|
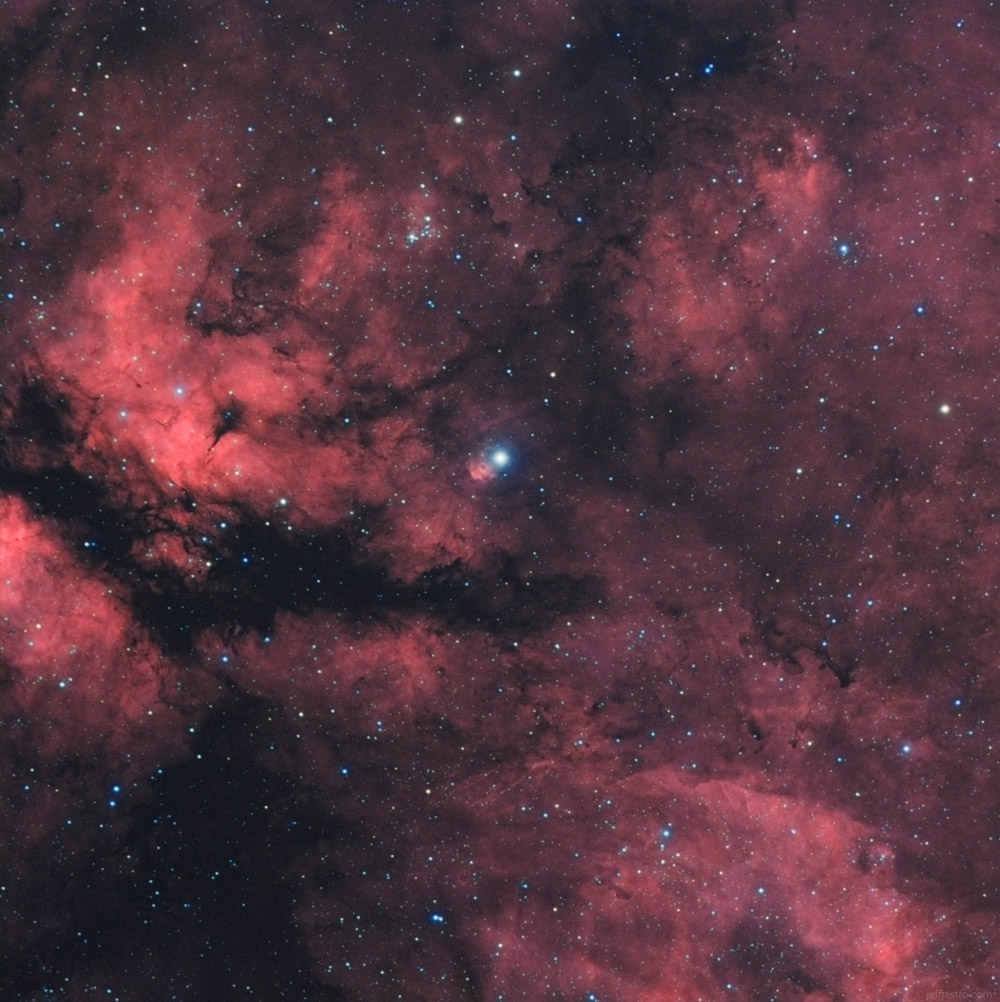
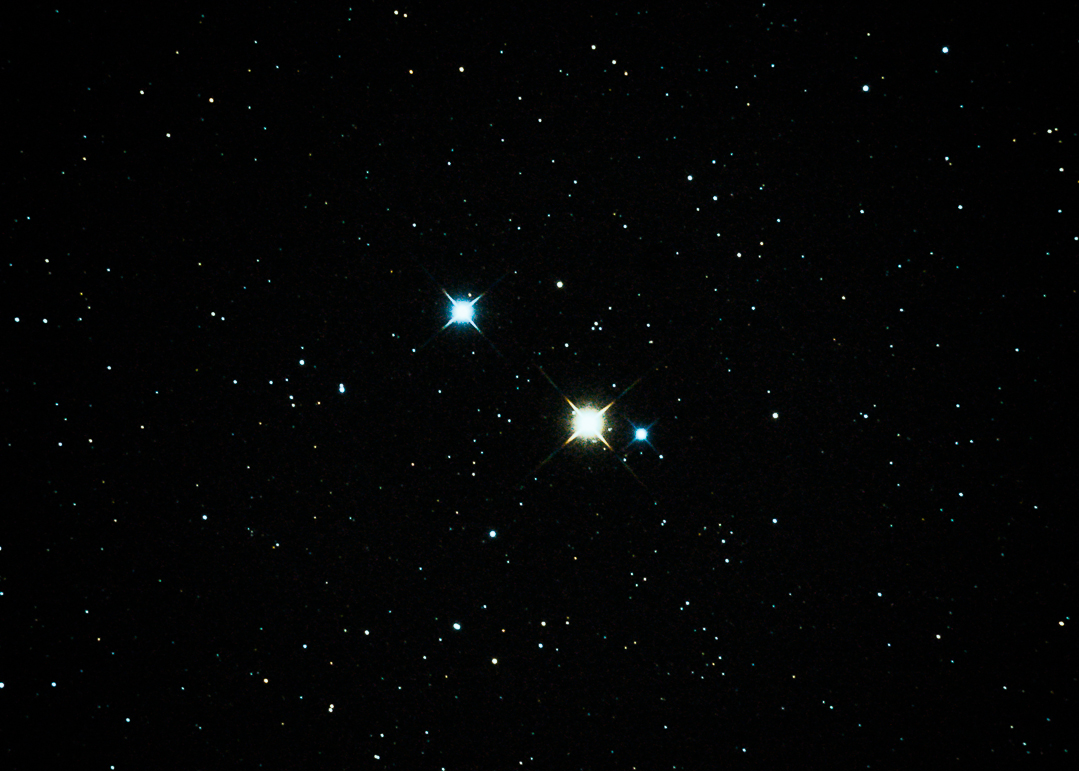
Gamma Cygni
Gamma Cygni (γ Cygni, abbreviated Gamma Cyg, γ Cyg), officially named Sadr , is a star in the northern constellation of Cygnus, forming the intersection of an asterism of five stars called the Northern Cross. Based upon parallax measurements obtained during the Hipparcos mission, it is approximately 1,800 light-years (560 parsecs) from the Sun. It forms the primary or 'A' component of a multiple star system designated WDS J20222+4015 (the secondary or 'BC' component is CCDM J20222+4015BC, a close pair of stars 40" away from γ Cygni). Nomenclature ''γ Cygni'' ( Latinised to ''Gamma Cygni'') is the star's Bayer designation. WDS J20222+4015A is its designation in the Washington Double Star Catalog. It bore the traditional name ''Sadr'' (also rendered ''Sadir'' or ''Sador''), derived from the Arabic صدر ''ṣadr'' "chest", the same word which gave rise to the star Schedar ( Alpha Cassiopeiae). In 2016, the International Astronomical Union organized a Working ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
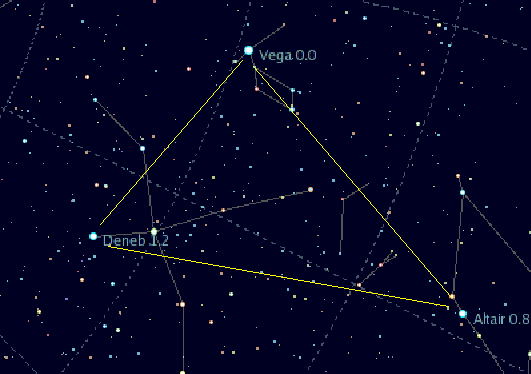
Cygnus (constellation)
Cygnus is a northern constellation on the plane of the Milky Way, deriving its name from the Latinized Greek word for swan. Cygnus is one of the most recognizable constellations of the northern summer and autumn, and it features a prominent asterism known as the Northern Cross (in contrast to the Southern Cross). Cygnus was among the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd century astronomer Ptolemy, and it remains one of the 88 modern constellations. Cygnus contains Deneb (ذنب, translit. ''ḏanab,'' tail)one of the brightest stars in the night sky and the most distant first-magnitude staras its "tail star" and one corner of the Summer Triangle. It also has some notable X-ray sources and the giant stellar association of Cygnus OB2. Cygnus is also known as the Northern Cross. One of the stars of this association, NML Cygni, is one of the largest stars currently known. The constellation is also home to Cygnus X-1, a distant X-ray binary containing a supergiant and unsee ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Latinisation Of Names
Latinisation (or Latinization) of names, also known as onomastic Latinisation, is the practice of rendering a ''non''-Latin name in a Latin style. It is commonly found with historical proper names, including personal names and toponyms, and in the standard binomial nomenclature of the life sciences. It goes further than romanisation, which is the transliteration of a word to the Latin alphabet from another script (e.g. Cyrillic). For authors writing in Latin, this change allows the name to function grammatically in a sentence through declension. In a scientific context, the main purpose of Latinisation may be to produce a name which is internationally consistent. Latinisation may be carried out by: * transforming the name into Latin sounds (e.g. for ), or * adding Latinate suffixes to the end of a name (e.g. for '' Meibom),'' or * translating a name with a specific meaning into Latin (e.g. for Italian ; both mean 'hunter'), or * choosing a new name based on some attri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Deneb
Deneb () is a first-magnitude star in the constellation of Cygnus, the swan. Deneb is one of the vertices of the asterism known as the Summer Triangle and the "head" of the Northern Cross. It is the brightest star in Cygnus and the 19th brightest star in the night sky, with an average apparent magnitude of +1.25. A blue-white supergiant, Deneb rivals Rigel as the most luminous first-magnitude star. However, its distance, and hence luminosity, is poorly known; its luminosity is somewhere between 55,000 and 196,000 times that of the Sun. Its Bayer designation is α Cygni, which is Latinised to Alpha Cygni, abbreviated to Alpha Cyg or α Cyg. Nomenclature ''α Cygni'' (Latinised to ''Alpha Cygni'') is the star's designation given by Johann Bayer in 1603. The traditional name ''Deneb'' is derived from the Arabic word for "tail", from the phrase ذنب الدجاجة ''Dhanab al-Dajājah'', or "tail of the hen". The IAU Working Group on Star Names has recogni ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
30 Cygni
30 Cygni is a class A5III (white giant) star in the constellation Cygnus. Its apparent magnitude is 4.83 and it is approximately 610 light years away based on parallax. The Bayer letter ο (omicron) has been variously applied to two or three of the stars 30, 31, and 32 Cygni. 30 Cygni has sometimes been designated as ο1 Cygni with the other two stars being ο2 and ο3 respectively. For clarity, it is preferred to use the Flamsteed designation A Flamsteed designation is a combination of a number and constellation name that uniquely identifies most naked eye stars in the modern constellations visible from southern England. They are named for John Flamsteed who first used them while co ... 30 Cygni rather than one of the Bayer designations. 30 Cygni is about six arc-minutes from 31 Cygni A and seven arc-minutes from 31 Cygni B. That pair is known as ο1 Cygni, while ο2 Cygni is a degree away. Both ο1 and ο2 are 4th magnitude stars. References {{Stars of Cyg ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Delta Cygni
Delta Cygni (δ Cygni, abbreviated Delta Cyg, δ Cyg) is a binary star of a combined third-magnitude in the constellation of Cygnus. It is also part of the Northern Cross asterism whose brightest star is Deneb. Based upon parallax measurements obtained during the Hipparcos mission, Delta Cygni is located roughly distant from the Sun. Delta Cygni's two components are designated Delta Cygni A (officially named Fawaris ) and B. More widely separated is a faint third component, a 12th magnitude star that is moving along with the others. Together they form a triple star system. Nomenclature ''δ Cygni'' ( Latinised to ''Delta Cygni'') is the binary's Bayer designation. The designations of the two components as ''Delta Cygni A'' and ''B'' derive from the convention used by the Washington Multiplicity Catalog (WMC) for multiple star systems, and adopted by the International Astronomical Union (IAU). Traditionally, Delta Cygni had no proper name. It belonged to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Girl (Chinese Constellation)
The Girl mansion (女宿, pinyin: Nǚ Xiù) is one of the Twenty-eight mansions of the Chinese constellations. It is one of the northern mansions of the Black Tortoise The Black Tortoise () is one of the Four Symbols of the Chinese constellations. Despite its English name, it is usually depicted as a tortoise entwined together with a snake. The name used in East Asian languages does not mention either anim .... Asterisms Notes {{Chinese constellation Chinese constellations ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chinese Astronomy
Astronomy in China has a long history stretching from the Shang dynasty, being refined over a period of more than 3,000 years. The ancient Chinese people have identified stars from 1300 BCE, as Chinese star names later categorized in the twenty-eight mansions have been found on oracle bones unearthed at Anyang, dating back to the mid-Shang dynasty. The core of the "mansion" (宿 ''xiù'') system also took shape around this period, by the time of King Wu Ding (1250–1192 BCE). Detailed records of astronomical observations began during the Warring States period (fourth century BCE) and flourished from the Han period onward. Chinese astronomy was equatorial, centered on close observation of circumpolar stars, and was based on different principles from those in traditional Western astronomy, where heliacal risings and settings of zodiac constellations formed the basic ecliptic framework. Joseph Needham has described the ancient Chinese as the most persistent and accurate ob ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Latin
Latin (, or , ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally a dialect spoken in the lower Tiber area (then known as Latium) around present-day Rome, but through the power of the Roman Republic it became the dominant language in the Italian region and subsequently throughout the Roman Empire. Even after the fall of Western Rome, Latin remained the common language of international communication, science, scholarship and academia in Europe until well into the 18th century, when other regional vernaculars (including its own descendants, the Romance languages) supplanted it in common academic and political usage, and it eventually became a dead language in the modern linguistic definition. Latin is a highly inflected language, with three distinct genders (masculine, feminine, and neuter), six or seven noun cases (nominative, accusative, genitive, dative, ablative, and vocative), five declensions, four verb conjug ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Al Achsasi Al Mouakket
Muḥammad al-Akhṣāṣī al-Muwaqqit ( ar, محمد الاخصاصي الموقت) was an Egyptian astronomer whose and catalogue of stars, ('Pearls of brilliance upon the solar operations'), was written at Cairo about 1650. Al-Akhsasi was a shaykh, a learned elder, of the Grand Mosque of the university of Cairo, where his name ''al-Muwaqqit'' reflected his position regulating the times and hours at the mosque. His name Akhsasi connects him in origin to a village in the Faiyum, southwest of Cairo. No copies of his book were known to Western astronomers or historians of science The history of science covers the development of science from ancient times to the present. It encompasses all three major branches of science: natural, social, and formal. Science's earliest roots can be traced to Ancient Egypt and Mesop ... until 1895;Knobel 1895. thus he did not appear in the standard French and English bibliographies and library catalogues of the 19th century. Notes { ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Multiple Star
A star system or stellar system is a small number of stars that orbit each other, bound by gravitational attraction. A large group of stars bound by gravitation is generally called a ''star cluster'' or ''galaxy'', although, broadly speaking, they are also star systems. Star systems are not to be confused with planetary systems, which include planets and similar bodies (such as comets). A star system of two stars is known as a ''binary star'', ''binary star system'' or ''physical double star''. If there are no tidal effects, no perturbation from other forces, and no transfer of mass from one star to the other, such a system is stable, and both stars will trace out an elliptical orbit around the barycenter of the system indefinitely. ''(See Two-body problem)''. Examples of binary systems are Sirius, Procyon and Cygnus X-1, the last of which probably consists of a star and a black hole. Multiple star systems A multiple star system consists of three or more stars that appear ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
IAU Working Group On Star Names
The International Astronomical Union (IAU) established a Working Group on Star Names (WGSN) in May 2016 to catalog and standardize proper names for stars for the international astronomical community. It operates under Division C – Education, Outreach and Heritage. The IAU states that it is keen to make a distinction between the terms ''name'' and ''designation''. To the IAU, ''name'' refers to the (usually colloquial) term used for a star in everyday conversation, while ''designation'' is solely alphanumerical, and used almost exclusively in official catalogues and for professional astronomy. (The WGSN notes that transliterated Bayer designations (e.g., Tau Ceti) are considered a special historical case and are treated as designations.) Terms of reference The terms of reference for the WGSN for the period 2016–2018 were approved by the IAU Executive Committee at its meeting on 6 May 2016. In summary, these are to: * establish IAU guidelines for the proposal and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
International Astronomical Union
The International Astronomical Union (IAU; french: link=yes, Union astronomique internationale, UAI) is a nongovernmental organisation with the objective of advancing astronomy in all aspects, including promoting astronomical research, outreach, education, and development through global cooperation. It was founded in 1919 and is based in Paris, France. The IAU is composed of individual members, who include both professional astronomers and junior scientists, and national members, such as professional associations, national societies, or academic institutions. Individual members are organised into divisions, committees, and working groups centered on particular subdisciplines, subjects, or initiatives. As of 2018, the Union had over 13,700 individual members, spanning 90 countries, and 82 national members. Among the key activities of the IAU is serving as a forum for scientific conferences. It sponsors nine annual symposia and holds a triannual General Assembly that sets policy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |