|
Enteropathy
Enteropathy refers to any pathology of the intestine. Although enteritis specifically refers to an inflammation of the intestine, and is thus a more specific term than "enteropathy", the two phrases are sometimes used interchangeably. __TOC__ Types Specific types of enteropathy include: * Enteropathy-associated T-cell lymphoma * Environmental enteropathy, also known as tropical enteropathy :An incompletely defined syndrome of inflammation related to the quality of the environment. Signs and symptoms include reduced absorptive capacity and reduced intestinal barrier function of the small intestine. It is widespread among children and adults in low- and middle-income countries. * Eosinophilic enteropathy :A condition in which eosinophils (a type of white blood cell) accumulate in the gastrointestinal tract and in the blood. Eosinophil build up in the gastrointestinal tract can result in polyp formation, tissue break down, inflammation, and ulcers. * Coeliac disease :A malabsorpt ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protein Losing Enteropathy
Protein losing enteropathy refers to any condition of the gastrointestinal tract (e.g. damage to the gut wall) that results in a net loss of protein from the body. Signs and symptoms The signs/symptoms of protein losing enteropathy are consistent with diarrhea, fever, and general abdominal discomfort. Swelling of the legs due to peripheral edema can also occur, however, if the PLE is related to a systemic disease such as congestive heart failure or constrictive pericarditis, then the symptoms could be of the primary disease development. Causes The causes of protein-losing enteropathy can include GI conditions (among other causes), like the following: Mechanism The pathophysiology of protein losing enteropathy is a result of plasma proteins loss, which enters GI tract ( lumen). PLE is a complication of a disorder, be it lymphatic obstruction or mucosal injury. In ''pediatric protein losing enteropathy'' there are several changes in epithelial cells causing PLE by augmenting ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Environmental Enteropathy
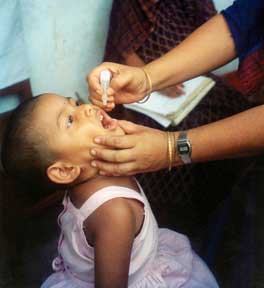
Environmental enteropathy (EE or tropical enteropathy or environmental enteric dysfunction) is a disorder of chronic intestinal inflammation. EE is most common amongst children living in low-resource settings. Acute symptoms are typically minimal or absent. EE can lead to malnutrition, anemia (iron-deficiency anemia and anemia of chronic inflammation), growth stunting, impaired brain development, and impaired response to oral vaccinations. The cause of EE is multifactorial. Overall, exposure to contaminated food and water leads to a generalized state of intestinal inflammation. The inflammatory response results in multiple pathological changes to the gastrointestinal tract: Smaller villi, larger crypts (called crypt hyperplasia), increased permeability, and inflammatory cell build-up within the intestines. These changes result in poor absorption of food, vitamins and minerals. Standardized, clinically practical diagnostic criteria do not exist. The most accurate diagnostic t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
IPEX Syndrome
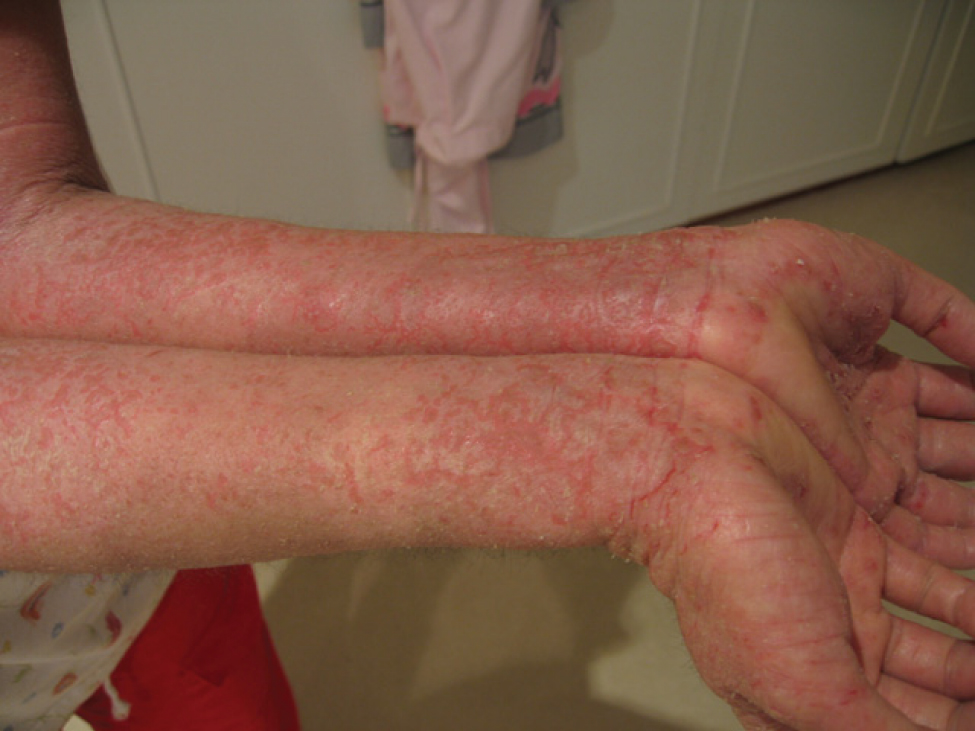
Immunodysregulation polyendocrinopathy enteropathy X-linked (or IPEX) syndrome is a rare disease linked to the dysfunction of the gene encoding transcription factor forkhead box P3 (FOXP3), widely considered to be the master regulator of the regulatory T cell lineage. It leads to the dysfunction of CD4+ regulatory T-cells and the subsequent autoimmunity. The disorder is one of the autoimmune polyendocrine syndromes and manifests with autoimmune enteropathy, psoriasiform or eczematous dermatitis, nail dystrophy, autoimmune endocrinopathies, and autoimmune skin conditions such as alopecia universalis and bullous pemphigoid. Management for IPEX has seen limited success in treating the syndrome by bone marrow transplantation. Presentation The most representative criterion for diagnose of IPEX syndrome is autoimmune enteropathy. First symptoms of enteropathy begin in first day of life and they are characterized by diarrhea, vomiting, gastritis, ileus and colitis. The second hallma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Radiation Enteropathy
Radiation enteropathy is a syndrome that may develop following abdominal or pelvic radiation therapy for cancer. Many affected people are cancer survivors who had treatment for cervical cancer or prostate cancer; it has also been termed pelvic radiation disease with radiation proctitis being one of the principal features. Signs and symptoms People who have been treated with radiotherapy for pelvic and other abdominal cancers frequently develop gastrointestinal symptoms. These include: * rectal bleeding * diarrhea and steatorrhea * other defecation disorders including fecal urgency and incontinence. * nutritional deficiencies and weight loss * abdominal pain and bloating * nausea, vomiting and fatigue Gastrointestinal symptoms are often found together with those in other systems including genitourinary disorders and sexual dysfunction. The burden of symptoms substantially impairs the patients' quality of life. Nausea, vomiting, fatigue, and diarrhea may happen early duri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Enteropathy-associated T-cell Lymphoma
Enteropathy-associated T-cell lymphoma (EATL), previously termed enteropathy-associated T-cell lymphoma, type I and at one time termed enteropathy-type T-cell lymphoma (ETTL), is a complication of coeliac disease in which a malignant T-cell lymphoma develops in areas of the small intestine affected by the disease's intense inflammation. While a relatively rare disease, it is the most common type of primary gastrointestinal T-cell lymphoma. EATL had been defined as a single type of small intestine lymphoma, but in 2008, the World Health Organization (WHO) divided the disease into two subtypes: 1) EATL type I, which occurs in individuals with coeliac disease, a chronic immune disorder causing inflammatory responses to dietary gluten primarily in the upper reaches (i.e. jejunum and duodenum) of the small intestine; and 2) EATL type II, a disorder similar to EATL type I that occurs without coeliac disease. While type I and II EATL share many similar features, post-2008 studies found ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Malabsorption
Malabsorption is a state arising from abnormality in absorption of food nutrients across the gastrointestinal (GI) tract. Impairment can be of single or multiple nutrients depending on the abnormality. This may lead to malnutrition and a variety of anaemias. Normally the human gastrointestinal tract digests and absorbs dietary nutrients with remarkable efficiency. A typical Western diet ingested by an adult in one day includes approximately 100 g of fat, 400 g of carbohydrate, 100 g of protein, 2 L of fluid, and the required sodium, potassium, chloride, calcium, vitamins, and other elements. Salivary, gastric, intestinal, hepatic, and pancreatic secretions add an additional 7–8 L of protein-, lipid-, and electrolyte-containing fluid to intestinal contents. This massive load is reduced by the small and large intestines to less than 200 g of stool that contains less than 8 g of fat, 1–2 g of nitrogen, and less than 20 mmol each of Na+, K+, Cl–, HCO3–, Ca2+, or Mg ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
FOXP3
FOXP3 ( forkhead box P3), also known as scurfin, is a protein involved in immune system responses. A member of the FOX protein family, FOXP3 appears to function as a master regulator of the regulatory pathway in the development and function of regulatory T cells. Regulatory T cells generally turn the immune response down. In cancer, an excess of regulatory T cell activity can prevent the immune system from destroying cancer cells. In autoimmune disease, a deficiency of regulatory T cell activity can allow other autoimmune cells to attack the body's own tissues. While the precise control mechanism has not yet been established, FOX proteins belong to the forkhead/winged-helix family of transcriptional regulators and are presumed to exert control via similar DNA binding interactions during transcription. In regulatory T cell model systems, the FOXP3 transcription factor occupies the promoters for genes involved in regulatory T-cell function, and may inhibit transcription of key ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coeliac Disease
Coeliac disease (British English) or celiac disease (American English) is a long-term autoimmune disorder, primarily affecting the small intestine, where individuals develop intolerance to gluten, present in foods such as wheat, rye and barley. Classic symptoms include gastrointestinal problems such as chronic diarrhoea, abdominal distention, malabsorption, loss of appetite, and among children failure to grow normally. This often begins between six months and two years of age. Non-classic symptoms are more common, especially in people older than two years. There may be mild or absent gastrointestinal symptoms, a wide number of symptoms involving any part of the body, or no obvious symptoms. Coeliac disease was first described in childhood; however, it may develop at any age. It is associated with other autoimmune diseases, such as Type 1 diabetes mellitus and Hashimoto's thyroiditis, among others. Coeliac disease is caused by a reaction to gluten, a group of various prote ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eosinophilic Gastroenteritis
Eosinophilic gastroenteritis (EG or EGE) is a rare and heterogeneous condition characterized by patchy or diffuse eosinophilic infiltration of gastrointestinal (GI) tissue, first described by Kaijser in 1937.Kaijser R. Zur Kenntnis der allergischen Affektionen des Verdauugskanals vom Standpunkt des Chirurgen aus. Arch Klin Chir 1937; 188:36–64. Presentation may vary depending on location as well as depth and extent of bowel wall involvement and usually runs a chronic relapsing course. It can be classified into mucosal, muscular and serosal types based on the depth of involvement. Any part of the GI tract can be affected, and isolated biliary tract involvement has also been reported. The stomach is the organ most commonly affected, followed by the small intestine and the colon. Signs and symptoms EG typically presents with a combination of chronic nonspecific GI symptoms which include abdominal pain, diarrhea, occasional nausea and vomiting, weight loss and abdominal distens ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Enteritis
Enteritis is inflammation of the small intestine. It is most commonly caused by food or drink contaminated with pathogenic microbes,Dugdale, David C., IIII, and George F Longretc"Enteritis" MedlinePlus Medical Encyclopedia, 18 October 2008. Accessed 24 August 2009. such as '' serratia'', but may have other causes such as NSAIDs, radiation therapy as well as autoimmune conditions like Crohn's disease and celiac disease. Symptoms include abdominal pain, cramping, diarrhea, dehydration, and fever. Related diseases of the gastrointestinal system include inflammation of the stomach and large intestine. Duodenitis, jejunitis and ileitis are subtypes of enteritis which are localised to a specific part of the small intestine. Inflammation of both the stomach and small intestine is referred to as gastroenteritis. Signs and symptoms Signs and symptoms of enteritis are highly variable and vary based on the specific cause and other factors such as individual variance and stage of d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gluten
Gluten is a structural protein naturally found in certain cereal grains. Although "gluten" often only refers to wheat proteins, in medical literature it refers to the combination of prolamin and glutelin proteins naturally occurring in all grains that have been proved capable of triggering celiac disease. These include any species of wheat (such as common wheat, durum, spelt, khorasan, emmer and einkorn), barley, rye and some oat cultivars, as well as any cross hybrids of these grains (such as triticale). Gluten makes up 75–85% of the total protein in bread wheat. Glutens, especially Triticeae glutens, have unique viscoelastic and adhesive properties, which give dough its elasticity, helping it rise and keep its shape and often leaving the final product with a chewy texture. These properties, and its relatively low cost, make gluten valuable to both food and non-food industries. Wheat gluten is composed of mainly two types of proteins: the glutenins and the gliadins ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
White Blood Cell
White blood cells, also called leukocytes or leucocytes, are the cells of the immune system that are involved in protecting the body against both infectious disease and foreign invaders. All white blood cells are produced and derived from multipotent cells in the bone marrow known as hematopoietic stem cells. Leukocytes are found throughout the body, including the blood and lymphatic system. All white blood cells have nuclei, which distinguishes them from the other blood cells, the anucleated red blood cells (RBCs) and platelets. The different white blood cells are usually classified by cell lineage (myeloid cells or lymphoid cells). White blood cells are part of the body's immune system. They help the body fight infection and other diseases. Types of white blood cells are granulocytes (neutrophils, eosinophils, and basophils), and agranulocytes (monocytes, and lymphocytes (T cells and B cells)). Myeloid cells ( myelocytes) include neutrophils, eosinophils, mast cells, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |