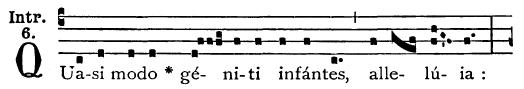|
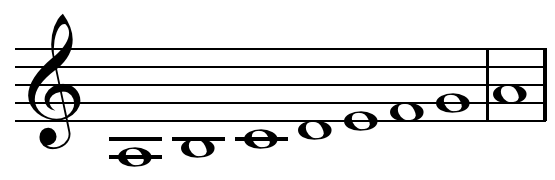
Gregorian Mode
A Gregorian mode (or church mode) is one of the eight systems of pitch organization used in Gregorian chant. History The name of Pope Gregory I was attached to the variety of chant that was to become the dominant variety in medieval western and central Europe (the diocese of Milan was the sole significant exception) by the Frankish cantors reworking Roman ecclesiastical song during the Carolingian period. The theoretical framework of modes arose later to describe the tonal structure of this chant repertory, and is not necessarily applicable to the other European chant dialects ( Old Roman, Mozarabic, Ambrosian, etc.). The repertory of Western plainchant acquired its basic forms between the sixth and early ninth centuries, but there are neither theoretical sources nor notated music from this period. By the late eighth century, a system of eight modal categories, for which there was no precedent in Ancient Greek theory, came to be associated with the repertory of Gregorian cha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Psalm Tone
In chant, a reciting tone (also called a recitation tone) can refer to either a repeated musical pitch or to the entire melodic formula for which that pitch is a structural note. In Gregorian chant, the first is also called tenor, dominant or tuba, while the second includes psalm tones (each with its own associated Gregorian mode) as well as simpler formulae for other readings and for prayers. Reciting tones in Gregorian chant Regular psalm tones Reciting tones occur in several parts of the Roman Rite. These include the accentus prayers and lessons chanted by the deacons or priests such as the Collect, Epistle, Gospel, Secret, Preface, Canon, and Postcommunion, as well as such regular texts as the Pater noster, Te Deum, and the Gloria in excelsis Deo. They are also sung in versicles and responds such as the ''Dominus vobiscum'' ("The Lord be with you") of the officiant followed by the ''Et cum spiritu tuo'' ("and with your spirit") of the choir. Some tones, presumably from t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tonic (music)
In music, the tonic is the first scale degree () of the diatonic scale (the first note of a scale) and the tonal center or final resolution tone that is commonly used in the final cadence in tonal (musical key-based) classical music, popular music, and traditional music. In the movable do solfège system, the tonic note is sung as ''do''. More generally, the tonic is the note upon which all other notes of a piece are hierarchically referenced. Scales are named after their tonics: for instance, the tonic of the C major scale is the note C. The triad formed on the tonic note, the tonic chord, is thus the most significant chord in these styles of music. In Roman numeral analysis, the tonic chord is typically symbolized by the Roman numeral "" if it is major and by "" if it is minor. These chords may also appear as seventh chords: in major, as M7, or in minor as 7 or rarely M7: The tonic is distinguished from the root, which is the reference note of a chord, rathe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Musical Mode
In music theory, the term mode or ''modus'' is used in a number of distinct senses, depending on context. Its most common use may be described as a type of musical scale coupled with a set of characteristic melodic and harmonic behaviors. It is applied to major and minor keys as well as the seven diatonic modes (including the former as Ionian and Aeolian) which are defined by their starting note or tonic. ( Olivier Messiaen's modes of limited transposition are strictly a scale type.) Related to the diatonic modes are the eight church modes or Gregorian modes, in which authentic and plagal forms of scales are distinguished by ambitus and tenor or reciting tone. Although both diatonic and Gregorian modes borrow terminology from ancient Greece, the Greek ''tonoi'' do not otherwise resemble their medieval/modern counterparts. Previously, in the Middle Ages the term modus was used to describe intervals, individual notes, and rhythms (see ). Modal rhythm was an essential ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pitch (music)
Pitch is a perception, perceptual property that allows sounds to be ordered on a frequency-related scale (music), scale, or more commonly, pitch is the quality that makes it possible to judge sounds as "higher" and "lower" in the sense associated with musical melody, melodies. Pitch is a major auditory system, auditory attribute of musical tones, along with duration (music), duration, loudness, and timbre. Pitch may be quantified as a frequency, but pitch is not a purely objective physical property; it is a subjective Psychoacoustics, psychoacoustical attribute of sound. Historically, the study of pitch and pitch perception has been a central problem in psychoacoustics, and has been instrumental in forming and testing theories of sound representation, processing, and perception in the auditory system. Perception Pitch and frequency Pitch is an auditory sensation in which a listener assigns musical tones to relative positions on a musical scale based primarily on their percep ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Note (music)
In music, notes are distinct and isolatable sounds that act as the most basic building blocks for nearly all of music. This discretization facilitates performance, comprehension, and analysis. Notes may be visually communicated by writing them in musical notation. Notes can distinguish the general pitch class or the specific pitch played by a pitched instrument. Although this article focuses on pitch, notes for unpitched percussion instruments distinguish between different percussion instruments (and/or different manners to sound them) instead of pitch. Note value expresses the relative duration of the note in time. Dynamics for a note indicate how loud to play them. Articulations may further indicate how performers should shape the attack and decay of the note and express fluctuations in a note's timbre and pitch. Notes may even distinguish the use of different extended techniques by using special symbols. The term ''note'' can refer to a specific musical event, for i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Psalm Tones
The Book of Psalms ( , ; ; ; ; , in Islam also called Zabur, ), also known as the Psalter, is the first book of the third section of the Tanakh (Hebrew Bible) called ('Writings'), and a book of the Old Testament. The book is an anthology of Hebrew religious hymns. In the Jewish and Western Christian traditions, there are 150 psalms, and several more in the Eastern Christian churches. The book is divided into five sections, each ending with a doxology, a hymn of praise. There are several types of psalms, including hymns or songs of praise, communal and individual laments, royal psalms, imprecation, and individual thanksgivings. The book also includes psalms of communal thanksgiving, wisdom, pilgrimage and other categories. Many of the psalms contain attributions to the name of King David and other Biblical figures including Asaph, the sons of Korah, Moses and Solomon. Davidic authorship of the Psalms is not accepted as historical fact by modern scholars, who view it as a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hypomixolydian Mode
Mixolydian mode may refer to one of three things: the name applied to one of the ancient Greek ''harmoniai'' or ''tonoi'', based on a particular octave species or scale; one of the medieval church modes; or a modern musical mode or diatonic scale, related to the medieval mode. (The Hypomixolydian mode of medieval music, by contrast, has no modern counterpart.) The modern diatonic mode is the scale forming the basis of both the rising and falling forms of Harikambhoji in Carnatic music, the classical music form of southern India, or Khamaj in Hindustani music, the classical music form of northern India. Greek Mixolydian The idea of a Mixolydian mode comes from the music theory of ancient Greece. The invention of the ancient Greek Mixolydian mode was attributed to Sappho, the poet and musician. However, what the ancient Greeks thought of as Mixolydian is very different from the modern interpretation of the mode. The prefix ''mixo''- (-) means "mixed", referring to its resembla ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hypolydian Mode
The Hypolydian mode, literally meaning "below Lydian", is the common name for the sixth of the eight church modes of medieval music theory. The name is taken from Ptolemy of Alexandria's term for one of his seven ''tonoi'', or transposition keys. This mode is the plagal counterpart of the authentic fifth mode. In medieval theory the Hypolydian mode was described either as (1) the diatonic octave species from C to the C an octave higher, divided at the final F (C–D–E–F + F–G–A–B–C) or (2) a mode with F as final and an ambitus from the C below the final to the D above it. The third above the final, A—corresponding to the reciting tone or "tenor" of the sixth psalm tone—was regarded as having an important melodic function in this mode. The sequence of intervals was therefore divided by the final into a lower tetrachord In music theory, a tetrachord (; ) is a series of four notes separated by three interval (music), intervals. In traditional music theory, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hypophrygian Mode
The Hypophrygian (deuterus plagalis) mode, literally meaning "below Phrygian (plagal second)", is a Mode (music), musical mode or diatonic scale in medieval Plainsong, chant theory, the fourth mode of church music. This mode is the plagal mode, plagal counterpart of the authentic third mode, which was called ''Phrygian mode, Phrygian''. In the Middle Ages and Renaissance this mode was described in two ways: the diatonic scale from B to B an octave above, divided at the mode final E (B–C–D–E + E–F–G–A–B); and as a mode with final E and Ambitus (music), ambitus from the A below to the C above. The note A above the final (the tenor of the corresponding fourth psalm tone) had an important melodic function. The melodic range of the ecclesiastical Hypophrygian mode therefore goes from the perfect fourth or perfect fifth, fifth below the tonic to the perfect fifth or minor sixth above. The name Hypophrygian originates in an octave species of Ancient Greece, ancient Greek ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hypodorian Mode
The Hypodorian mode, a musical term literally meaning 'below Dorian', derives its name from a ''tonos'' or octave species of ancient Greece which, in its diatonic genus, is built from a tetrachord consisting (in rising direction) of a semitone followed by two whole tones. The rising scale for the octave is a single tone followed by two conjoint tetrachords of this type. This is roughly the same as playing all the white notes of a piano from A to A: A , B C D E , (E) F G A. Although this scale in medieval theory was employed in Dorian and Hypodorian, from the mid-sixteenth century and in modern music theory they came to be known as the Aeolian and Hypoaeolian modes. The term Hypodorian came to be used to describe the second mode of Western church music. This mode is the plagal counterpart of the authentic first mode, which was also called ''Dorian''. The ecclesiastical Hypodorian mode was defined in two ways: (1) as the diatonic octave species from A to A, divided at the mo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |