Deneb on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Deneb () is a first-magnitude star in the
 ''α Cygni'' (Latinised to ''Alpha Cygni'') is the star's designation given by
''α Cygni'' (Latinised to ''Alpha Cygni'') is the star's designation given by
 The 19th brightest star in the night sky, Deneb culminates each year on October 23 at 6 PM and September 7 at 9 PM, corresponding to
The 19th brightest star in the night sky, Deneb culminates each year on October 23 at 6 PM and September 7 at 9 PM, corresponding to
 Deneb is the prototype of the
Deneb is the prototype of the
 Names similar to Deneb have been given to at least seven different stars, most notably Deneb Kaitos, the brightest star in the constellation of
Names similar to Deneb have been given to at least seven different stars, most notably Deneb Kaitos, the brightest star in the constellation of
constellation
A constellation is an area on the celestial sphere in which a group of visible stars forms Asterism (astronomy), a perceived pattern or outline, typically representing an animal, mythological subject, or inanimate object.
The origins of the e ...
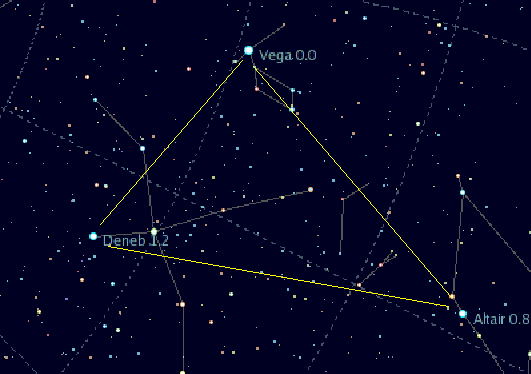
of Cygnus, the swan. Deneb is one of the vertices of the asterism known as the Summer Triangle and the "head" of the Northern Cross. It is the brightest star
A star is an astronomical object comprising a luminous spheroid of plasma (physics), plasma held together by its gravity. The List of nearest stars and brown dwarfs, nearest star to Earth is the Sun. Many other stars are visible to the naked ...
in Cygnus and the 19th brightest star in the night sky
The night sky is the nighttime appearance of celestial objects like stars, planets, and the Moon, which are visible in a clear sky between sunset and sunrise, when the Sun is below the horizon.
Natural light sources in a night sky include ...
, with an average apparent magnitude
Apparent magnitude () is a measure of the brightness of a star or other astronomical object observed from Earth. An object's apparent magnitude depends on its intrinsic luminosity, its distance from Earth, and any extinction of the object's li ...
of +1.25. A blue-white supergiant
Supergiants are among the most massive and most luminous stars. Supergiant stars occupy the top region of the Hertzsprung–Russell diagram with absolute visual magnitudes between about −3 and −8. The temperature range of supergiant stars spa ...
, Deneb rivals Rigel
Rigel is a blue supergiant star in the constellation of Orion. It has the Bayer designation β Orionis, which is Latinized to Beta Orionis and abbreviated Beta Ori or β Ori. Rigel is the brightest and most massive componentand ...
as the most luminous first-magnitude star. However, its distance, and hence luminosity, is poorly known; its luminosity is somewhere between 55,000 and 196,000 times that of the Sun. Its Bayer designation
A Bayer designation is a stellar designation in which a specific star is identified by a Greek or Latin letter followed by the genitive form of its parent constellation's Latin name. The original list of Bayer designations contained 1,564 stars. ...
is α Cygni, which is Latinised to Alpha Cygni, abbreviated to Alpha Cyg or α Cyg.
Nomenclature
 ''α Cygni'' (Latinised to ''Alpha Cygni'') is the star's designation given by
''α Cygni'' (Latinised to ''Alpha Cygni'') is the star's designation given by Johann Bayer
Johann Bayer (1572 – 7 March 1625) was a German lawyer and uranographer (celestial cartographer). He was born in Rain, Lower Bavaria, in 1572. At twenty, in 1592 he began his study of philosophy and law at the University of Ingolstadt, a ...
in 1603. The traditional name ''Deneb'' is derived from the Arabic
Arabic (, ' ; , ' or ) is a Semitic languages, Semitic language spoken primarily across the Arab world.Semitic languages: an international handbook / edited by Stefan Weninger; in collaboration with Geoffrey Khan, Michael P. Streck, Janet C ...
word for "tail", from the phrase ذنب الدجاجة ''Dhanab al-Dajājah'', or "tail of the hen". The IAU Working Group on Star Names
The International Astronomical Union (IAU) established a Working Group on Star Names (WGSN) in May 2016 to catalog and standardize proper names for stars for the international astronomical community. It operates under Division C – Education ...
has recognised the name ''Deneb'' for this star, and it is entered in their Catalog of Star Names.
''Denebadigege'' was used in the '' Alfonsine Tables'',
other variants include ''Deneb Adige'', ''Denebedigege'' and ''Arided''. This latter name was derived from ''Al Ridhādh'', a name for the constellation. Johann Bayer
Johann Bayer (1572 – 7 March 1625) was a German lawyer and uranographer (celestial cartographer). He was born in Rain, Lower Bavaria, in 1572. At twenty, in 1592 he began his study of philosophy and law at the University of Ingolstadt, a ...
called it ''Arrioph'', derived from ''Aridf'' and ''Al Ridf'', 'the hindmost' or ''Gallina''. German poet and author Philippus Caesius termed it ''Os rosae'', or ''Rosemund'' in German, or ''Uropygium'' – the parson's nose.
The names ''Arided'' and ''Aridif'' have fallen out of use.
An older traditional name is Arided , from the Arabic ''ar-ridf'' 'the one sitting behind the rider' (or just 'the follower'), perhaps referring to the other major stars of Cygnus, which were called ''al-fawāris'' 'the riders'.
Observation
 The 19th brightest star in the night sky, Deneb culminates each year on October 23 at 6 PM and September 7 at 9 PM, corresponding to
The 19th brightest star in the night sky, Deneb culminates each year on October 23 at 6 PM and September 7 at 9 PM, corresponding to summer
Summer is the hottest of the four temperate seasons, occurring after spring and before autumn. At or centred on the summer solstice, the earliest sunrise and latest sunset occurs, daylight hours are longest and dark hours are shortest, wit ...
evenings in the northern hemisphere
The Northern Hemisphere is the half of Earth that is north of the Equator. For other planets in the Solar System, north is defined as being in the same celestial hemisphere relative to the invariable plane of the solar system as Earth's Nort ...
. It never dips below the horizon at or above 45° north latitude, just grazing the northern horizon at its lowest point at such locations as Minneapolis
Minneapolis () is the largest city in Minnesota, United States, and the county seat of Hennepin County. The city is abundant in water, with thirteen lakes, wetlands, the Mississippi River, creeks and waterfalls. Minneapolis has its origins ...
, Montréal
Montreal ( ; officially Montréal, ) is the second-most populous city in Canada and most populous city in the Canadian province of Quebec. Founded in 1642 as '' Ville-Marie'', or "City of Mary", it is named after Mount Royal, the triple-p ...
and Turin
Turin ( , Piedmontese language, Piedmontese: ; it, Torino ) is a city and an important business and cultural centre in Northern Italy. It is the capital city of Piedmont and of the Metropolitan City of Turin, and was the first Italian capital ...
. In the southern hemisphere, Deneb is not visible south of 45° parallel south, so it just barely rises above the horizon in South Africa
South Africa, officially the Republic of South Africa (RSA), is the southernmost country in Africa. It is bounded to the south by of coastline that stretch along the South Atlantic and Indian Oceans; to the north by the neighbouring countri ...
, southern Australia
Australia, officially the Commonwealth of Australia, is a Sovereign state, sovereign country comprising the mainland of the Australia (continent), Australian continent, the island of Tasmania, and numerous List of islands of Australia, sma ...
, and northern New Zealand
New Zealand ( mi, Aotearoa ) is an island country in the southwestern Pacific Ocean. It consists of two main landmasses—the North Island () and the South Island ()—and over 700 smaller islands. It is the sixth-largest island count ...
during the southern winter.
Deneb is located at the tip of the Northern Cross asterism made up of the brightest stars in Cygnus, the others being Albireo
Albireo is a double star designated Beta Cygni (β Cygni, abbreviated Beta Cyg, β Cyg). The International Astronomical Union uses the name "Albireo" specifically for the brightest star in the system. Although designated ' beta', ...
(Beta Cygni), Gamma Cygni
Gamma Cygni (γ Cygni, abbreviated Gamma Cyg, γ Cyg), officially named Sadr , is a star in the northern constellation of Cygnus, forming the intersection of an asterism of five stars called the Northern Cross. Based upon parallax mea ...
, Delta Cygni
Delta Cygni (δ Cygni, abbreviated Delta Cyg, δ Cyg) is a binary star of a combined third-magnitude in the constellation of Cygnus. It is also part of the Northern Cross asterism whose brightest star is Deneb. Based upon paralla ...
, and Epsilon Cygni
Epsilon Cygni (ε Cygni, abbreviated Epsilon Cyg, ε Cyg) is multiple star system in the constellation of Cygnus. With an apparent visual magnitude of 2.48, it is readily visible to the naked eye at night as one of the brighter membe ...
. It also lies at one vertex
Vertex, vertices or vertexes may refer to:
Science and technology Mathematics and computer science
*Vertex (geometry), a point where two or more curves, lines, or edges meet
* Vertex (computer graphics), a data structure that describes the positio ...
of the prominent and widely spaced asterism called the Summer Triangle, shared with the first-magnitude
Magnitude may refer to:
Mathematics
*Euclidean vector, a quantity defined by both its magnitude and its direction
*Magnitude (mathematics), the relative size of an object
*Norm (mathematics), a term for the size or length of a vector
*Order of ...
stars Vega
Vega is the brightest star in the northern constellation of Lyra. It has the Bayer designation α Lyrae, which is Latinised to Alpha Lyrae and abbreviated Alpha Lyr or α Lyr. This star is relatively close at only from the Sun, an ...
in the constellation Lyra
Lyra (; Latin for lyre, from Greek ''λύρα'') is a small constellation. It is one of the 48 listed by the 2nd century astronomer Ptolemy, and is one of the modern 88 constellations recognized by the International Astronomical Union. Lyra was ...
and Altair
Altair is the brightest star in the constellation of Aquila and the twelfth-brightest star in the night sky. It has the Bayer designation Alpha Aquilae, which is Latinised from α Aquilae and abbreviated Alpha Aql ...
in Aquila.
This outline of stars is the approximate shape of a right triangle
A right triangle (American English) or right-angled triangle (British), or more formally an orthogonal triangle, formerly called a rectangled triangle ( grc, ὀρθόσγωνία, lit=upright angle), is a triangle in which one angle is a right an ...
, with Deneb located at one of the acute angles.
The spectra of Alpha Cygni has been observed by astronomers since at least 1888, and by 1910 the variable radial velocity
The radial velocity or line-of-sight velocity, also known as radial speed or range rate, of a target with respect to an observer is the temporal rate of change, rate of change of the distance or Slant range, range between the two points. It is e ...
had become apparent. This led to the early suggestion by E. B. Frost that this is a binary star
A binary star is a system of two stars that are gravitationally bound to and in orbit around each other. Binary stars in the night sky that are seen as a single object to the naked eye are often resolved using a telescope as separate stars, in wh ...
system. In 1935, the work of G. F. Paddock and others had established that this star was variable
Variable may refer to:
* Variable (computer science), a symbolic name associated with a value and whose associated value may be changed
* Variable (mathematics), a symbol that represents a quantity in a mathematical expression, as used in many ...
in luminosity with a dominant period of 11.7 days and possibly with other, lower amplitude periods. By 1954, closer examination of the star's calcium H and K lines showed a stationary core, which indicated the variable velocity was instead being caused by motion of the star's atmosphere. This variation ranged from +6 to −9 km/s around the star's mean radial velocity. Other, similar supergiants were found to have variable velocities, with this star being a typical member.
Pole star
Due to the Earth'saxial precession
In astronomy, axial precession is a gravity-induced, slow, and continuous change in the orientation of an astronomical body's rotational axis. In the absence of precession, the astronomical body's orbit would show axial parallelism. In particu ...
, Deneb will be an approximate pole star
A pole star or polar star is a star, preferably bright, nearly aligned with the axis of a rotating astronomical body.
Currently, Earth's pole stars are Polaris (Alpha Ursae Minoris), a bright magnitude-2 star aligned approximately with its ...
(7° off of the north celestial pole) at around 9800 AD. The north pole of Mars
Mars is the fourth planet from the Sun and the second-smallest planet in the Solar System, only being larger than Mercury (planet), Mercury. In the English language, Mars is named for the Mars (mythology), Roman god of war. Mars is a terr ...
points to the midpoint of the line connecting Deneb and the star Alderamin
Alpha Cephei (α Cephei, abbreviated Alpha Cep, α Cep), officially named Alderamin , is a second magnitude star in the constellation of Cepheus near the northern pole. The star is relatively close to Earth at 49 light years (''ly'').
...
.
Physical characteristics
Deneb's adopted distance from the Earth is around . This is derived by a variety of different methods, including spectral luminosity classes, atmospheric modelling, stellar evolution models, assumed membership of the Cygnus OB7 association, and direct measurement of angular diameter. These methods give different distances, and all have significant margins of error. The original derivation of aparallax
Parallax is a displacement or difference in the apparent position of an object viewed along two different lines of sight and is measured by the angle or semi-angle of inclination between those two lines. Due to foreshortening, nearby objects ...
using measurements from the astrometric satellite Hipparcos
''Hipparcos'' was a scientific satellite of the European Space Agency (ESA), launched in 1989 and operated until 1993. It was the first space experiment devoted to precision astrometry, the accurate measurement of the positions of celestial obj ...
gave an uncertain result of 1.01 ± 0.57 mas that was consistent with this distance. However, a more recent reanalysis gives the much larger parallax whose distance is barely half the current accepted value. One 2008 calculation using the Hipparcos data puts the most likely distance at , with an uncertainty of around 15%. The controversy over whether the direct Hipparcos measurements can be ignored in favour of a wide range of indirect stellar models and interstellar distance scales is similar to the better known situation with the Pleiades
The Pleiades (), also known as The Seven Sisters, Messier 45 and other names by different cultures, is an asterism and an open star cluster containing middle-aged, hot B-type stars in the north-west of the constellation Taurus. At a distance of ...
.
Deneb's absolute magnitude
Absolute magnitude () is a measure of the luminosity of a celestial object on an inverse Logarithmic scale, logarithmic Magnitude (astronomy), astronomical magnitude scale. An object's absolute magnitude is defined to be equal to the apparent mag ...
is estimated as −8.4, placing it among the visually brightest stars known, with an estimated luminosity nearly . This is towards the upper end of values published over the past few decades, which vary between and .
Deneb is the most luminous first magnitude star, that is, stars with a brighter apparent magnitude than 1.5. Deneb is also the most distant of the 30 brightest stars by a factor of almost 2. Based on its temperature and luminosity, and also on direct measurements of its tiny angular diameter
The angular diameter, angular size, apparent diameter, or apparent size is an angular distance describing how large a sphere or circle appears from a given point of view. In the vision sciences, it is called the visual angle, and in optics, it is ...
(a mere 0.002 seconds of arc), Deneb appears to have a diameter of about 200 times that of the Sun; if placed at the center of the Solar System
The Solar SystemCapitalization of the name varies. The International Astronomical Union, the authoritative body regarding astronomical nomenclature, specifies capitalizing the names of all individual astronomical objects but uses mixed "Solar S ...
, Deneb would extend out to the orbit of the Earth
Earth orbits the Sun at an average distance of 149.60 million km (92.96 million mi) in a counterclockwise direction as viewed from above the Northern Hemisphere. One complete orbit takes days (1 sidereal year), during which time Earth ...
. It is one of the largest white 'A' spectral type stars known.
Deneb is a bluish-white star of spectral type
In astronomy, stellar classification is the classification of stars based on their stellar spectrum, spectral characteristics. Electromagnetic radiation from the star is analyzed by splitting it with a Prism (optics), prism or diffraction grati ...
A2Ia, with a surface temperature of 8,500 kelvin
The kelvin, symbol K, is the primary unit of temperature in the International System of Units (SI), used alongside its prefixed forms and the degree Celsius. It is named after the Belfast-born and University of Glasgow-based engineer and phys ...
. Since 1943, its spectrum
A spectrum (plural ''spectra'' or ''spectrums'') is a condition that is not limited to a specific set of values but can vary, without gaps, across a continuum. The word was first used scientifically in optics to describe the rainbow of colors i ...
has served as one of the stable references by which other stars are classified. Its mass is estimated at 19 . Stellar wind
A stellar wind is a flow of gas ejected from the upper atmosphere of a star. It is distinguished from the bipolar outflows characteristic of young stars by being less collimated, although stellar winds are not generally spherically symmetric.
D ...
s causes matter to be lost at an average rate of per year, 100,000 times the Sun's rate of mass loss or equivalent to about one Earth mass
An Earth mass (denoted as M_\mathrm or M_\oplus, where ⊕ is the standard astronomical symbol for Earth), is a unit of mass equal to the mass of the planet Earth. The current best estimate for the mass of Earth is , with a relative uncertainty ...
per 500 years.
Evolutionary state
Deneb spent much of its early life as anO-type main-sequence star
An O-type main-sequence star (O V) is a main-sequence (core hydrogen-burning) star of spectral type O and luminosity class V. These stars have between 15 and 90 times the mass of the Sun and surface temperatures between 30,000 and 50,000 K. T ...
of about , but it has now exhausted the hydrogen
Hydrogen is the chemical element with the symbol H and atomic number 1. Hydrogen is the lightest element. At standard conditions hydrogen is a gas of diatomic molecules having the formula . It is colorless, odorless, tasteless, non-toxic, an ...
in its core and expanded to become a supergiant. Stars in the mass range of Deneb eventually expand to become the most luminous red supergiants
Red supergiants (RSGs) are stars with a supergiant luminosity class ( Yerkes class I) of spectral type K or M. They are the largest stars in the universe in terms of volume, although they are not the most massive or luminous. Betelgeuse and Anta ...
, and within a few million years their cores will collapse producing a supernova
A supernova is a powerful and luminous explosion of a star. It has the plural form supernovae or supernovas, and is abbreviated SN or SNe. This transient astronomical event occurs during the last evolutionary stages of a massive star or when ...
explosion. It is now known that red supergiants up to a certain mass explode as the commonly seen type II-P supernova
A Type II supernova (plural: ''supernovae'' or ''supernovas'') results from the rapid collapse and violent explosion of a massive star. A star must have at least 8 times, but no more than 40 to 50 times, the mass of the Sun () to undergo th ...
e, but more massive ones lose their outer layers to become hotter again. Depending on their initial masses and the rate of mass loss, they may explode as yellow hypergiant
A yellow hypergiant (YHG) is a massive star with an extended atmosphere, a spectral class from A to K, and, starting with an initial mass of about 20–60 solar masses, has lost as much as half that mass. They are amongst the most visually lumino ...
s or luminous blue variable
Luminous blue variables (LBVs) are massive evolved stars that show unpredictable and sometimes dramatic variations in their spectra and brightness. They are also known as S Doradus variables after S Doradus, one of the brightest stars of the Larg ...
s, or they may become Wolf-Rayet stars before exploding in a type Ib or Ic supernova. Identifying whether Deneb is currently evolving towards a red supergiant or is currently evolving bluewards again would place valuable constraints on the classes of stars that explode as red supergiants and those that explode as hotter stars.
Stars evolving red-wards for the first time are most likely fusing hydrogen in a shell around a helium
Helium (from el, ἥλιος, helios, lit=sun) is a chemical element with the symbol He and atomic number 2. It is a colorless, odorless, tasteless, non-toxic, inert, monatomic gas and the first in the noble gas group in the periodic table. ...
core that has not yet grown hot enough to start fusion to carbon
Carbon () is a chemical element with the symbol C and atomic number 6. It is nonmetallic and tetravalent
In chemistry, the valence (US spelling) or valency (British spelling) of an element is the measure of its combining capacity with o ...
and oxygen
Oxygen is the chemical element with the symbol O and atomic number 8. It is a member of the chalcogen group in the periodic table, a highly reactive nonmetal, and an oxidizing agent that readily forms oxides with most elements as wel ...
. Convection has begun dredging
Dredging is the excavation of material from a water environment. Possible reasons for dredging include improving existing water features; reshaping land and water features to alter drainage, navigability, and commercial use; constructing da ...
up fusion products but these do not reach the surface. Post-red supergiant stars are expected to show those fusion products at the surface due to stronger convection during the red supergiant phase and due to loss of the obscuring outer layers of the star. Deneb is thought to be increasing its temperature after a period as a red supergiant, although current models do not exactly reproduce the surface elements showing in its spectrum.
Variable star
 Deneb is the prototype of the
Deneb is the prototype of the Alpha Cygni
Deneb () is a first-magnitude star in the constellation of Cygnus, the swan. Deneb is one of the vertices of the asterism known as the Summer Triangle and the "head" of the Northern Cross. It is the brightest star in Cygnus and th ...
(α Cygni) variable star
A variable star is a star whose brightness as seen from Earth (its apparent magnitude) changes with time. This variation may be caused by a change in emitted light or by something partly blocking the light, so variable stars are classified as ...
s, whose small irregular amplitudes and rapid pulsations can cause its magnitude to vary anywhere between 1.21 and 1.29. Its variable velocity discovered by Lee in 1910, but it was not formally placed as a unique class of variable stars until the 1985 4th edition of the General Catalogue of Variable Stars. The cause of the pulsations of Alpha Cygni variable stars are not fully understood, but their irregular nature seems to be due to beat
Beat, beats or beating may refer to:
Common uses
* Patrol, or beat, a group of personnel assigned to monitor a specific area
** Beat (police), the territory that a police officer patrols
** Gay beat, an area frequented by gay men
* Battery (c ...
ing of multiple pulsation periods. Analysis of radial velocities determined 16 different harmonic pulsation modes with periods ranging between 6.9 and 100.8 days. A longer period of about 800 days probably also exists.
Possible spectroscopic companion
Deneb has been reported as a possible single line spectroscopicbinary
Binary may refer to:
Science and technology Mathematics
* Binary number, a representation of numbers using only two digits (0 and 1)
* Binary function, a function that takes two arguments
* Binary operation, a mathematical operation that t ...
with a period of about 850 days, where the spectral lines from the star suggest cyclical radial velocity changes. Later investigations have found no evidence supporting the existence of a companion.
Etymology and cultural significance
 Names similar to Deneb have been given to at least seven different stars, most notably Deneb Kaitos, the brightest star in the constellation of
Names similar to Deneb have been given to at least seven different stars, most notably Deneb Kaitos, the brightest star in the constellation of Cetus
Cetus () is a constellation, sometimes called 'the whale' in English. The Cetus (mythology), Cetus was a sea monster in Greek mythology which both Perseus and Heracles needed to slay. Cetus is in the region of the sky that contains other water- ...
; Deneb Algedi, the brightest star in Capricornus
Capricornus is one of the constellations of the zodiac. Its name is Latin for "horned goat" or "goat horn" or "having horns like a goat's", and it is commonly represented in the form of a sea goat: a mythical creature that is half goat, half f ...
; and Denebola
Denebola is the second-brightest star in the zodiac constellation of Leo.The two components of the γ Leonis double star, which are unresolved to the naked eye, have a combined magnitude brighter than it. It has the Bayer designatio ...
, the second brightest star in Leo. All these stars are referring to the tail of the animals that their respective constellations represent.
In Chinese, (), meaning '' Celestial Ford'', refers to an asterism consisting of Deneb, Gamma Cygni
Gamma Cygni (γ Cygni, abbreviated Gamma Cyg, γ Cyg), officially named Sadr , is a star in the northern constellation of Cygnus, forming the intersection of an asterism of five stars called the Northern Cross. Based upon parallax mea ...
, Delta Cygni
Delta Cygni (δ Cygni, abbreviated Delta Cyg, δ Cyg) is a binary star of a combined third-magnitude in the constellation of Cygnus. It is also part of the Northern Cross asterism whose brightest star is Deneb. Based upon paralla ...
, 30 Cygni, Nu Cygni
Nu Cygni, Latinized from ν Cygni, is a binary star system in the constellation Cygnus. Its apparent magnitude is 3.94 and it is approximately 374 light years away based on parallax. The brighter component is a magnitude 4.07 A-type g ...
, Tau Cygni
Tau Cygni, Latinised from τ Cygni, is a binary star system in the constellation Cygnus, approximately 69 light years away from Earth. This visual binary system has a period of 49.6 years.
The main star, 4th magnitude GJ 822.1 A, is a ...
, Upsilon Cygni
Upsilon Cygni, Latinized from υ Cygni, is a star in the northern constellation of Cygnus. It is visible to the naked eye, having an apparent visual magnitude of 4.43. Based upon an annual parallax shift of , it lies at a distance of r ...
, Zeta Cygni
Zeta Cygni (ζ Cyg) is a binary star system in the northern constellation of Cygnus, the swan. It has an apparent visual magnitude of 3.26 and, based upon parallax measurements, is about away.
The primary component, ζ Cyg A is a g ...
and Epsilon Cygni
Epsilon Cygni (ε Cygni, abbreviated Epsilon Cyg, ε Cyg) is multiple star system in the constellation of Cygnus. With an apparent visual magnitude of 2.48, it is readily visible to the naked eye at night as one of the brighter membe ...
. Consequently, the Chinese name
Chinese names or Chinese personal names are names used by individuals from Greater China and other parts of the Chinese-speaking world throughout East and Southeast Asia (ESEA). In addition, many names used in Japan, Korea and Vietnam are often a ...
for Deneb itself is (, en, the Fourth Star of the Celestial Ford).
In the Chinese love story of Qi Xi
The Qixi Festival ( zh, 七夕), also known as the Qiqiao Festival ( zh, 七巧, links=no), is a Chinese festival celebrating the annual meeting of Zhinü and Niulang in Chinese mythology... The festival is celebrated on the seventh day of the ...
, Deneb marks the magpie
Magpies are birds of the Corvidae family. Like other members of their family, they are widely considered to be intelligent creatures. The Eurasian magpie, for instance, is thought to rank among the world's most intelligent creatures, and is one ...
bridge across the Milky Way
The Milky Way is the galaxy that includes our Solar System, with the name describing the galaxy's appearance from Earth: a hazy band of light seen in the night sky formed from stars that cannot be individually distinguished by the naked eye ...
, which allows the separated lovers Niu Lang (Altair
Altair is the brightest star in the constellation of Aquila and the twelfth-brightest star in the night sky. It has the Bayer designation Alpha Aquilae, which is Latinised from α Aquilae and abbreviated Alpha Aql ...
) and Zhi Nü (Vega
Vega is the brightest star in the northern constellation of Lyra. It has the Bayer designation α Lyrae, which is Latinised to Alpha Lyrae and abbreviated Alpha Lyr or α Lyr. This star is relatively close at only from the Sun, an ...
) to be reunited on one special night of the year in late summer. In other versions of the story, Deneb is a fairy who acts as chaperone when the lovers meet.
Namesakes
USS ''Arided'' was aUnited States Navy
The United States Navy (USN) is the maritime service branch of the United States Armed Forces and one of the eight uniformed services of the United States. It is the largest and most powerful navy in the world, with the estimated tonnage ...
''Crater''-class cargo ship named after the star. SS ''Deneb'' was an Italian merchant vessel that bore this name from 1951 until she was scrapped in 1966.
In fiction
The star Deneb, and hypothetical planets orbiting it, have been used many times inliterature
Literature is any collection of written work, but it is also used more narrowly for writings specifically considered to be an art form, especially prose fiction, drama, and poetry. In recent centuries, the definition has expanded to include ...
, film
A film also called a movie, motion picture, moving picture, picture, photoplay or (slang) flick is a work of visual art that simulates experiences and otherwise communicates ideas, stories, perceptions, feelings, beauty, or atmosphere ...
, electronic game
An electronic game is a game that uses electronics to create an interactive system with which a player can play. Video games are the most common form today, and for this reason the two terms are often used interchangeably. There are other common ...
s, and music
Music is generally defined as the art of arranging sound to create some combination of form, harmony, melody, rhythm or otherwise expressive content. Exact definitions of music vary considerably around the world, though it is an aspect ...
. Examples include several episodes of the ''Star Trek
''Star Trek'' is an American science fiction media franchise created by Gene Roddenberry, which began with the eponymous 1960s television series and quickly became a worldwide pop-culture phenomenon. The franchise has expanded into vari ...
'' TV series
A television show – or simply TV show – is any content produced for viewing on a television set which can be broadcast via over-the-air, satellite, or cable, excluding breaking news, advertisements, or trailers that are typically placed betw ...
, the ''Silver Surfer
The Silver Surfer is a fictional character appearing in American comic books published by Marvel Comics. The character also appears in a number of movies, television, and video game adaptations. The character was created by Jack Kirby and first a ...
'' comic book, the Rush album
An album is a collection of audio recordings issued on compact disc (CD), Phonograph record, vinyl, audio tape, or another medium such as Digital distribution#Music, digital distribution. Albums of recorded sound were developed in the early ...
s ''A Farewell to Kings
''A Farewell to Kings'' is the fifth studio album by Canadian rock band Rush, released in September 1977 by Anthem Records. After touring their previous album '' 2112'' (1976), which saw the group reach a new critical and commercial peak, they ...
'' and '' Hemispheres'', the '' Descent: FreeSpace – The Great War'' computer game
Video games, also known as computer games, are electronic games that involves interaction with a user interface or input device such as a joystick, game controller, controller, computer keyboard, keyboard, or motion sensing device to gener ...
, '' Stellaris'', and the science fiction
Science fiction (sometimes shortened to Sci-Fi or SF) is a genre of speculative fiction which typically deals with imaginative and futuristic concepts such as advanced science and technology, space exploration, time travel, parallel unive ...
novel
A novel is a relatively long work of narrative fiction, typically written in prose and published as a book. The present English word for a long work of prose fiction derives from the for "new", "news", or "short story of something new", itsel ...
'' Hyperion''.
See also
*List of bright stars
This is a list of stars arranged by their apparent magnitude – their brightness as observed from Earth. It includes all stars brighter than magnitude +2.50 in visible light, measured using a ''V''-band filter in the UBV photometric system. Stars ...
References
{{Portal bar, Astronomy, Stars, Outer space A-type supergiants Alpha Cygni variables Emission-line stars Northern pole stars Cygnus (constellation) Cygni, Alpha BD+44 3541 Cygni, 50 197345 102098 7924 Stars named from the Arabic language Arabic words and phrases