|
Excess Molar Quantity
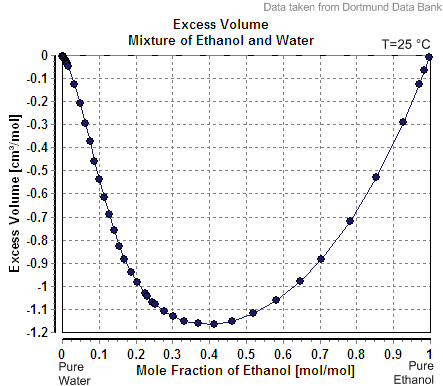
In chemical thermodynamics, excess properties are properties of mixtures which quantify the non- ideal behavior of real mixtures. They are defined as the difference between the value of the property in a real mixture and the value that would exist in an ideal solution under the same conditions. The most frequently used excess properties are the excess volume, excess enthalpy, and excess chemical potential. The excess volume (), internal energy (), and enthalpy () are identical to the corresponding mixing properties; that is, :\begin V^E &= \Delta V_\text \\ H^E &= \Delta H_\text \\ U^E &= \Delta U_\text \end These relationships hold because the volume, internal energy, and enthalpy changes of mixing are zero for an ideal solution. Definition By definition, excess properties are related to those of the ideal solution by: :z^E = z - z^\text Here, the superscript IS denotes the value in the ideal solution, a superscript E denotes the excess molar property, and z denotes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chemical Thermodynamics
Chemical thermodynamics is the study of the interrelation of heat and work with chemical reactions or with physical changes of state within the confines of the laws of thermodynamics. Chemical thermodynamics involves not only laboratory measurements of various thermodynamic properties, but also the application of mathematical methods to the study of chemical questions and the ''spontaneity'' of processes. The structure of chemical thermodynamics is based on the first two laws of thermodynamics. Starting from the first and second laws of thermodynamics, four equations called the "fundamental equations of Gibbs" can be derived. From these four, a multitude of equations, relating the thermodynamic properties of the thermodynamic system can be derived using relatively simple mathematics. This outlines the mathematical framework of chemical thermodynamics. History In 1865, the German physicist Rudolf Clausius, in his ''Mechanical Theory of Heat'', suggested that the principles o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Apparent Molar Property
In thermodynamics, an apparent molar property of a solution component in a mixture or solution is a quantity defined with the purpose of isolating the contribution of each component to the non-ideality of the mixture. It shows the change in the corresponding solution property (for example, volume) per mole of that component added, when all of that component is added to the solution. It is described as ''apparent'' because it appears to represent the molar property of that component ''in solution'', provided that the properties of the other solution components are assumed to remain constant during the addition. However this assumption is often not justified, since the values of apparent molar properties of a component may be quite different from its molar properties in the pure state. For instance, the volume of a solution containing two components identified as solvent and solute is given by : V=V_0 + ^\phi_1 \ =\tilde_ n_ + ^\phi\tilde_1 n_1 \, where is the volume of the pure ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
San Diego, California
San Diego ( , ; ) is a city on the Pacific Ocean coast of Southern California located immediately adjacent to the Mexico–United States border. With a 2020 population of 1,386,932, it is the eighth most populous city in the United States and the seat of San Diego County, the fifth most populous county in the United States, with 3,338,330 estimated residents as of 2019. The city is known for its mild year-round climate, natural deep-water harbor, extensive beaches and parks, long association with the United States Navy, and recent emergence as a healthcare and biotechnology development center. San Diego is the second largest city in the state of California, after Los Angeles. Historically home to the Kumeyaay people, San Diego is frequently referred to as the "Birthplace of California", as it was the first site visited and settled by Europeans on what is now the U.S. west coast. Upon landing in San Diego Bay in 1542, Juan Rodríguez Cabrillo claimed the are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Academic Press
Academic Press (AP) is an academic book publisher founded in 1941. It was acquired by Harcourt, Brace & World in 1969. Reed Elsevier bought Harcourt in 2000, and Academic Press is now an imprint of Elsevier. Academic Press publishes reference books, serials and online products in the subject areas of: * Communications engineering * Economics * Environmental science * Finance * Food science and nutrition * Geophysics * Life sciences * Mathematics and statistics * Neuroscience * Physical sciences * Psychology Well-known products include the ''Methods in Enzymology'' series and encyclopedias such as ''The International Encyclopedia of Public Health'' and the ''Encyclopedia of Neuroscience''. See also * Akademische Verlagsgesellschaft (AVG) — the German predecessor, founded in 1906 by Leo Jolowicz (1868–1940), the father of Walter Jolowicz Walter may refer to: People * Walter (name), both a surname and a given name * Little Walter, American blues harmonica player ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Upper Saddle River, New Jersey
Upper Saddle River is a borough in Bergen County, New Jersey. As of the 2010 United States Census, the borough's population was 8,208,DP-1 - Profile of General Population and Housing Characteristics: 2010 for Upper Saddle River borough, Bergen County, New Jersey , . Accessed February 16, 2012. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prentice Hall
Prentice Hall was an American major educational publisher owned by Savvas Learning Company. Prentice Hall publishes print and digital content for the 6–12 and higher-education market, and distributes its technical titles through the Safari Books Online e-reference service. History On October 13, 1913, law professor Charles Gerstenberg and his student Richard Ettinger founded Prentice Hall. Gerstenberg and Ettinger took their mothers' maiden names, Prentice and Hall, to name their new company. Prentice Hall became known as a publisher of trade books by authors such as Norman Vincent Peale; elementary, secondary, and college textbooks; loose-leaf information services; and professional books. Prentice Hall acquired the training provider Deltak in 1979. Prentice Hall was acquired by Gulf+Western in 1984, and became part of that company's publishing division Simon & Schuster. S&S sold several Prentice Hall subsidiaries: Deltak and Resource Systems were sold to National Educatio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Virial Expansion
The classical virial expansion expresses the pressure P of a many-particle system in equilibrium as a power series in the density: Z \equiv \frac = A + B\rho + C\rho^2 + \cdots where Z is called the compressibility factor. This is the virial equation of state, the most general function relating pressure, , density, , and temperature, , of fluids. It was first proposed by Kamerlingh Onnes.Kamerlingh Onnes H., Expression of state of gases and liquids by means of series, KNAW Proceedings, 4, 1901-1902, Amsterdam, 125-147 (1902). The compressibility factor is a dimensionless quantity, indicating how much a real fluid deviates from an ideal gas. ''A'' is the first virial coefficient, which has a constant value of 1. It makes the statement that at low density, all fluids behave like ideal gases. The virial coefficients , , , etc., are temperature-dependent, and are generally presented as Taylor series in terms of . Second and third virial coefficients The second, , and third, , ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Volume Concentration
In chemistry and fluid mechanics, the volume fraction φ''i'' is defined as the volume of a constituent ''V''''i'' divided by the volume of all constituents of the mixture ''V'' prior to mixing: :\phi_i = \frac Being dimensionless, its unit is 1; it is expressed as a number, e.g., 0.18. It is the same concept as volume percent (vol%) except that the latter is expressed with a denominator of 100, e.g., 18%. The volume fraction coincides with the volume concentration in ideal solutions where the volumes of the constituents are additive (the volume of the solution is equal to the sum of the volumes of its ingredients). The sum of all volume fractions of a mixture is equal to 1: :\sum_^ V_i = V ; \qquad \sum_^ \phi_i = 1 The volume fraction (percentage by volume, vol%) is one way of expressing the composition of a mixture with a dimensionless quantity; mass fraction (percentage by weight, wt%) and mole fraction (percentage by moles, mol%) are others. Volume concentration and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Solubility Equilibrium
Solubility equilibrium is a type of dynamic equilibrium that exists when a chemical compound in the solid state is in chemical equilibrium with a solution of that compound. The solid may dissolve unchanged, with dissociation, or with chemical reaction with another constituent of the solution, such as acid or alkali. Each solubility equilibrium is characterized by a temperature-dependent ''solubility product'' which functions like an equilibrium constant. Solubility equilibria are important in pharmaceutical, environmental and many other scenarios. Definitions A solubility equilibrium exists when a chemical compound in the solid state is in chemical equilibrium with a solution containing the compound. This type of equilibrium is an example of dynamic equilibrium in that some individual molecules migrate between the solid and solution phases such that the rates of dissolution and precipitation are equal to one another. When equilibrium is established and the solid has not all disso ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lattice Energy
In chemistry, the lattice energy is the energy change upon formation of one mole of a crystalline ionic compound from its constituent ions, which are assumed to initially be in the gaseous state. It is a measure of the cohesive forces that bind ionic solids. The size of the lattice energy is connected to many other physical properties including solubility, hardness, and volatility. Since it generally cannot be measured directly, the lattice energy is usually deduced from experimental data via the Born–Haber cycle. Lattice energy and lattice enthalpy The concept of lattice energy was originally applied to the formation of compounds with structures like rocksalt (NaCl) and sphalerite (ZnS), where the ions occupy high-symmetry crystal lattice sites. In the case of NaCl, lattice energy is the energy change of the reaction : Na+ (g) + Cl− (g) → NaCl (s) which amounts to −786 kJ/mol. Some chemistry textbooks as well as the widely used CRC Handbook of Chemistry an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heat Of Mixing
In thermodynamics, the enthalpy of mixing (also heat of mixing and excess enthalpy) is the enthalpy liberated or absorbed from a substance upon mixing. When a substance or compound is combined with any other substance or compound, the enthalpy of mixing is the consequence of the new interactions between the two substances or compounds. This enthalpy, if released exothermically, can in an extreme case cause an explosion. Enthalpy of mixing can often be ignored in calculations for mixtures where other heat terms exist, or in cases where the mixture is ideal. The sign convention is the same as for enthalpy of reaction: when the enthalpy of mixing is positive, mixing is endothermic, while negative enthalpy of mixing signifies exothermic mixing. In ideal mixtures, the enthalpy of mixing is null. In non-ideal mixtures, the thermodynamic activity of each component is different from its concentration by multiplying with the activity coefficient. One approximation for calculating the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heat Of Melting
In thermodynamics, the enthalpy of fusion of a substance, also known as (latent) heat of fusion, is the change in its enthalpy resulting from providing energy, typically heat, to a specific quantity of the substance to change its state from a solid to a liquid, at constant pressure. It is the amount of energy required to convert one mole of solid into liquid For example, when melting 1 kg of ice (at 0 °C under a wide range of pressures), 333.55 kJ of energy is absorbed with no temperature change. The heat of solidification (when a substance changes from liquid to solid) is equal and opposite. This energy includes the contribution required to make room for any associated change in volume by displacing its environment against ambient pressure. The temperature at which the phase transition occurs is the melting point or the freezing point, according to context. By convention, the pressure is assumed to be unless otherwise specified. Overview The 'enthalpy' of fusi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.jpg)


