|
Großvaterfelsen
The Teufelsmauer (Ore Mountains), Teufelsmauer (German for "Devil's Wall") is a famous natural rock formation located in the Harz, Harz Mountains of central Germany. It stretches across the state of Saxony-Anhalt and is known for its striking, jagged sandstone cliffs and unique geological structure. Formed over Millions of Years Ahead of Man, millions of years, the Teufelsmauer was shaped by erosion and tectonic activity. The rock wall is part of the Northern Harz Boundary Fault and is considered one of the oldest rock formations in the region. The Teufelsmauer is surrounded by legends. One popular myth says the devil tried to claim land from God and built the wall overnight, but failed to complete it before sunrise—hence the name "Devil’s Wall." Today, it is a 'protected natural monumen1'' and a popular hiking and sightseeing destination, attracting nature lovers, photographers, and tourists alike The Teufelsmauer (''Devil's Wall'') is a rock formation made of hard sandst ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Blankenburg (Harz)
Blankenburg (Harz) () is a town and health resort in the Harz (district), district of Harz in Saxony-Anhalt, Germany, at the north foot of the Harz Mountains, southwest of Halberstadt. It has been largely rebuilt since an 1836 fire, and possesses a castle with various collections, a museum of antiquities, an old town hall and churches. There are pine-needle baths and a psychiatric hospital. The nearby ridge of rocks called the ''Teufelsmauer'' ('Devil's Wall') offers views across the plain and into the deep gorges of the Harz. Geography The town of Blankenburg (Harz) lies on the northern edge of the Harz mountains at a height of about 234 metres. It is located west of Quedlinburg, south of Halberstadt and east of Wernigerode. The stream known as the Goldbach (Bode), Goldbach flows through the district of Oesig northwest of the town centre. Divisions The town Blankenburg (Harz) consists of Blankenburg proper and the following ''Ortschaften'' or municipal divisions: [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Teufelsmauer (Ore Mountains)
The Teufelsmauer is a rock massif in the valley of the Black Pockau between Pobershau and Germany's state border with the Czech Republic. It is made of red and gray gneiss Gneiss (pronounced ) is a common and widely distributed type of metamorphic rock. It is formed by high-temperature and high-pressure metamorphic processes acting on formations composed of igneous or sedimentary rocks. This rock is formed under p .... The valley is also known as the Schwarzwasser ("Black Water"). The countryside is very attractive. A channel called the ''Grüne Graben'' ("Green Ditch") runs down the western slopes of the valley that used to provide the necessary water for the mines near Pobershau. The Teufelsmauer is known today for its rock climbing. Geography of the Ore Mountains {{Saxony-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Großvater 1
"Großvater" ("grandfather") is a song recorded in 1985 by Austrian pop rock Pop rock (also typeset as pop/rock) is a fusion genre and form of rock music characterized by a strong commercial appeal, with more emphasis on professional songwriting and recording craft, and less emphasis on attitude than standard rock musi ... group S.T.S. In this song - which reached #63 in Austria - Steinbäcker sings about the loving relationship to his grandfather. {{DEFAULTSORT:Grossvater 1986 singles S.T.S. songs 1985 songs ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Northern Harz Boundary Fault
The Northern Harz Boundary Fault ( or ''Harznordrandverwerfung'') is a geological fault where the Harz Block, which consists of rocks formed during the Palaeozoic Era and folded in the course of Hercynian mountain building, borders on the Subhercynian Basin or Harz Foreland. The fault is also known in English as the Harz North Rim Fault or Harznordrand Thrust (Fault).Nielsen, Ole (2008). ''Salt tectonics'' amy.opera,com Accessed on 28 Nov 2010. The northern edge of the Harz is oriented in a Hercynian (WNW-ESE) direction and runs from Neuekrug- Hahausen via Langelsheim, Goslar, Bad Harzburg, Ilsenburg, Wernigerode, Blankenburg, Thale and Gernrode to the area of Ballenstedt. The Northern Harz Boundary Fault forms the southern border of the Northeast German Basin, a part of the Central European Basin. The Subhercynian Basin, also known as the Harz Foreland, is a small sub-basin of the Northeast German Basin. This intracontinental basin that has been subsided since the Permian ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Muschelkalk
The Muschelkalk (German for "shell-bearing limestone"; ) is a sequence of sedimentary rock, sedimentary rock strata (a lithostratigraphy, lithostratigraphic unit) in the geology of central and western Europe. It has a Middle Triassic (240 to 230 million years) age and forms the middle part of the three-part Germanic Trias (that gives the Triassic its name) lying above the older Buntsandstein and below the younger Keuper. The Muschelkalk ("mussel-chalk") consists of a sequence of limestone and Dolomite (rock), dolomite Bed (geology), beds. In the past, the time span in which the Muschelkalk was deposited could also be called "Muschelkalk". In modern stratigraphy, however, the name only applies to the layers of rock. Occurrence The name ''Muschelkalk'' was first used by German geologist Georg Christian Füchsel (1722-1773). In 1834, Friedrich August von Alberti included it into the Triassic system (stratigraphy), system. The name indicates a characteristic feature of the unit, name ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lias Group
The Lias Group or Lias is a lithostratigraphic unit (a sequence of rock strata) found in a large area of western Europe, including the British Isles, the North Sea, the Low Countries and the north of Germany. It consists of marine limestones, shales, marls and clays. ''Lias'' is a Middle English term for hard limestone, used in this specific sense by geologists since 1833. In the past, geologists used ''Lias'' not only for the sequence of rock layers, but also for the timespan during which they were formed. It was thus an alternative name for the Early Jurassic epoch of the geologic timescale. It is now more specifically known that the Lias is Rhaetian to Toarcian in age (over a period of 20 million years between ) and thus also includes a part of the Triassic. The use of the name "Lias" for a unit of time is therefore slowly disappearing. Subdivisions In southern England, the Lias Group is often divided into Lower, Middle and Upper subgroups. In Southern England the Lias i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stratigraphy
Stratigraphy is a branch of geology concerned with the study of rock layers (strata) and layering (stratification). It is primarily used in the study of sedimentary and layered volcanic rocks. Stratigraphy has three related subfields: lithostratigraphy (lithologic stratigraphy), biostratigraphy (biologic stratigraphy), and chronostratigraphy (stratigraphy by age). Historical development Catholic priest Nicholas Steno established the theoretical basis for stratigraphy when he introduced the law of superposition, the principle of original horizontality and the principle of lateral continuity in a 1669 work on the fossilization of organic remains in layers of sediment. The first practical large-scale application of stratigraphy was by William Smith in the 1790s and early 19th century. Known as the "Father of English geology", Smith recognized the significance of strata or rock layering and the importance of fossil markers for correlating strata; he created the first geo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
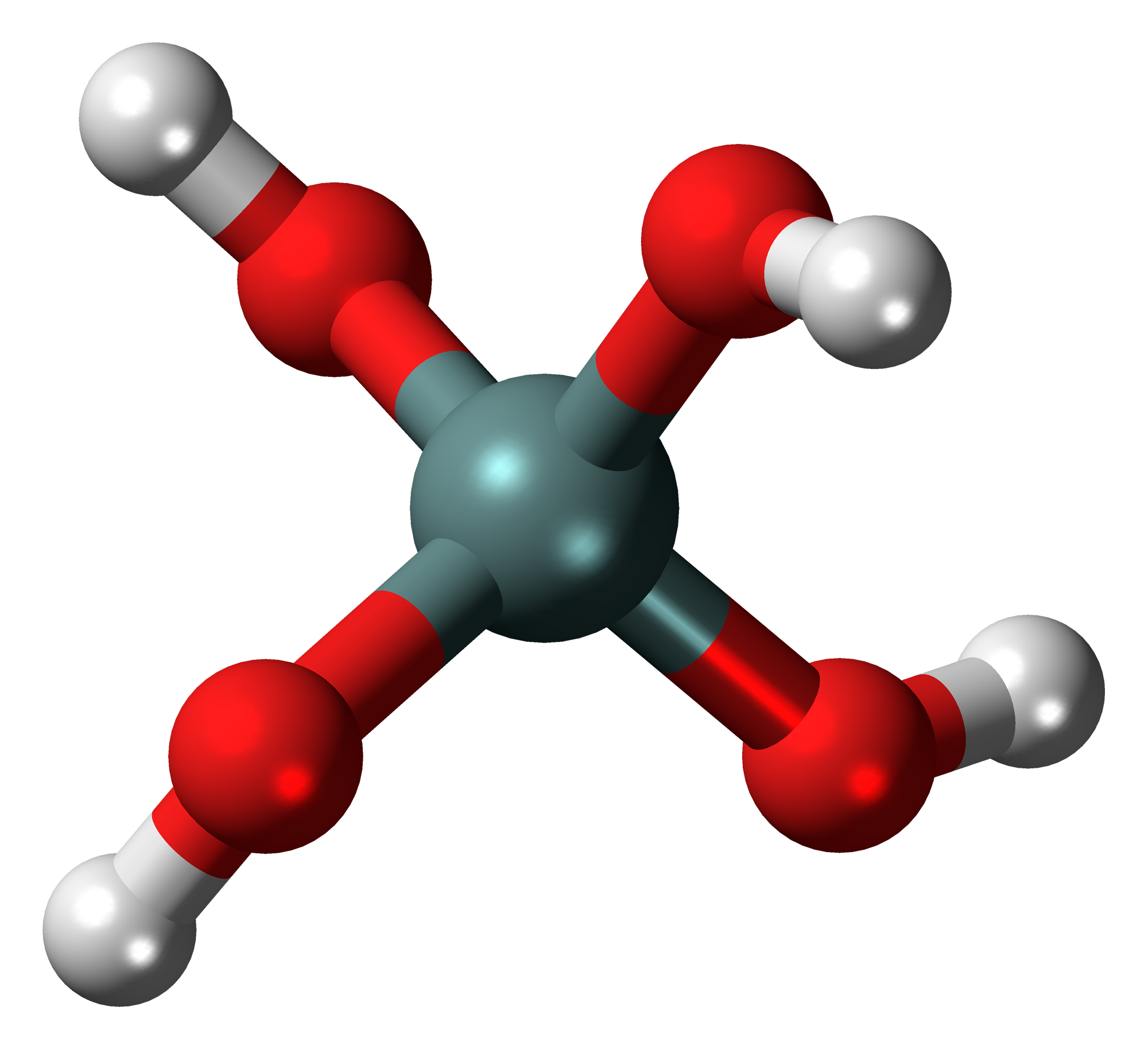
Silicic Acid
In chemistry, a silicic acid () is any chemical compound containing the element silicon attached to oxide () and hydroxyl () groups, with the general formula or, equivalently, . Orthosilicic acid is a representative example. Silicic acids are rarely observed in isolation, but are thought to exist in aqueous solutions, including seawater, and play a role in biomineralization. They are typically colorless weak acids that are sparingly soluble in water. Like the silicate anions, which are their better known conjugate bases, silicic acids are proposed to be oligomeric or polymeric. No Monomer, simple silicic acid has ever been identified, since these species are primarily of theoretical interest. Depending on the number of silicon atoms present, there are mono- and polysilicic (di-, tri-, tetrasilicic, etc.) acids. Well defined silicic acids have not been obtained in a form that has been characterized by X-ray crystallography. Examples Reactions Silicic acids can be seen as hy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neocomian
In geology, Neocomian was a name given to the lowest stage of the Cretaceous system. It is generally considered to encompass the interval now covered by the Berriasian, Valanginian and Hauterivian, from approximately 145 to 130 Ma. It was introduced by Jules Thurmann in 1835 on account of the development of these rocks at Neuchâtel (Neocomum), Switzerland. It has been employed in more than one sense. In the type area the rocks have been divided into two sub-stages, a lower, Valanginian (from Valengin, Pierre Jean Édouard Desor, 1854) and an upper, Hauterivian (from Hauterive, Eugène Renevier, 1874); there is also another local sub-stage, the infra-Valanginian or Berriasian (from Berrias, Henri Coquand, 1876). These three sub-stages constitute the Neocomian in its restricted sense. Adolf von Koenen and other German geologists extend the use of the term to include the whole of the Lower Cretaceous up to the top of the Gault or Albian The Albian is both an age (geology), age o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cretaceous
The Cretaceous ( ) is a geological period that lasted from about 143.1 to 66 mya (unit), million years ago (Mya). It is the third and final period of the Mesozoic Era (geology), Era, as well as the longest. At around 77.1 million years, it is the ninth and longest geological period of the entire Phanerozoic. The name is derived from the Latin , 'chalk', which is abundant in the latter half of the period. It is usually abbreviated K, for its German translation . The Cretaceous was a period with a relatively warm climate, resulting in high Sea level#Local and eustatic, eustatic sea levels that created numerous shallow Inland sea (geology), inland seas. These oceans and seas were populated with now-extinct marine reptiles, ammonites, and rudists, while dinosaurs continued to dominate on land. The world was largely ice-free, although there is some evidence of brief periods of glaciation during the cooler first half, and forests extended to the poles. Many of the dominant taxonomic gr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Normalnull
("standard zero") or (short N. N. or NN) is an outdated official vertical datum used in Germany. Elevations using this reference system were to be marked (“meters above standard zero”). has been replaced by (NHN). History In 1878 reference heights were taken from the Amsterdam Ordnance Datum and transferred to the New Berlin Observatory in order to define the 1879. has been defined as a level going through an imaginary point 37.000 m below . When the New Berlin Observatory was demolished in 1912 the reference point was moved east to the village of (now part of the town of , Brandenburg, Germany).: . In: ' 1958, vol 14, issue 2, p. 62–66 References {{Authority control Vertical datums Geography of Germany ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hamburger Wappen in central Germany.
The appearance of this sandstone formation, with its three steep, soaring pinnacles of rock, recalls the coat of arms of the Hanseatic city of Hamburg with its three towers.
Next to it is a rock cave known as the ''Kuhstall'' ("Cow shed").
Not far from the ''Hamburger Wappen'' is control point no. 74 on the Harzer Wandernadel hiking network.
Rock formations of the Harz
Rock formations of Saxony-Anhalt
{{SaxonyAnhalt-geo-stub ...
The Hamburger Wappen (" Hamburg coat of arms") is a highly unusual rock feature on the Teufelsmauer ("Devil's Wall") rock formation not far from Timmenrode in the Harz Mountains The Harz (), also called the Harz Mountains, is a Mittelgebirge, highland area in northern Germany. It has the highest elevations for that region, and its rugged terrain extends across parts of Lower Saxony, Saxony-Anhalt, and Thuringia. The nam ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |