Hypophrygian mode on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 The Hypophrygian (deuterus plagalis) mode, literally meaning "below Phrygian (plagal second)", is a
The Hypophrygian (deuterus plagalis) mode, literally meaning "below Phrygian (plagal second)", is a 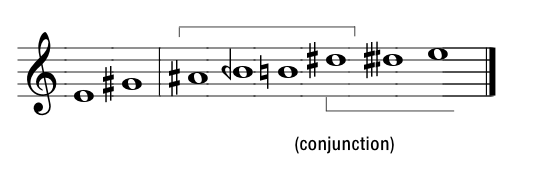 The name Hypophrygian originates in an
The name Hypophrygian originates in an
 The Hypophrygian (deuterus plagalis) mode, literally meaning "below Phrygian (plagal second)", is a
The Hypophrygian (deuterus plagalis) mode, literally meaning "below Phrygian (plagal second)", is a musical mode
In music theory, the term mode or ''modus'' is used in a number of distinct senses, depending on context.
Its most common use may be described as a type of musical scale coupled with a set of characteristic melodic and harmonic behaviors. It ...
or diatonic scale
In music theory a diatonic scale is a heptatonic scale, heptatonic (seven-note) scale that includes five whole steps (whole tones) and two half steps (semitones) in each octave, in which the two half steps are separated from each other by eith ...
in medieval chant
A chant (from French ', from Latin ', "to sing") is the iterative speaking or singing of words or sounds, often primarily on one or two main pitches called reciting tones. Chants may range from a simple melody involving a limited set of no ...
theory, the fourth mode of church music. This mode is the plagal counterpart of the authentic third mode, which was called '' Phrygian''. In the Middle Ages and Renaissance this mode was described in two ways: the diatonic scale from B to B an octave above, divided at the mode final E (B–C–D–E + E–F–G–A–B); and as a mode with final E and ambitus
In ancient Roman law, ''ambitus'' was a crime of political corruption, mainly a candidate's attempt to influence the outcome (or direction) of an election through bribery or other forms of soft power. The Latin word ''ambitus'' is the origin of ...
from the A below to the C above. The note A above the final (the tenor of the corresponding fourth psalm tone) had an important melodic function. The melodic range of the ecclesiastical Hypophrygian mode therefore goes from the perfect fourth
A fourth is a interval (music), musical interval encompassing four staff positions in the music notation of Western culture, and a perfect fourth () is the fourth spanning five semitones (half steps, or half tones). For example, the ascending int ...
or fifth below the tonic to the perfect fifth or minor sixth above.
 The name Hypophrygian originates in an
The name Hypophrygian originates in an octave species
In the musical system of ancient Greece, an octave species (εἶδος τοῦ διὰ πασῶν, or σχῆμα τοῦ διὰ πασῶν) is a specific sequence of interval (music), intervals within an octave. In ''Elementa harmonica'', Ar ...
of ancient Greek
Ancient Greek (, ; ) includes the forms of the Greek language used in ancient Greece and the classical antiquity, ancient world from around 1500 BC to 300 BC. It is often roughly divided into the following periods: Mycenaean Greek (), Greek ...
music theory. According to Aristoxenus
Aristoxenus of Tarentum (; born 375, fl. 335 BC) was a Ancient Greece, Greek Peripatetic school, Peripatetic philosopher, and a pupil of Aristotle. Most of his writings, which dealt with philosophy, ethics and music, have been lost, but one musi ...
, this octave species was originally described around the year 400 BC by the Harmonicist school of Eratocles in terms of the enharmonic genus
In the musical system of ancient Greece, genus (Greek: γένος 'genos'' pl. γένη 'genē'' Latin: ''genus'', pl. ''genera'' "type, kind") is a term used to describe certain classes of intonations of the two movable notes within a tetrach ...
of the tetrachord
In music theory, a tetrachord (; ) is a series of four notes separated by three interval (music), intervals. In traditional music theory, a tetrachord always spanned the interval of a perfect fourth, a 4:3 frequency proportion (approx. 498 cent (m ...
: a series of rising intervals of two quarter tone
A quarter tone is a pitch halfway between the usual notes of a chromatic scale or an interval about half as wide (orally, or logarithmically) as a semitone, which itself is half a whole tone. Quarter tones divide the octave by 50 cents each, a ...
s followed by a ditone
In music, a ditone (, from , "of two tones") is the interval of a major third. The size of a ditone varies according to the sizes of the two tones of which it is compounded. The largest is the Pythagorean ditone, with a ratio of 81:64, also ca ...
, together spanning a perfect fourth
A fourth is a interval (music), musical interval encompassing four staff positions in the music notation of Western culture, and a perfect fourth () is the fourth spanning five semitones (half steps, or half tones). For example, the ascending int ...
. The Dorian octave species begins with this tetrachord, which is followed by a whole tone and another tetrachord to complete the octave with a pattern of ¼, ¼, 2, 1, ¼, ¼, and 2 tones. This pattern is rotated downward one degree for the Hypolydian, and one more for the Hypophrygian, for an octave species of 2, 1, ¼, ¼, 2, ¼, and ¼ tones.
The name was appropriated by Ptolemy of Alexandria for one of his seven ''tonoi'', or transposition keys. Ptolemy's system differed from the earlier Aristoxenian model, which had thirteen transpositional levels each a semitone from its neighbours. Ptolemy substituted a diatonic sequence of seven transpositions pitched either a whole tone or a semitone apart. The entire double-octave scale system was then transposed onto each of these relative pitch levels, requiring (in modern terms) a different key signature in each case, and therefore a different sequence of whole and half steps in the fixed central octave span. The Hypophrygian transposition was the second-lowest of these, a whole tone above the Hypodorian. A whole tone higher was the Hypolydian, followed a semitone higher still by the Dorian, then after another whole tone by the Phrygian, and so on. Four centuries later, the term was taken from Ptolemy in exactly the same sense by Boethius
Anicius Manlius Severinus Boethius, commonly known simply as Boethius (; Latin: ''Boetius''; 480–524 AD), was a Roman Roman Senate, senator, Roman consul, consul, ''magister officiorum'', polymath, historian, and philosopher of the Early Middl ...
, who described these seven names as "toni, tropi, vel modi" (tones, tropes or modes) in the fourth book of his ''De institutione musica''. In the late 9th century, in the Carolingian treatises ''Alia musica'' and in a commentary on it called the ''Nova expositio'', this set of seven terms, supplemented by an eighth name, "Hypermixolydian", was given a new sense, designating a set of diatonic octave species, described as the tonal embodiments of the eight modes of Gregorian chant.
''Missa Mi-mi'' (''Missa quarti toni'') by Johannes Ockeghem
Johannes Ockeghem ( – 6 February 1497) was a Franco-Flemish composer and singer of early Renaissance music. Ockeghem was a significant European composer in the period between Guillaume Du Fay and Josquin des Prez, and he was—with his colle ...
is a well-known example of a work written in the Hypophrygian mode.
References
*Further reading
* * * * {{Modes Modes (music)