|
Fluorothiazinone
Fluorothiazinone (CL-55, Ftortiazinon, Фтортиазинон) is an antibiotic drug, first developed in Russia in 2010 and active against various species of Gram-negative bacteria through inhibition of the type III secretion system (T3SS). It has seen limited clinical use in Russia and is in clinical trials which may eventually see it accepted for use more widely. See also * List of Russian drugs This page is a list of Russian drugs, or drugs that were developed in Russia, the former Soviet Union, and/or post-Soviet countries. Many Russian drugs are indicated for enhancing physical, mental, and/or cognitive performance, including drugs d ... * Aurodox * Triazavirin References {{reflist Amides Antibiotics Catechols Ethoxy compounds Experimental drugs Fluorobenzene derivatives Russian drugs Thiadiazines ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Russian Drugs
This page is a list of Russian drugs, or drugs that were developed in Russia, the former Soviet Union, and/or post-Soviet countries. Many Russian drugs are indicated for enhancing physical, mental, and/or cognitive performance, including drugs described as nootropics or cognitive enhancers, drugs combatting fatigue, so-called adaptogens or actoprotectors, and others. There have been concerns about Russian drugs in the Western world owing to allegedly lower standards of medical evidence in Russia compared to the West, for instance in the case of the Russian COVID vaccine Sputnik V. Some Russian drugs have been attempted to be repurposed and developed by pharmaceutical companies for use in the West, such as phenylpiracetam (fonturacetam), (''R'')-phenylpiracetam (MRZ-9547), Noopept (omberacetam), and armesocarb (the active enantiomer of mesocarb). List of Russian drugs * Aceclidine (Glaucostat, Glaunorm, Glaudin) – parasympathomimetic miotic * Acetomepregenol (ACM; mepre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
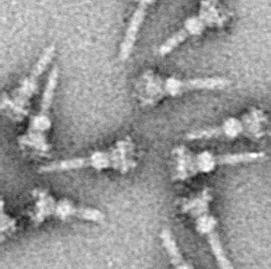
Aurodox
Aurodox (X-5108, goldinomycin) is a naturally occurring polyketide antibiotic drug, first isolated in 1972 from '' Streptomyces goldiniensis''. It is active against various species of Gram-positive bacteria through inhibition of the type III secretion system (T3SS), and while its chemical properties make it unsuitable for use in human medicine directly, it is used in antibiotic research and related compounds may be developed for medical use. See also * Fluorothiazinone Fluorothiazinone (CL-55, Ftortiazinon, Фтортиазинон) is an antibiotic drug, first developed in Russia in 2010 and active against various species of Gram-negative bacteria through inhibition of the type III secretion system (T3SS). It ... References {{reflist Antibiotics Conjugated dienes Pyrans Pyridones Tetrahydrofurans Polyenes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antibiotic
An antibiotic is a type of antimicrobial substance active against bacteria. It is the most important type of antibacterial agent for fighting pathogenic bacteria, bacterial infections, and antibiotic medications are widely used in the therapy, treatment and antibiotic prophylaxis, prevention of such infections. They may either bactericide, kill or bacteriostatic agent, inhibit the growth of bacteria. A limited number of antibiotics also possess antiprotozoal activity. Antibiotics are not effective against viruses such as the common cold or influenza; drugs which inhibit viruses are termed antiviral drugs or antivirals rather than antibiotics. Sometimes, the term ''antibiotic''—literally "opposing life", from the Greek language, Greek roots ἀντι ''anti'', "against" and βίος ''bios'', "life"—is broadly used to refer to any substance used against microbes, but in the usual medical usage, antibiotics (such as penicillin) are those produced naturally (by one microorgani ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gram-negative Bacteria
Gram-negative bacteria are bacteria that do not retain the crystal violet stain used in the Gram staining method of bacterial differentiation. They are characterized by their cell envelopes, which are composed of a thin peptidoglycan cell wall sandwiched between an inner cytoplasmic cell membrane and a bacterial outer membrane. Gram-negative bacteria are found in virtually all environments on Earth that support life. The gram-negative bacteria include the model organism '' Escherichia coli'', as well as many pathogenic bacteria, such as '' Pseudomonas aeruginosa'', '' Chlamydia trachomatis'', and '' Yersinia pestis''. They are a significant medical challenge as their outer membrane protects them from many antibiotics (including penicillin), detergents that would normally damage the inner cell membrane, and lysozyme, an antimicrobial enzyme produced by animals that forms part of the innate immune system. Additionally, the outer leaflet of this membrane comprises a compl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Type III Secretion System
The type III secretion system (T3SS or TTSS), also called the injectisome, is one of the bacterial secretion systems used by bacteria to secrete their effector proteins into the host's cells to promote virulence and colonisation. The T3SS is a needle-like protein complex found in several species of pathogenic gram-negative bacteria. Overview The term Type III secretion system was coined in 1993. This secretion system is distinguished from at least five other secretion systems found in gram-negative bacteria. Many animal and plant associated bacteria possess similar T3SSs. These T3SSs are similar as a result of divergent evolution and phylogenetic analysis supports a model in which gram-negative bacteria can transfer the T3SS gene cassette horizontally to other species. The most researched T3SSs are from species of '' Shigella'' (causes bacillary dysentery), ''Salmonella'' (typhoid fever), ''Escherichia coli'' (Gut flora, some strains cause food poisoning), '' Vibrio'' (gas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Triazavirin
Riamilovir (TZV, Triazavirin) is a broad-spectrum antiviral drug developed in Russia through a joint effort of Ural Federal University, Russian Academy of Sciences, Ural Center for Biopharma Technologies and Medsintez Pharmaceutical. It has a novel triazolotriazine core, which represents a new structural class of non-nucleoside antiviral drugs. The main principle action of triazavirin is to inhibit the synthesis of viral ribonucleic acid (RNA) and the replication of viral genomic fragments through its synthetic analogue to the bases of purine nucleosides. Uses It was originally developed as a potential treatment for pandemic influenza strains such as H5N1, and most of the testing that has been done has focused on its anti-influenza activity. However, triazavirin has also been found to have antiviral activity against a number of other viruses including tick-borne encephalitis virus, and is also being investigated for potential application against a lethal influenza infection a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amides
In organic chemistry, an amide, also known as an organic amide or a carboxamide, is a compound with the general formula , where R, R', and R″ represent organic groups or hydrogen atoms. The amide group is called a peptide bond when it is part of the main chain of a protein, and an isopeptide bond when it occurs in a side chain, such as in the amino acids asparagine and glutamine. It can be viewed as a derivative of a carboxylic acid () with the hydroxyl group () replaced by an amine group (); or, equivalently, an acyl (alkanoyl) group () joined to an amine group. Common examples of amides are acetamide (), benzamide (), and dimethylformamide (). Amides are qualified as primary, secondary, and tertiary according to whether the amine subgroup has the form , , or , where R and R' are groups other than hydrogen. The core of amides is called the amide group (specifically, carboxamide group). Amides are pervasive in nature and technology. Proteins and important plastic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antibiotics
An antibiotic is a type of antimicrobial substance active against bacteria. It is the most important type of antibacterial agent for fighting bacterial infections, and antibiotic medications are widely used in the treatment and prevention of such infections. They may either kill or inhibit the growth of bacteria. A limited number of antibiotics also possess antiprotozoal activity. Antibiotics are not effective against viruses such as the common cold or influenza; drugs which inhibit viruses are termed antiviral drugs or antivirals rather than antibiotics. Sometimes, the term ''antibiotic''—literally "opposing life", from the Greek roots ἀντι ''anti'', "against" and βίος ''bios'', "life"—is broadly used to refer to any substance used against microbes, but in the usual medical usage, antibiotics (such as penicillin) are those produced naturally (by one microorganism fighting another), whereas non-antibiotic antibacterials (such as sulfonamides and antise ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Catechols
Catechol ( or ), also known as pyrocatechol or 1,2-dihydroxybenzene, is a toxic organic compound with the molecular formula . It is the ''ortho'' isomer of the three isomeric benzenediols. This colorless compound occurs naturally in trace amounts. It was first discovered by destructive distillation of the plant extract catechin. About 20,000 tonnes of catechol are now synthetically produced annually as a commodity organic chemical, mainly as a precursor to pesticides, flavors, and fragrances. Catechol occurs as feathery white crystals that are very rapidly soluble in water. Isolation and synthesis Catechol was first isolated in 1839 by Edgar Hugo Emil Reinsch (1809–1884) by distilling it from the solid tannic preparation catechin, which is the residuum of catechu, the boiled or concentrated juice of ''Mimosa catechu'' ('' Acacia catechu''). Upon heating catechin above its decomposition point, a substance that Reinsch first named ''Brenz-Katechusäure'' (burned catechu a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Experimental Drugs
An experiment is a procedure carried out to support or refute a hypothesis, or determine the efficacy or likelihood of something previously untried. Experiments provide insight into cause-and-effect by demonstrating what outcome occurs when a particular factor is manipulated. Experiments vary greatly in goal and scale but always rely on repeatable procedure and logical analysis of the results. There also exist natural experimental studies. A child may carry out basic experiments to understand how things fall to the ground, while teams of scientists may take years of systematic investigation to advance their understanding of a phenomenon. Experiments and other types of hands-on activities are very important to student learning in the science classroom. Experiments can raise test scores and help a student become more engaged and interested in the material they are learning, especially when used over time. Experiments can vary from personal and informal natural comparisons ( ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fluorobenzene Derivatives
Fluorobenzene is the chemical compound with the formula C6H5F, often abbreviated PhF. A colorless liquid, it is a precursor to many fluorophenyl compounds. Preparation PhF was first reported in 1886 by O. Wallach at the University of Bonn, who prepared the compound in two steps. Phenyldiazonium chloride was first converted to a triazene using piperidine: : hN2l + 2 (CH2)5NH → PhN=N-N(CH2)5 + CH2)5NH2l The triazine was then cleaved with hydrofluoric acid: :PhN=N-N(CH2)5 + 2 HF → PhF + N2 + CH2)5NH2 Historical note: in Wallach's era, the element fluorine was symbolized with "Fl". Thus, his procedure is subtitled "Fluorbenzol, C6H5Fl". On the laboratory scale, PhF is prepared by the thermal decomposition of the benzenediazonium tetrafluoroborate: :PhN2BF4 → PhF + BF3 + N2 According to the procedure, solid hN2F4 is heated with a flame to initiate an exothermic reaction, which also affords boron trifluoride and nitrogen gas. Product PhF and BF3 are r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |