|
Făgăraș Depression
Făgăraș (; , ) is a city in central Romania, located in Brașov County. It lies on the Olt River and has a population of 26,284 as of 2021. It is situated in the historical region of Transylvania, and is the main city of a subregion, Țara Făgărașului. Geography The city is located at the foothills of the Făgăraș Mountains, on their northern side. It is traversed by the DN1 road, west of Brașov and east of Sibiu. On the east side of the city, between an abandoned field and a gas station, lies the geographical center of Romania, at . The Olt River flows east to west on the north side of the city; its left tributary, the Berivoi River, discharges into the Olt on the west side of the city, after receiving the waters of the Racovița River. The Berivoi and the Racovița were used to bring water to a since-closed major chemical plant located on the outskirts of the city. The small part of the city that lies north of the Olt is known as ''Galați''. A former village firs ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Făgăraș Citadel
Făgăraș Citadel ( , , ) is a History, historic Ancient monument, monument in Făgăraș, Brașov County, Romania. History The construction of the fortress started in 1310, on the site of a wooden fortification with earth Rampart (fortification), ramparts from the 12th century. Archeological research shows that the old fortification was violently destroyed around the middle of the 13th century, presumably in connection with the Mongol invasion of Europe, Mongol invasion of 1241. Located halfway between Brașov and Sibiu and close to Wallachia, the Făgăraș Citadel provided a defensive position against possible incursions into south-eastern Transylvania. In 1526, consolidated the citadel, doubling the thickness of the walls. In 1541, the Ottoman Empire, Ottomans attacked the fortress and captured Mailat, who died in captivity at Yedikule Fortress in Istanbul. Gáspár Bekes, owner of the citadel between 1567 and 1573, constructed the moat around the fortress, the excavated ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fraxinus
''Fraxinus'' (), commonly called ash, is a genus of plants in the olive and lilac family, Oleaceae, and comprises 45–65 species of usually medium-to-large trees, most of which are deciduous trees, although some Subtropics, subtropical species are evergreen trees. The genus is widespread throughout much of Europe, Asia, and North America. The leaves are opposite leaves, opposite (rarely in Whorl (botany), whorls of three), and mostly pinnate, pinnately compound, though simple in a few species. The seeds, popularly known as "keys" or "helicopter seeds", are a type of fruit known as a samara (fruit), samara. Some ''Fraxinus'' species are Dioecy, dioecious, having male and female flowers on separate plants but sex in ash is expressed as a continuum between male and female individuals, dominated by unisexual trees. With age, ash may change their sexual function from predominantly male and hermaphrodite towards femaleness; if grown as an ornamental and both sexes are present, ashes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Andrew II Of Hungary
Andrew II (, , , ; 117721 September 1235), also known as Andrew of Jerusalem, was King of Hungary and King of Croatia, Croatia between 1205 and 1235. He ruled the Principality of Halych from 1188 until 1189/1190, and again between 1208/1209 and 1210. He was the younger son of Béla III of Hungary, who entrusted him with the administration of the newly conquered Principality of Halych in 1188. Andrew's rule was unpopular, and the boyars (or noblemen) expelled him. Béla III willed property and money to Andrew, obliging him to lead a crusade to the Holy Land. Instead, Andrew forced his elder brother, King Emeric of Hungary, to cede Kingdom of Croatia (1102–1526), Croatia and Dalmatia as an appanage to him in 1197. The following year, Andrew occupied Zachlumia, Hum. Although Andrew did not stop conspiring against Emeric, the dying king made Andrew guardian of his son, Ladislaus III of Hungary, Ladislaus III, in 1204. After the premature death of Ladislaus, Andrew ascended the thr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vlach
Vlach ( ), also Wallachian and many other variants, is a term and exonym used from the Middle Ages until the Modern Era to designate speakers of Eastern Romance languages living in Southeast Europe—south of the Danube (the Balkan peninsula) and north of the Danube. Although it has also been used to name present-day Romanians, the term "Vlach" today refers primarily to speakers of the Eastern Romance languages who live south of the Danube, in Albania, Bulgaria, northern Greece, North Macedonia and eastern Serbia. These people include the ethnic groups of the Aromanians, the Megleno-Romanians and, in Serbia, the Timok Romanians. The term also became a synonym in the Balkans for the social category of shepherds, and was also used for non-Romance-speaking peoples, in recent times in the western Balkans derogatively. The term is also used to refer to the ethnographic group of Moravian Vlachs who speak a Slavic language but originate from Romanians, as well as for Morlachs and I ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Middle Ages
In the history of Europe, the Middle Ages or medieval period lasted approximately from the 5th to the late 15th centuries, similarly to the post-classical period of global history. It began with the fall of the Western Roman Empire and transitioned into the Renaissance and the Age of Discovery. The Middle Ages is the middle period of the three traditional divisions of Western history: classical antiquity, the medieval period, and the modern period. The medieval period is itself subdivided into the Early, High, and Late Middle Ages. Population decline, counterurbanisation, the collapse of centralised authority, invasions, and mass migrations of tribes, which had begun in late antiquity, continued into the Early Middle Ages. The large-scale movements of the Migration Period, including various Germanic peoples, formed new kingdoms in what remained of the Western Roman Empire. In the 7th century, North Africa and the Middle East—once part of the Byzantine Empire� ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
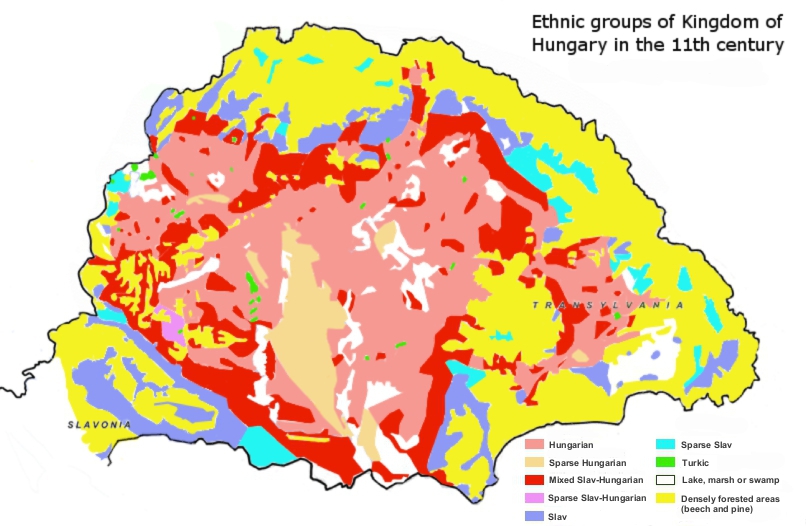
Kingdom Of Hungary
The Kingdom of Hungary was a monarchy in Central Europe that existed for nearly a millennium, from 1000 to 1946 and was a key part of the Habsburg monarchy from 1526-1918. The Principality of Hungary emerged as a Christian kingdom upon the Coronation of the Hungarian monarch, coronation of the first king Stephen I of Hungary, Stephen I at Esztergom around the year 1000;Kristó Gyula – Barta János – Gergely Jenő: Magyarország története előidőktől 2000-ig (History of Hungary from the prehistory to 2000), Pannonica Kiadó, Budapest, 2002, , pp. 37, 113, 678 ("Magyarország a 12. század második felére jelentős európai tényezővé, középhatalommá vált."/"By the 12th century Hungary became an important European factor, became a middle power.", "A Nyugat részévé vált Magyarország.../Hungary became part of the West"), pp. 616–644 his family (the Árpád dynasty) led the monarchy for 300 years. By the 12th century, the kingdom became a European power. Du ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Folk Etymology
Folk etymology – also known as (generative) popular etymology, analogical reformation, (morphological) reanalysis and etymological reinterpretation – is a change in a word or phrase resulting from the replacement of an unfamiliar form by a more familiar one through popular usage. The form or the meaning of an archaic, foreign, or otherwise unfamiliar word is reinterpreted as resembling more familiar words or morphemes. The term ''folk etymology'' is a loan translation from German ''Volksetymologie'', coined by Ernst Förstemann in 1852. Folk etymology is a productive process in historical linguistics, language change, and social interaction. Reanalysis of a word's history or original form can affect its spelling, pronunciation, or meaning. This is frequently seen in relation to loanwords or words that have become archaic or obsolete. Folk/popular etymology may also refer to a popular false belief about the etymology of a word or phrase that does not lead to a change in t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
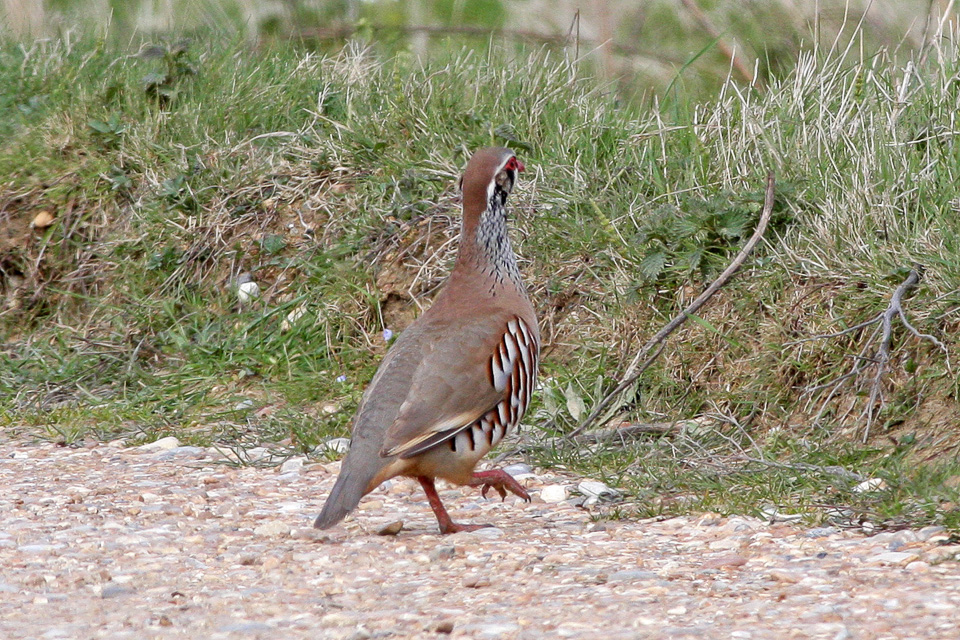
Partridge
A partridge is a medium-sized Galliformes, galliform bird in any of several genera, with a wide Indigenous (ecology), native distribution throughout parts of Europe, Asia and Africa. Several species have been introduced to the Americas. They are sometimes grouped in the Perdicinae subfamily of the Phasianidae (pheasants, quail, etc.). However, molecular research suggests that partridges are not a distinct taxon within the family Phasianidae, but that some species are closer to the pheasants, while others are closer to the junglefowl. Description Partridges are medium-sized Game (hunting), game birds, generally intermediate in size between the larger pheasants, smaller quail; they're ground-dwelling birds that feature variable plumage colouration across species, with most tending to grey and brown. Range and habitat Partridges are native to Europe, Asia, Africa, and the Middle East. Some species are found nesting on steppes or agricultural land, while other species prefer mor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hungarian Language
Hungarian, or Magyar (, ), is an Ugric language of the Uralic language family spoken in Hungary and parts of several neighboring countries. It is the official language of Hungary and one of the 24 official languages of the European Union. Outside Hungary, it is also spoken by Hungarians, Hungarian communities in southern Slovakia, western Ukraine (Zakarpattia Oblast, Transcarpathia), central and western Romania (Transylvania), northern Serbia (Vojvodina), northern Croatia, northeastern Slovenia (Prekmurje), and eastern Austria (Burgenland). It is also spoken by Hungarian diaspora communities worldwide, especially in North America (particularly the Hungarian Americans, United States and Canada) and Israel. With 14 million speakers, it is the Uralic family's most widely spoken language. Classification Hungarian is a member of the Uralic language family. Linguistic connections between Hungarian and other Uralic languages were noticed in the 1670s, and the family's existenc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
István Kniezsa
István Kniezsa (1 December 1898, Trsztena, Austria-Hungary, now Trstená, Slovakia – 15 March 1965, Budapest, Hungary) was a Hungary, Hungarian Linguistics, linguist and Slavic studies, Slavist, corresponding (1939) and regular (1947) member of the Hungarian Academy of Sciences. He was one of the most significant figures in Hungarian language historical research in the 20th century, achieving significant scientific results in the study of place and personal names in the Carpathian basin, Carpathian Basin, in researching the medieval state and writing practice of the Hungarian language, as well as in the exploration of foreign words of Slavic origin. His major contribution was to the research of Slavic loanwords in the Hungarian language and toponymy. He was awarded by Kossuth Prize in 1953. Works According to an investigation based on place-names in the medieval Kingdom of Hungary made by István Kniezsa, 511 settlements of Transylvania and Banat appear in documents at the end ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |