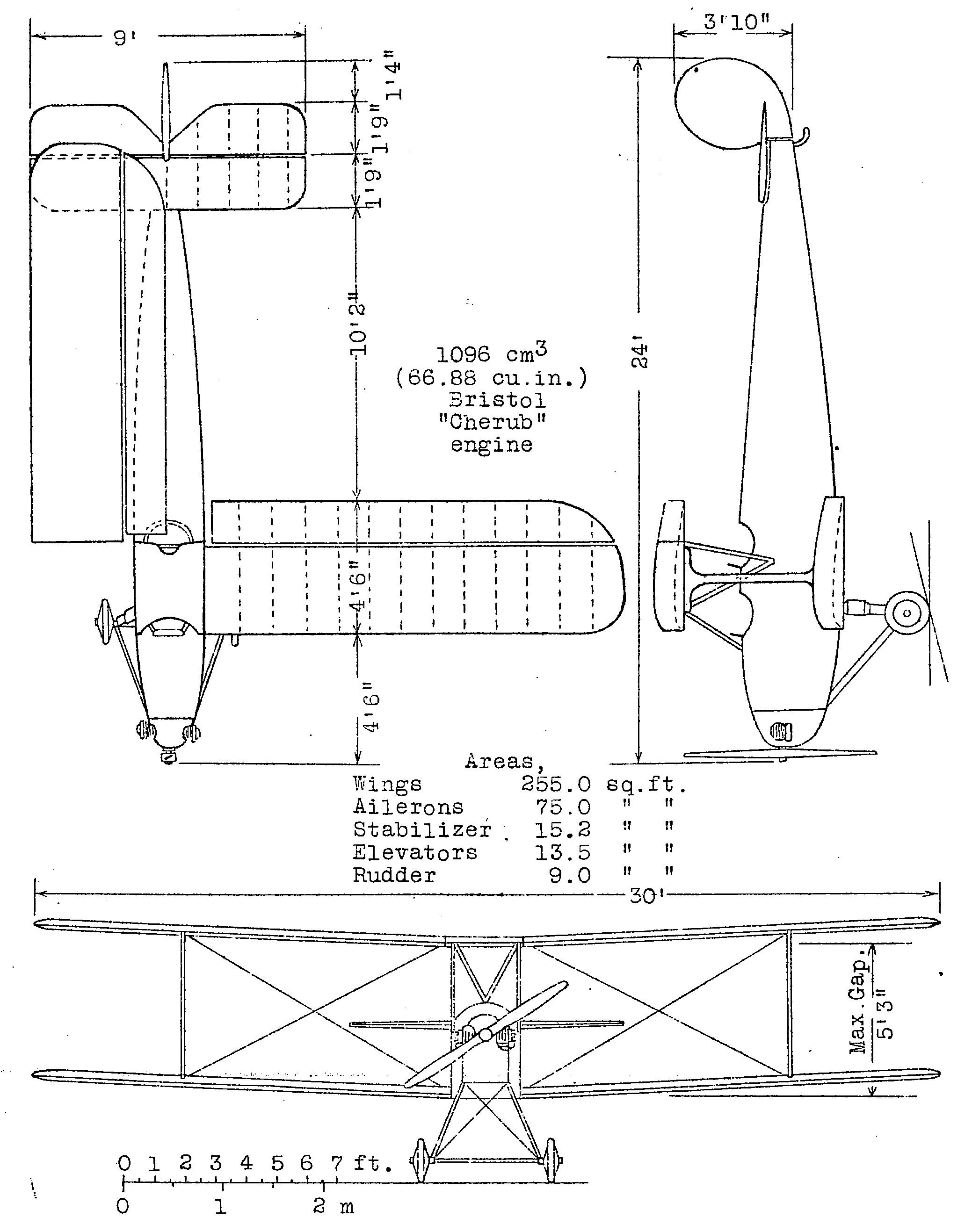
Avro Avis
The Avro 562 Avis was a two-seat light biplane designed and built by the A.V.Roe and Company Limited at Hamble for the 1924 Lympne Light Aeroplane Trials. Design and development The Avis was a single-bay unstaggered biplane with full-span ailerons on both upper and lower wings. It had a fixed landing gear with a tailskid and could be powered by a nose-mounted 32 hp Bristol Cherub II engine or a 35 hp Blackburne Thrush radial piston engine.Jackson 1990, p. 222. It had tandem open cockpits. First flown with the Thrush engine prior to the trials, it was refitted with the Cherub, and first flown with this engine by Bert Hinkler at Lympne on 30 September 1924. On the next day it won the Grosvenor Cup at a speed of 65.87 mph.Jackson 1990, pp. 222–223. For the 1926 trials it was re-engined with a 38 hp Blackburne Thrush, being eliminated after a forced landing. In 1927, it was re-engined again with a Bristol Cherub The Bristol Cherub is a British two-cylin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bert Hinkler
Herbert John Louis Hinkler (8 December 1892 – 7 January 1933), better known as Bert Hinkler, was a pioneer Australian aviator (dubbed "Australian Lone Eagle") and inventor. He designed and built early aircraft before being the first person to fly solo from England to Australia, completed on 22 February 1928, and the first person to fly solo across the Southern Atlantic Ocean. He married in 1932 at the age of 39, and died less than a year later after crashing into remote countryside near Florence, Italy during a solo flight record attempt. Early life Hinkler was born in Bundaberg, Queensland, the son of John William Hinkler, a Prussian-born stockman, and his wife Frances Atkins (née Bonney) Hinkler.''Pioneer airman's;memory lives on.'' Heidelberger Leader (Australia). NEWS; Pg. 14. 12 November 2003. In his childhood, Hinkler would observe ibis flying near a lake at his school. After gaining an understanding on the principles of flight, he constructed two gliders. In 1912 he ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alliott Verdon Roe
Sir Edwin Alliott Verdon Roe OBE, Hon. FRAeS, FIAS (26 April 1877 – 4 January 1958) was a pioneer English pilot and aircraft manufacturer, and founder in 1910 of the Avro company. After experimenting with model aeroplanes, he made flight trials in 1907–1908 with a full-size aeroplane at Brooklands, near Weybridge in Surrey, and became the first Englishman to fly an all-British machine a year later, with a triplane, on the Walthamstow Marshes. Early life Roe was born in Patricroft, Eccles, Lancashire, the son of Edwin Roe, a doctor, and Annie Verdon. He was the elder brother of Humphrey Verdon Roe. Roe left home when he was 14 to go to Canada where he had been offered training as a surveyor. When he arrived in British Columbia he discovered that a slump in the silver market meant that there was little demand for surveyors, so he spent a year doing odd jobs, then returned to England. There he served as an apprentice with the Lancashire & Yorkshire Railway. He later tried ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hastingleigh
Hastingleigh is a small civil parish centred on an escarpment of the Kent Downs. The parish is three miles east of Wye and ten miles south of Canterbury, extending to the hill-scape of the Devil's Kneading Trough, on the North Downs Way with views towards Ashford, Romney Marsh and the patchy remnant forest of The Weald (between the Greensand Ridge and South Downs). Amenities Common amenities are a garage and a public house. History Hastingleigh gets its name from the Haestingas, a Jutish tribe that lived in the area. The village was in existence before the Domesday Book and originally lay in the valley by the Church of England church ( St. Mary the Virgin) but following the plague, the main settlement was relocated to its current position. The church is made of stone, in the Early English style, and has a tower containing one bell: there is a brass to John Halke, d.1604, and Amia his wife, d.1596: The maternal grandparents of Dr. William Harvey; his mother Joane was born at ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |