|
External Oblique
The abdominal external oblique muscle (also external oblique muscle or exterior oblique) is the largest and outermost of the three flat abdominal muscles of the lateral anterior abdomen. Structure The external oblique is situated on the lateral and anterior parts of the abdomen. It is broad, thin, and irregularly quadrilateral, its muscular portion occupying the side, its aponeurosis the anterior wall of the abdomen. In most humans, the oblique is not visible, due to subcutaneous fat deposits and the small size of the muscle. It arises from eight fleshy digitations, each from the external surfaces and inferior borders of the fifth to twelfth ribs (lower eight ribs). These digitations are arranged in an oblique line which runs inferiorly and anteriorly, with the upper digitations being attached close to the cartilages of the corresponding ribs, the lowest to the apex of the cartilage of the last rib, the intermediate ones to the ribs at some distance from their cartilages. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ribs
The rib cage or thoracic cage is an endoskeletal enclosure in the thorax of most vertebrates that comprises the ribs, vertebral column and sternum, which protect the vital organs of the thoracic cavity, such as the heart, lungs and great vessels and support the shoulder girdle to form the core (anatomy), core part of the axial skeleton. A typical human skeleton, human thoracic cage consists of 12 pairs of ribs and the adjoining costal cartilages, the sternum (along with the manubrium and xiphoid process), and the 12 thoracic vertebrae articulating with the ribs. The thoracic cage also provides attachments for extrinsic skeletal muscles of the neck, upper limbs, upper abdomen and back, and together with the overlying skin and associated fascia and muscles, makes up the thoracic wall. In tetrapods, the rib cage intrinsically holds the muscles of respiration (thoracic diaphragm, diaphragm, intercostal muscles, etc.) that are crucial for active inhalation and forced exhalation, and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aponeurosis
An aponeurosis (; : aponeuroses) is a flattened tendon by which muscle attaches to bone or fascia. Aponeuroses exhibit an ordered arrangement of collagen fibres, thus attaining high tensile strength in a particular direction while being vulnerable to tensional or shear forces in other directions. They have a shiny, whitish-silvery color, are histologically similar to tendons, and are very sparingly supplied with blood vessels and nerves. When dissected, aponeuroses are papery and peel off by sections. The primary regions with thick aponeuroses are in the ventral abdominal region, the dorsal lumbar region, the ventriculus in birds, and the palmar (palms) and plantar (soles) regions. Anatomy Anterior abdominal aponeuroses The anterior abdominal aponeuroses are located just superficial to the rectus abdominis muscle. It has for its borders the external oblique, pectoralis muscles, and the latissimus dorsi. Posterior lumbar aponeuroses The posterior lumbar aponeuroses are sit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
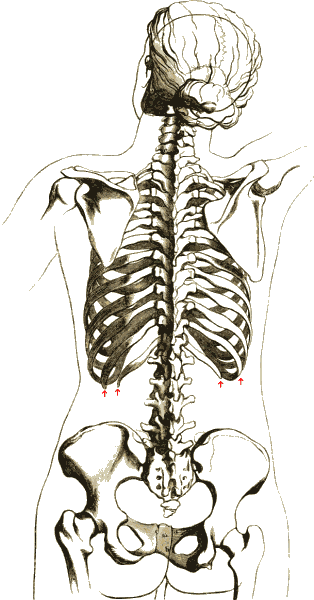
Spine Flexors
Spine or spinal may refer to: Science Biology * Spinal column, also known as the backbone * Dendritic spine, a small membranous protrusion from a neuron's dendrite * Thorns, spines, and prickles, needle-like structures in plants * Spine (zoology), needle-like structures in animals * SPINE (molecular biology) (strep–protein interaction experiment), a method for the detection of protein interactions Medicine * Spinal anaesthesia or "a spinal", an injection generally through a fine needle, usually long * The Spine, a set of national service within the UK NHS Connecting for Health Arts, entertainment and media * ''The Spine'' (album), a 2004 They Might Be Giants album, including the songs "Spine" and "Spines" * ''Spine'' (film), American film * ''The Spine'' (film), a 2009 animated short by Chris Landreth * ''Spine'' (video game), an upcoming video game * ''The Spine'', a novel by Ladislav Bublík Fictional entities * Spinal (''Killer Instinct''), a fictional character from t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Muscles Of The Torso
Muscle is a soft tissue, one of the four basic types of animal tissue. There are three types of muscle tissue in vertebrates: skeletal muscle, cardiac muscle, and smooth muscle. Muscle tissue gives skeletal muscles the ability to contract. Muscle tissue contains special contractile proteins called actin and myosin which interact to cause movement. Among many other muscle proteins, present are two regulatory proteins, troponin and tropomyosin. Muscle is formed during embryonic development, in a process known as myogenesis. Skeletal muscle tissue is striated consisting of elongated, multinucleate muscle cells called muscle fibers, and is responsible for movements of the body. Other tissues in skeletal muscle include tendons and perimysium. Smooth and cardiac muscle contract involuntarily, without conscious intervention. These muscle types may be activated both through the interaction of the central nervous system as well as by innervation from peripheral plexus or endocrin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Valsalva Maneuver
The Valsalva maneuver is performed by a forceful attempt of exhalation against a closed airway, usually done by closing one's mouth and pinching one's nose shut while expelling air, as if blowing up a balloon. Variations of the maneuver can be used either in medicine, medical examination as a test of cardiac function and autonomic nervous system, autonomic nervous control of the heart (because the maneuver raises the pressure in the lungs), or to clear the ears and paranasal sinuses, sinuses (that is, to equalize pressure between them) when ambient pressure changes, as in scuba diving, hyperbaric oxygen therapy, or air travel. A modified version is done by expiring against a closed glottis. This will elicit the cardiovascular responses described below but will not force air into the Eustachian tubes. History The technique is named after Antonio Maria Valsalva, a 17th-century physician and anatomist from Bologna whose principal scientific interest was the human ear. He descri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Abdominal Internal Oblique Muscle
The abdominal internal oblique muscle, also internal oblique muscle or interior oblique, is an abdominal muscle in the abdominal wall that lies below the external oblique muscle and just above the transverse abdominal muscle. Structure Its fibers run perpendicular to the external oblique muscle, beginning in the thoracolumbar fascia of the lower back, the anterior 2/3 of the iliac crest (upper part of hip bone) and the lateral half of the inguinal ligament. The muscle fibers run from these points superomedially (up and towards midline) to the muscle's insertions on the inferior borders of the 10th through 12th ribs and the linea alba. In males, the cremaster muscle is also attached to the internal oblique. Nerve supply The internal oblique is supplied by the lower intercostal nerves, as well as the iliohypogastric nerve and the ilioinguinal nerve. Function The internal oblique performs two major functions. Firstly as an accessory muscle of respiration, it acts as an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Inguinal Canal
The inguinal canal is a passage in the anterior abdominal wall on each side of the body (one on each side of the midline), which in males, convey the spermatic cords and in females, the round ligament of the uterus. The inguinal canals are larger and more prominent in males. Structure The inguinal canals are situated just above the medial half of the inguinal ligament. The canals are approximately 4 to 6 cm long, angled anteroinferiorly and medially. In males, its diameter is normally 2 cm (±1 cm in standard deviation) at the deep inguinal ring.The diameter has been estimated to be ±2.2cm ±1.08cm in Africans, and 2.1 cm ±0.41cm in Europeans. A first-order approximation is to visualize each canal as a cylinder. Walls To help define the boundaries, these canals are often further approximated as boxes with six sides. Not including the two rings, the remaining four sides are usually called the "anterior wall", "inferior wall ("floor")", "superior wall ("roof")", and "po ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aponeurosis Of The External Oblique Muscle
The aponeurosis of the abdominal external oblique muscle is a thin but strong membranous structure, the fibers of which are directed downward and medially. It is joined with that of the opposite muscle along the middle line, and covers the whole of the front of the abdomen; above, it is covered by and gives origin to the lower fibers of the pectoralis major; below, its fibers are closely aggregated together, and extend obliquely across from the anterior superior iliac spine to the pubic tubercle and the pectineal line to form the inguinal ligament. In the middle line, it interlaces with the aponeurosis of the opposite muscle, forming the linea alba, which extends from the xiphoid process to the pubic symphysis. That portion of the aponeurosis which extends between the anterior superior iliac spine and the pubic tubercle is a thick band, folded inward, and continuous below with the fascia lata; it is called the inguinal ligament. The portion which is reflected from the inguina ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Midclavicular Line
{{short description, None Anatomical lines, or "reference lines," are theoretical lines drawn through anatomical structures and are used to describe anatomical location. The following reference lines are identified in '' Terminologia Anatomica'': * Anterior median line * Lateral sternal line: A vertical line corresponding to the lateral margin of the sternum. * Parasternal line: A vertical line equidistant from the sternal and mid-clavicular lines. * Mid-clavicular line: A vertical line passing through the midpoint of the clavicle. * Mammillary line * Anterior axillary line: A vertical line on the anterior torso marked by the anterior axillary fold. * Midaxillary line: A vertical line passing through the apex of the axilla. * Posterior axillary line: A vertical line passing through the posterior axillary fold. * Scapular line: A vertical line passing through the inferior angle of the scapula. * Paravertebral line: A vertical line corresponding to the tips of the transverse proc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Latissimus Dorsi
The latissimus dorsi () is a large, flat muscle on the back that stretches to the sides, behind the arm, and is partly covered by the trapezius on the back near the midline. The word latissimus dorsi (plural: ''latissimi dorsi'') comes from Latin and means "broadest [muscle] of the back", from "latissimus" () and "dorsum" (). The pair of muscles are commonly known as "lats", especially among bodybuilders. The latissimus dorsi is responsible for Extension (kinesiology), extension, adduction, transverse extension also known as horizontal abduction (or horizontal extension), flexion from an extended position, and (medial) internal rotation of the shoulder joint. It also has a synergistic role in extension and Anatomical terms of motion, lateral flexion of the lumbar spine. Due to bypassing the scapulothoracic joints and attaching directly to the spine, the actions the latissimi dorsi have on moving the arms can also influence the movement of the scapulae, such as their downward ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Serratus Anterior
The serratus anterior is a muscle of the chest. It originates at the side of the chest from the upper 8 or 9 ribs; it inserts along the entire length of the anterior aspect of the medial border of the scapula. It is innervated by the long thoracic nerve from the brachial plexus. The serratus anterior acts to pull the scapula forward around the thorax. The muscle is named from Latin: ''serrare'' = to saw (referring to the shape); and ''anterior'' = on the front side of the body. Structure Origin Serratus anterior normally originates by nine or ten muscle slips – arising from either the 1st to 8th ribs, or the 1st to 9th ribs; because two slips usually arise from the 2nd rib, the number of slips is greater than the number of ribs from which they originate. Insertion The muscle is inserted along the medial border of the scapula between the superior and inferior angle of the scapula. The muscle is divided into three parts according to the points of insertion: * the se ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Adipose
Adipose tissue (also known as body fat or simply fat) is a loose connective tissue composed mostly of adipocytes. It also contains the stromal vascular fraction (SVF) of cells including preadipocytes, fibroblasts, Blood vessel, vascular endothelial cells and a variety of White blood cell, immune cells such as adipose tissue macrophages. Its main role is to store energy in the form of lipids, although it also cushions and Thermal insulation, insulates the body. Previously treated as being hormonally inert, in recent years adipose tissue has been recognized as a major endocrine organ, as it produces hormones such as leptin, estrogen, resistin, and cytokines (especially TNF-alpha, TNFα). In obesity, adipose tissue is implicated in the chronic release of pro-inflammatory markers known as adipokines, which are responsible for the development of metabolic syndromea constellation of diseases including type 2 diabetes, cardiovascular disease and atherosclerosis. Adipose tissue is d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |