|
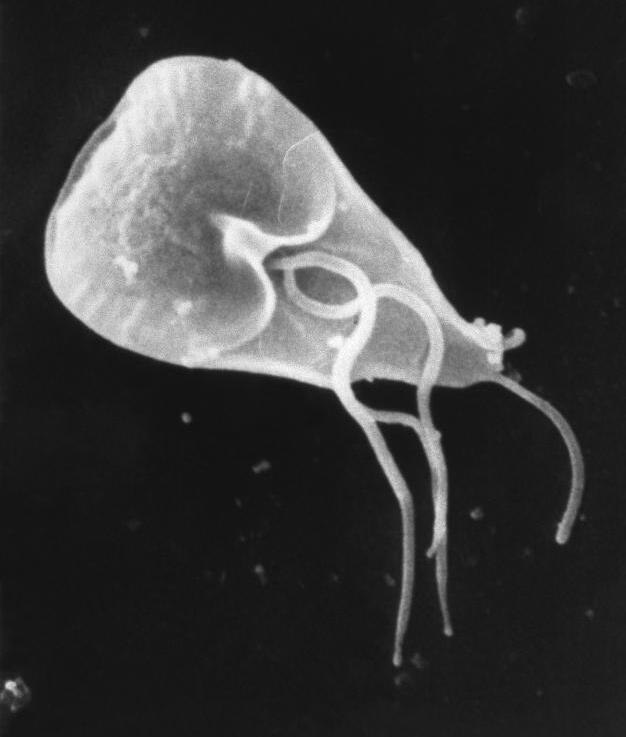
Gill Hyperplasia
Gill hyperplasia is a medical condition consisting of the inflammation, hyperplasia, or hypertrophy of gill tissue, caused by disease, poor water quality, or injury of the gills. Gill function is often impaired, causing significant oxidative stress. Anabantiformes endure hyperplasia better than other species due to the possession of a labyrinth organ. Gill hyperplasia is frequently accompanied with symptoms including lethargy, lack of appetite, and floating near inlets. Secondary bacterial infections and septicemia may occur as a result of deterioration in respiratory function. Causes Chronic irritation of the gills is the primary cause of gill hyperplasia. Continuous ammonia nitrogen exposure has been found to lead to a substantial increase in cases, as well as exposure to heavy metals, and injury to the gills. Some parasitic, protozoan, and bacterial species may also cause gill hyperplasia. Infections known to cause gill hyperplasia listed below * Chilodonella * Trichodina * ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fish Disease And Parasites
Like humans and other animals, fish suffer from diseases and parasites. Fish defences against disease are specific and non-specific. Non-specific defences include skin and scales, as well as the mucus layer secreted by the epidermis that traps microorganisms and inhibits their growth. If pathogens breach these defences, fish can develop inflammatory responses that increase the flow of blood to infected areas and deliver white blood cells that attempt to destroy the pathogens. Specific defences are specialised responses to particular pathogens recognised by the fish's body, that is adaptative immune responses. In recent years, vaccines have become widely used in aquaculture and ornamental fish, for example vaccines for commercial food fishes like Aeromonas salmonicida, furunculosis in salmon and Lactococcosis\Streptococcosis in farmed grey mullet, Tilapia and koi herpes virus in koi. Some commercially important fish diseases are VHS, ICH, and whirling disease. Parasites ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hyperplasia
Hyperplasia (from ancient Greek ὑπέρ ''huper'' 'over' + πλάσις ''plasis'' 'formation'), or hypergenesis, is an enlargement of an organ or tissue caused by an increase in the amount of organic tissue that results from cell proliferation. It may lead to the gross enlargement of an organ, and the term is sometimes confused with benign neoplasia or benign tumor. Hyperplasia is a common preneoplastic response to stimulus. Microscopically, cells resemble normal cells but are increased in numbers. Sometimes cells may also be increased in size (hypertrophy). Hyperplasia is different from hypertrophy in that the adaptive cell change in hypertrophy is an increase in the ''size'' of cells, whereas hyperplasia involves an increase in the ''number'' of cells. Causes Hyperplasia may be due to any number of causes, including proliferation of basal layer of epidermis to compensate skin loss, chronic inflammatory response, hormonal dysfunctions, or compensation for damage ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hypertrophy
Hypertrophy is the increase in the volume of an organ or tissue due to the enlargement of its component cells. It is distinguished from hyperplasia, in which the cells remain approximately the same size but increase in number.Updated by Linda J. Vorvick. 8/14/1Hyperplasia/ref> Although hypertrophy and hyperplasia are two distinct processes, they frequently occur together, such as in the case of the hormonally-induced proliferation and enlargement of the cells of the uterus during pregnancy. Eccentric hypertrophy is a type of hypertrophy where the walls and chamber of a hollow organ undergo growth in which the overall size and volume are enlarged. It is applied especially to the left ventricle of heart. Sarcomeres are added in series, as for example in dilated cardiomyopathy (in contrast to hypertrophic cardiomyopathy, a type of concentric hypertrophy, where sarcomeres are added in parallel). Gallery File:*+ * Photographic documentation on sexual education - Hypertrophy o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oxidative Stress
Oxidative stress reflects an imbalance between the systemic manifestation of reactive oxygen species and a biological system's ability to readily detoxify the reactive intermediates or to repair the resulting damage. Disturbances in the normal redox state of cells can cause toxic effects through the production of peroxides and free radicals that damage all components of the cell, including proteins, lipids, and DNA. Oxidative stress from oxidative metabolism causes base damage, as well as strand breaks in DNA. Base damage is mostly indirect and caused by the reactive oxygen species generated, e.g., O2− ( superoxide radical), OH ( hydroxyl radical) and H2O2 ( hydrogen peroxide). Further, some reactive oxidative species act as cellular messengers in redox signaling. Thus, oxidative stress can cause disruptions in normal mechanisms of cellular signaling. In humans, oxidative stress is thought to be involved in the development of attention deficit hyperactivity disorder, cancer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anabantiformes
The Anabantiformes , collectively known as Labyrinth fish. are an order of air-breathing freshwater ray-finned fish with two suborders, five families (Channidae, Aenigmachannidae, Anabantidae, Helostomatidae, and Osphronemidae) and having at least 207 species. In addition, some authorities expand the order to include the suborder Nandoidei, which includes three families - the Nandidae, Badidae and Pristolepididae - that appear to be closely related to the Anabantiformes. The order, and these three related families (classified as ''incertae sedis'' by the 5th edition of ''Fishes of the World''), are part of a monophyletic clade which is a sister clade to the Ovalentaria, the other orders in the clade being Synbranchiformes, Carangiformes, Istiophoriformes and Pleuronectiformes. This clade is sometimes referred to as the Carangaria but is left unnamed and unranked in ''Fishes of the World''. This group of fish are found in Asia and Africa, with some species introduced in U ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protozoan Infection
Protozoan infections are parasitic diseases caused by organisms formerly classified in the kingdom Protozoa. They are usually contracted by either an insect vector or by contact with an infected substance or surface and include organisms that are now classified in the supergroups Excavata, Amoebozoa, SAR, and Archaeplastida. Protozoan infections are responsible for diseases that affect many different types of organisms, including plants, animals, and some marine life. Many of the most prevalent and deadly human diseases are caused by a protozoan infection, including African sleeping sickness, amoebic dysentery, and malaria. The species originally termed "protozoa" are not closely related to each other and only have superficial similarities (eukaryotic, unicellular, motile, though with exceptions). The terms "protozoa" (and protist) are usually discouraged in the modern biosciences. However, this terminology is still encountered in medicine. This is partially because of the conse ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hyperplasia Vs Hypertrophy
Hyperplasia (from ancient Greek ὑπέρ ''huper'' 'over' + πλάσις ''plasis'' 'formation'), or hypergenesis, is an enlargement of an organ or tissue caused by an increase in the amount of organic tissue that results from cell proliferation. It may lead to the gross enlargement of an organ, and the term is sometimes confused with benign neoplasia or benign tumor. Hyperplasia is a common preneoplastic response to stimulus. Microscopically, cells resemble normal cells but are increased in numbers. Sometimes cells may also be increased in size (hypertrophy). Hyperplasia is different from hypertrophy in that the adaptive cell change in hypertrophy is an increase in the ''size'' of cells, whereas hyperplasia involves an increase in the ''number'' of cells. Causes Hyperplasia may be due to any number of causes, including proliferation of basal layer of epidermis to compensate skin loss, chronic inflammatory response, hormonal dysfunctions, or compensation for damage ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trichodina
Trichodina is a genus of ciliate alveolates that is ectocommensal or parasitic on aquatic animals, particularly fish. They are characterised by the presence of a ring of interlocking cytoskeletal denticles, which provide support for the cell and allow for adhesion to surfaces including fish tissue. Taxonomy Trichodinids are members of the peritrichous ciliates, a paraphyletic group within the Oligohymenophorea. Specifically, they are mobiline peritrichs because they are capable of locomotion, as opposed to sessiline peritrichs such as ''Vorticella'' and '' Epistylis'', which adhere to the substrate via a stalk or lorica. There are over 150 species in the genus ''Trichodina''. '' Trichodinella'', '' Tripartiella'', '' Hemitrichodina'', '' Paratrichodina'' and '' Vauchomia'' are similar genera. Morphology Trichodinids are round ciliates that may be disc-shaped or hemispherical. The cytostome (cell mouth) is on the surface that faces away from the host; this is termed the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amyloodinium Ocellatum
''Amyloodinium ocellatum'' (Brown, 1931) is a cosmopolitan ectoparasite dinoflagellate of numerous aquatic organisms living in brackish and seawater environments. The dinoflagellate is endemic in temperate and tropical areas, and is capable of successfully adapting to a variety of different environments and to a great number of hosts, having been identified in four phyla of aquatic organisms: Chordata, Arthropoda, Mollusca and Platyhelminthes. Moreover, it is the only dinoflagellate capable of infecting teleosts and elasmobranchs . The parasite represents a serious problem for both reared and aquarium fish, since amyloodiniosis, the infection caused by this protozoan, can lead the host to death in less than 12 hours, with acute morbidity and mortality around 100%. However, these two parameters vary considerably on the basis of farming typology, parasite burden, fish species and season considered. In general, amyloodiniosis is typically present in land- or lagoon-based reari ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ichthyophthirius Multifiliis
''Ichthyophthirius multifiliis'', often termed "Ich", is a parasitic ciliate described by the French parasitologist Fouquet in 1876. Only one species is found in the genus which also gave name to the family. The name literally translates as "the fish louse with many children". The parasite can infect most freshwater fish species and, in contrast to many other parasites, shows very low host specificity. It penetrates gill epithelia, skin and fins of the fish host and resides as a feeding stage (the trophont) inside the epidermis. It is visible as a white spot on the surface of the fish but, due to its internal microhabitat, it is a true endoparasite and not an ectoparasite. It causes a disease commonly referred to as white spot disease due to the macroscopically visible trophonts (up to 1 mm in diameter) in the skin and fins. The trophont, continuously rotating, is surrounded by host cells (epidermal cells and leukocytes), producing a minute elevation of the skin. These light ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dactylogyrus
''Dactylogyrus'' is a genus of monogeneans in the Dactylogyridae family. Like other monogeneans, species of ''Dactylogyrus'' only have one host required to complete their life cycle. Introduction Members of ''Dactylogyrus'' (common name: Gill Fluke) are oviparous (egg-laying) monogeneans trematodes that have two pairs of anchors. These anchors can be used to latch onto the gills of a host, particularly freshwater fish such as carp. In heavily infected fish, ''Dactylogyrus'' can also be found on the buccal cavity, and at times fins and skin of the freshwater fish. Species ''Dactylogyrus'' is one of the most speciose genus of helminths, with more than 900 species described. Consequently, in 1996, it was estimated that the taxonomy was "in a state of considerable confusion". Anatomy Other characteristics of ''Dactylogyrus'' species include the appearance of four eye-spots, 14 marginal hooks (7 pairs), one to two connective bars and two needle-like structures and spindle-s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fish Diseases
Like humans and other animals, fish suffer from diseases and parasites. Fish defences against disease are specific and non-specific. Non-specific defences include skin and scales, as well as the mucus layer secreted by the epidermis that traps microorganisms and inhibits their growth. If pathogens breach these defences, fish can develop inflammatory responses that increase the flow of blood to infected areas and deliver white blood cells that attempt to destroy the pathogens. Specific defences are specialised responses to particular pathogens recognised by the fish's body, that is adaptative immune responses. In recent years, vaccines have become widely used in aquaculture and ornamental fish, for example vaccines for commercial food fishes like Aeromonas salmonicida, furunculosis in salmon and Lactococcosis\Streptococcosis in farmed grey mullet, Tilapia and koi herpes virus in koi. Some commercially important fish diseases are VHS, ICH, and whirling disease. Parasites ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.jpg)