|
Göktürk–Persian Wars
The term Turco-Persian wars can refer to two sets of conflicts between Turkic states and Persian states: The Göktürk–Persian wars, between the Göktürks and the Sasanian Empire: * Perso-Turkic war of 588–589 * Perso-Turkic war of 627–629 The Ottoman–Persian Wars, between the Ottoman Empire and a succession of Persian dynasties: * Ottoman–Safavid War (1532–1555) * Ottoman–Safavid War (1578–1590) * Ottoman–Safavid War (1603–1612) * Ottoman–Safavid War (1616–1618) * Ottoman–Safavid War (1623–1639) * Ottoman–Persian War (1730–1735) * Ottoman–Persian War (1743–1746) The Ottoman–Persian War of 1743–1746 or Ottoman–Iranian War of 1743–1746 was fought between the Ottoman Empire and Afsharid Iran. Background Persia attempted to ratify the Treaty of Constantinople (1736), Treaty of Constantinople, by ... * Ottoman–Persian War (1775–1776) * Ottoman–Persian War (1821–1823) {{DEFAULTSORT:Turco-Persian Wars ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Göktürks
The Göktürks (; ), also known as Türks, Celestial Turks or Blue Turks, were a Turkic people in medieval Inner Asia. The Göktürks, under the leadership of Bumin Qaghan (d. 552) and his sons, succeeded the Rouran Khaganate as the main power in the region and established the First Turkic Khaganate, one of several nomadic dynasties that would shape the future geolocation, culture, and dominant beliefs of Turkic peoples. Etymology Origin As an ethnonym, the etymology of ''Turk'' is still unknown. It is generally believed that the name ''Türk'' may have come from Old Turkic migration-term , which means 'created, born'. As a word in Turkic languages, ''Turk'' may mean "strong, strength, ripe" or "flourishing, in full strength". It may also mean ripe as for a fruit or "in the prime of life, young, and vigorous" for a person. The name ''Gök-türk'' emerged from the Modern Turkish reading of the word ''Kök'' as ''Gök'' with assumption of equivalence to "sky" in Moder ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sasanian Empire
The Sasanian Empire (), officially Eranshahr ( , "Empire of the Iranian peoples, Iranians"), was an List of monarchs of Iran, Iranian empire that was founded and ruled by the House of Sasan from 224 to 651. Enduring for over four centuries, the length of the Sasanian dynasty's reign over ancient Iran was second only to the directly preceding Arsacid dynasty of Parthia. Founded by Ardashir I, whose rise coincided with the decline of Arsacid influence in the face of both internal and external strife, the House of Sasan was highly determined to restore the legacy of the Achaemenid Empire by expanding and consolidating the Iranian nation's dominions. Most notably, after defeating Artabanus IV of Parthia during the Battle of Hormozdgan in 224, it began competing far more zealously with the neighbouring Roman Empire than the Arsacids had, thus sparking a new phase of the Roman–Iranian Wars. This effort by Ardashir's dynasty ultimately re-established Iran as a major power of late an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Perso-Turkic War Of 588–589
The Perso-Turkic War was fought during 588–589 between the Sasanian Empire and Hephthalite principalities and its lord the Göktürks. The conflict started with the invasion of the Sasanian Empire by the Turks and ended with a decisive Sasanian victory and the reconquest of lost lands. Background In 557, Khosrow I (), the king (''shah'') of the Sasanian Empire, who had greatly increased the authority of his empire, decided to put an end to the Hephthalite Empire domination over Central Asia. He thus allied with the Göktürks in order to defeat the Hephthalites. The campaign was successful and the region north of the Oxus went to the Turks whilst the south came under Sasanian rule. An agreement was established between Khosrow I and the Turkic Khagan Istämi which set the Oxus as the frontier between the two empires. However, in 588, the Turkic Khagan (known as Sabeh/Saba in Persian sources), together with his Hephthalite subjects, invaded the Sasanian territories south of t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Perso-Turkic War Of 627–629
The Perso-Turkic war of 627–629 was the final conflict between the Sasanian Empire and the Western Turkic Khaganate. Unlike the previous two wars, it was not fought in Central Asia, but in Transcaucasia. Hostilities were initiated in 627 AD by Tong Yabghu Qaghan of the Western Göktürks and Emperor Heraclius of the Byzantine Empire. Opposing them were the Sassanid Persians, allied with the Avars. The war was fought against the background of the last Byzantine-Sassanid War and served as a prelude to the dramatic events that changed the balance of powers in the Middle East for centuries to come ( Battle of Nineveh, Islamic conquest of Persia). Background Following the first siege of Constantinople by the Avars and Persians, the beleaguered Byzantine Emperor Heraclius found himself politically isolated. He could not rely on the Christian Armenian potentates of Transcaucasia, since they were branded as heretics by the Orthodox Church, and even the king of Iberia preferr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ottoman–Persian Wars
The Ottoman–Persian Wars also called the Ottoman–Iranian Wars were a series of wars between the Ottoman Empire and the Safavid, Afsharid, Zand, and Qajar dynasties of Iran (also known as Persia) through the 16th–19th centuries. The Ottomans consolidated their control of what is today Turkey in the 15th century, and gradually came into conflict with the emerging neighboring Iranian state, led by Ismail I of the Safavid dynasty. The two states were arch rivals, and were also divided by religious grounds, the Ottomans being staunchly Sunni and the Safavids being Shia. A series of military conflicts ensued for centuries during which the two empires competed for control over eastern Anatolia, the Caucasus, and Iraq. Among the numerous treaties, the Treaty of Zuhab of 1639 is usually considered as the most significant, as it fixed present Turkey–Iran and Iraq–Iran borders. In later treaties, there were frequent references to the Treaty of Zuhab. See also * Ottoman� ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ottoman–Safavid War (1532–1555)
The Ottoman–Safavid War of 1532–1555 was one of the many military conflicts fought between the two arch rivals, the Ottoman Empire led by Suleiman the Magnificent, and the Safavid Empire led by Tahmasp I. Ottoman territorial gains were confirmed in the Peace of Amasya. Background The war was triggered by territorial disputes between the two empires, especially when the Bey of Bitlis decided to put himself under Persian protection.''The Cambridge history of Islam'' by Peter Malcolm Holt, Ann K. S. Lambton, Bernard Lewis p. 33/ref> Also, Tahmasp had the governor of Baghdad, a sympathiser of Suleiman, assassinated. On the diplomatic front, the Safavids had been engaged in discussions with the Habsburgs for the formation of a Habsburg–Persian alliance that would attack the Ottoman Empire on two fronts. Two Iraqi Expedition The Ottomans, first under the Grand Vizier Ibrahim Pasha, and later joined by Suleiman himself, successfully attacked Safavid Iraq, recaptured Bitlis, a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ottoman–Safavid War (1578–1590)
The Ottoman–Safavid War of 1578–1590 was one of the many wars between the neighboring arch rivals of Safavid Empire and the Ottoman Empire. Starting with several years prior to the war and up to including most of the war itself, the Safavids were experiencing significant domestic issues and rivalling noble factions within the court since the death of Shah Tahmasp I. The Ottomans decided to declare war in 1577–1578 to exploit the chaos. The war, despite swift Ottoman victories in the first few years and large amounts of support from the Ottoman vassal Crimean Khanate during several stages of the war, eventually becoming geo-politically and military relatively stable for several years with both parties losing and winning smaller battles till around 1580. It eventually had a turning point following the Battle of Torches on 7–11 May 1583 and the assassination of the Safavid generals Mirza Salman Jaberi and Hamza Mirza. Following these turns of events and internal chaos in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ottoman–Safavid War (1603–1612)
The Ottoman–Safavid war of 1603–1612 consisted of two wars between Safavid Iran under Abbas the Great, Shah Abbas I and the Ottoman Empire under Mehmed III and his son Ahmed I. The first war began in 1603 and ended with a Safavid victory in 1612, when they regained and reestablished their suzerainty over the Caucasus and Western Iran, which had been lost at the Treaty of Constantinople (1590), Treaty of Constantinople in 1590. Course Safavid attack and early successes (1603–1604) As a result of the Ottoman–Safavid War (1578–1590) the Ottoman Empire, Ottomans had gained swaths of the Safavid territories in the northwest and west, including Shirvan Beylarbeylik, Shirvan, Dagestan, most of Azerbaijan (Iran), Azerbaijan, Kingdom of Kartli, Kartli, Kingdom of Kakheti, Kakheti, Luristan, and Khuzestan. Abbas I of Persia, Abbas I had recently undertaken a major reform of the Safavid army through the English gentleman of fortune Robert Shirley and the shah's favorite ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ottoman–Safavid War (1616–1618)
The Ottoman–Safavid War of 1616–1618 was a brief war between the Ottoman Empire and Safavid Iran. After the Ottoman–Safavid war (1603–1612), the Ottomans and Safavids had signed the Treaty of Nasuh Pasha, in which their borders were changed back to the previous one under Selim I and Shah Ismail I. In exchange, the Safavid ruler Shah Abbas I promised to send the Ottomans 200 pack-loads of silk each year. In 1616, the Ottomans used the Safavids' failure to deliver the silk as a pretext to start another war. At the end of August 1616, a sizable Ottoman army led by the grand vizier Öküz Mehmed Pasha besieged Erivan. Abbas harassed the Ottoman supply lines, and by the time winter was nearing, Mehmed Pasha ended the siege and retreated, leading to death of many of soldiers due to the cold weather. Due to his setback, he was replaced by Damat Halil Pasha as the new grand vizier. In 1618, with the assistance of Tatar and Georgian warriors, Halil Pasha launched another Ottom ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
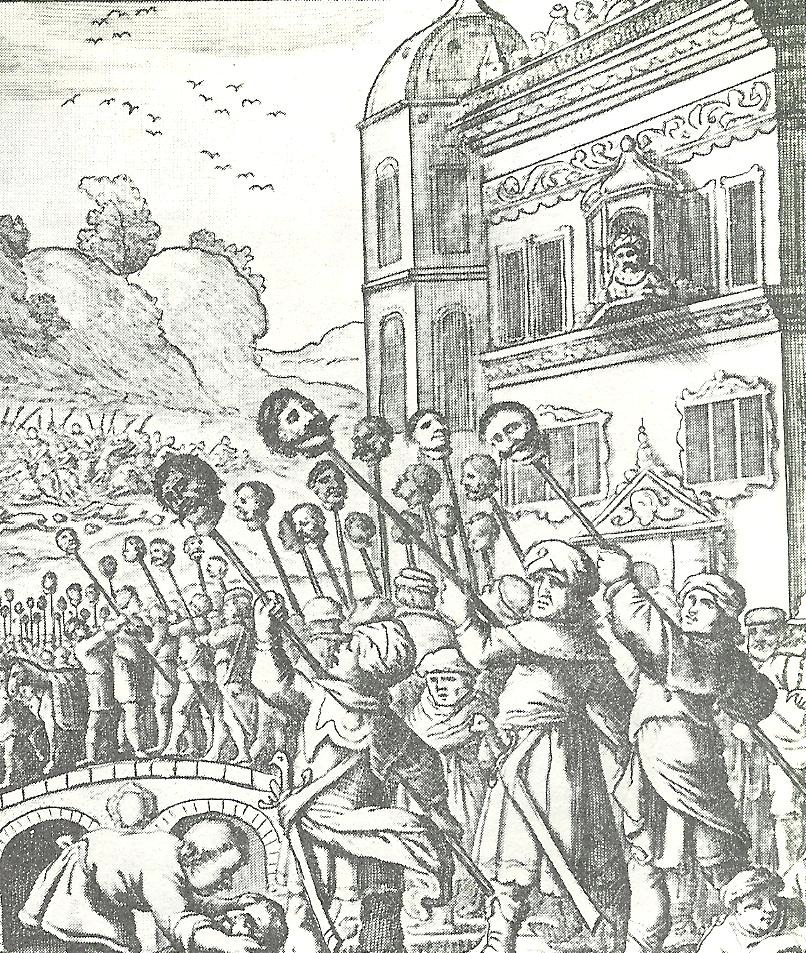
Ottoman–Safavid War (1623–1639)
The Ottoman–Safavid War of 1623–1639 was a conflict fought between the Ottoman Empire and Safavid Iran, then the two major powers of Western Asia, over control of Mesopotamia. After initial Safavid success in recapturing Baghdad and most of modern Iraq, having lost it for 90 years, the war became a stalemate as the Safavids were unable to press further into the Ottoman Empire, and the Ottomans themselves were distracted by wars in Europe and weakened by internal turmoil. Eventually, the Ottomans were able to recover Baghdad, taking heavy losses in Capture of Baghdad (1638), the final siege, and the signing of the Treaty of Zuhab ended the war in an Ottoman victory. Roughly speaking, the treaty restored the borders of Peace of Amasya, 1555, with the Safavids keeping Safavid Daghestan, Daghestan, Safavid Shirvan, Shirvan, eastern History of Georgia (country), Georgia, and Eastern Armenia, while western Georgia and Western Armenia decisively came under Ottoman rule. The eastern ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ottoman–Persian War (1730–1735)
The Ottoman–Persian War of 1730–1735 was a conflict between the forces of Safavid Iran and those of the Ottoman Empire from 1730 to 1735. After Ottoman support had failed to keep the Ghilzai Afghan (ethnonym), Afghan invaders on the Iranian throne, the Ottoman possessions in western Iran, which were granted to them by the Hotak dynasty, came under risk of re-incorporation into the newly resurgent Iranian Empire. The talented Safavid general, Nader Shah, Nader, gave the Ottomans an ultimatum to withdraw, which the Ottomans chose to ignore. A series of campaigns followed, with each side gaining the upper hand in a succession of tumultuous events that spanned half a decade. Finally, the Battle of Yeghevārd, Iranian victory at Yeghevard made the Ottomans sue for peace and recognize Iranian territorial integrity and Iranian hegemony over the Caucasus. Events In the spring of 1730, Nader attacked the Ottoman Empire, Ottomans and regained most of the territory lost during the c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ottoman–Persian War (1743–1746)
The Ottoman–Persian War of 1743–1746 or Ottoman–Iranian War of 1743–1746 was fought between the Ottoman Empire and Afsharid Iran. Background Persia attempted to ratify the Treaty of Constantinople (1736), Treaty of Constantinople, by demanding that the Ja'fari, also known as the Imamiyyah was to be accepted as a fifth legal Islamic schools and branches, sect of Islam. In 1743, Nader Shah declared war on the Ottoman Empire. He demanded the surrender of Baghdad. The Persians had captured Baghdad in 1623 and Mosul in 1624, but the Ottomans had recaptured Mosul in 1625 and Baghdad in 1638. The Treaty of Zuhab in 1639 between the Ottoman Empire and the Safavid Iran, Safavid Empire had resulted in peace for 85 years. During the fall of the Safavid dynasty, Russia and the Ottoman Empire agreed to divide the northwest and the Caspian region of Persia, but with the advent of Nader Shah, the Russians and the Turks withdrew from the region. Nader Shah waged war against the Ottoma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |