|
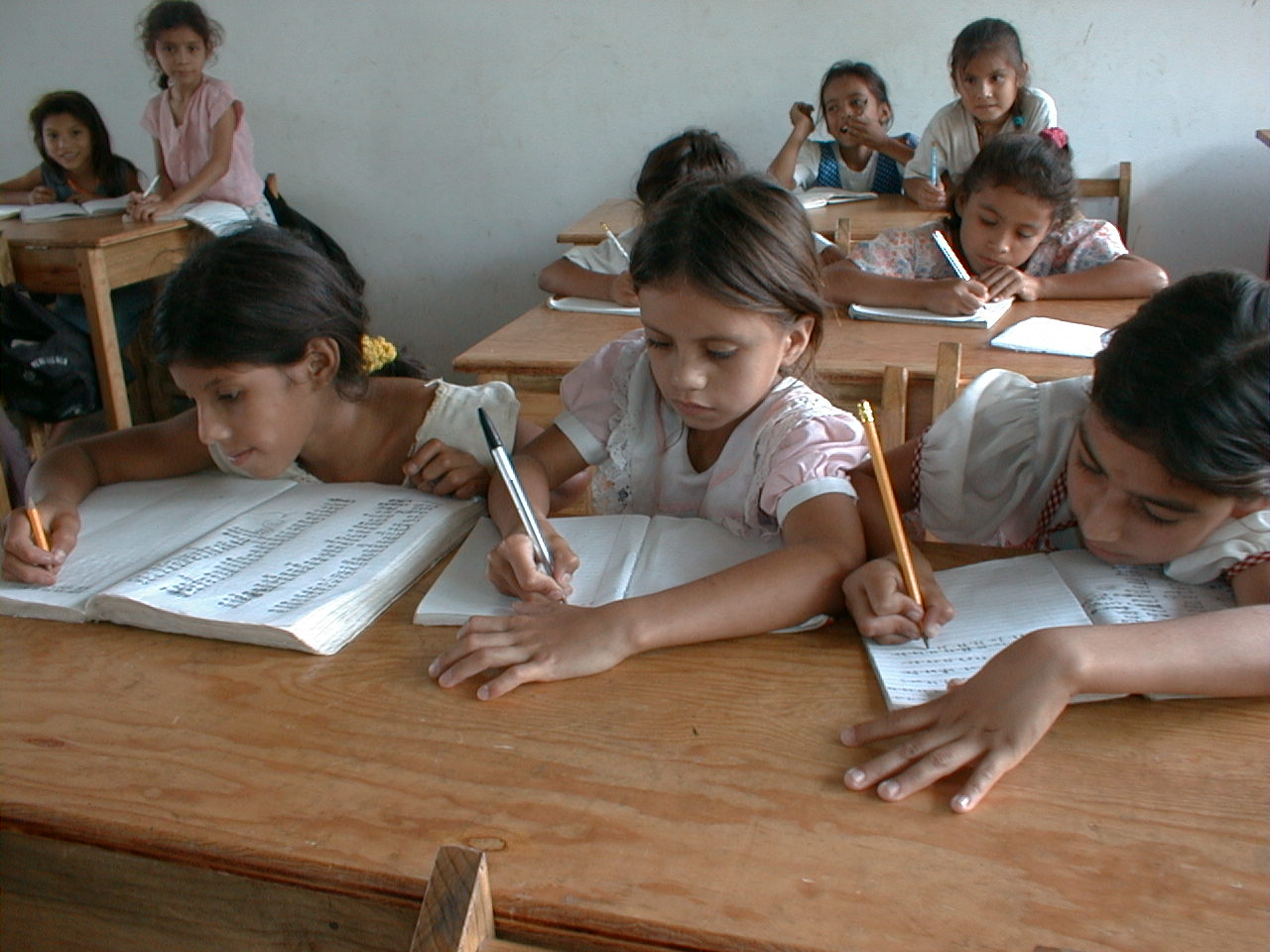
Exercise Book
An exercise book or composition book is a notebook that is used in schools to copy down schoolwork and notes. A student will usually have different exercise books for each separate lesson or subject. The exercise book format is different for some subjects: for the majority of subjects, the exercise book will contain lined paper with a margin, but for other subjects such as mathematics, the exercise book will contain squared paper to aid in the drawing of graphs, tables or other diagrams. Exercise books may act as a primary record of students' learning efforts. For younger pupils, books are often collected at the end of each lesson for review, scoring, or grading. Loose worksheets may be pasted into the book so that they are bound with other work. In some schools, exercise books may be colour-coded depending on the subject. For example, biology might be green and algebra blue. The exercise book was also called ''version book'' historically, and is called ''khata'' in In ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Graph Paper
Graph paper, coordinate paper, grid paper, or squared paper is writing paper that is printed with fine lines making up a regular grid. It is available either as loose leaf paper or bound in notebooks or graph books. It is commonly found in mathematics and engineering education settings, exercise books, and in laboratory notebooks. The lines are often used as guides for mathematical notation, plotting graph of a function, graphs of functions or experimental data, and drawing curves. History The Metropolitan Museum of Art owns a pattern book dated to around 1596 in which each page bears a grid woodblock printing, printed with a woodblock. The owner has used these grids to create block pictures in black and white and in colour. The first commercially published "coordinate paper" is usually attributed to a Dr. Buxton of England, who patented paper printed with a rectangular coordinate grid, in 1794. A century later, E. H. Moore, a distinguished mathematician at the University of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Punctuation
Punctuation marks are marks indicating how a piece of writing, written text should be read (silently or aloud) and, consequently, understood. The oldest known examples of punctuation marks were found in the Mesha Stele from the 9th century BC, consisting of points between the words and horizontal strokes between sections. The alphabet-based writing began with no spaces, no capitalization, no vowels (see abjad), and with only a few punctuation marks, as it was mostly aimed at recording business transactions. Only with the Greek playwrights (such as Euripides and Aristophanes) did the ends of sentences begin to be marked to help actors know when to make a pause during performances. Punctuation includes Space (punctuation), space between words and both obsolete and modern signs. By the 19th century, the punctuation marks were used hierarchically, according to their weight. Six marks, proposed in 1966 by the French author Hervé Bazin, could be seen as predecessors of emoticons and e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Grammar
In linguistics, grammar is the set of rules for how a natural language is structured, as demonstrated by its speakers or writers. Grammar rules may concern the use of clauses, phrases, and words. The term may also refer to the study of such rules, a subject that includes phonology, morphology (linguistics), morphology, and syntax, together with phonetics, semantics, and pragmatics. There are, broadly speaking, two different ways to study grammar: traditional grammar and #Theoretical frameworks, theoretical grammar. Fluency in a particular language variety involves a speaker internalizing these rules, many or most of which are language acquisition, acquired by observing other speakers, as opposed to intentional study or language teaching, instruction. Much of this internalization occurs during early childhood; learning a language later in life usually involves more direct instruction. The term ''grammar'' can also describe the linguistic behaviour of groups of speakers and writer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Multiplication Table
In mathematics, a multiplication table (sometimes, less formally, a times table) is a mathematical table used to define a multiplication binary operation, operation for an algebraic system. The decimal multiplication table was traditionally taught as an essential part of elementary arithmetic around the world, as it lays the foundation for arithmetic operations with base-ten numbers. Many educators believe it is necessary to memorize the table up to 9 × 9. History Pre-modern times The oldest known multiplication tables were used by the Babylonian mathematics, Babylonians about 4000 years ago. However, they used a base of 60. The oldest known tables using a base of 10 are the Chinese mathematics, Chinese Tsinghua Bamboo Slips#Decimal multiplication table, decimal multiplication table on bamboo strips dating to about 305 BC, during China's Warring States period. The multiplication table is sometimes attributed to the ancient Greek mathematician Pythagoras (570–495 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Metric System
The metric system is a system of measurement that standardization, standardizes a set of base units and a nomenclature for describing relatively large and small quantities via decimal-based multiplicative unit prefixes. Though the rules governing the metric system have changed over time, the modern definition, the International System of Units (SI), defines the metric prefixes and seven base units: metre (m), kilogram (kg), second (s), ampere (A), kelvin (K), Mole (unit), mole (mol), and candela (cd). An SI derived unit is a named combination of base units such as hertz (cycles per second), Newton (unit), newton (kg⋅m/s2), and tesla (unit), tesla (1 kg⋅s−2⋅A−1) and in the case of Celsius a shifted scale from Kelvin. Certain units have been Non-SI units mentioned in the SI#Units officially accepted for use with the SI, officially accepted for use with the SI. Some of these are decimalised, like the litre and electronvolt, and are considered "metric". Others, like ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Imperial System
The imperial system of units, imperial system or imperial units (also known as British Imperial or Exchequer Standards of 1826) is the system of units first defined in the British Weights and Measures Act 1824 and continued to be developed through a series of Weights and Measures Acts and amendments. The imperial system developed from earlier English units as did the related but differing system of customary units of the United States. The imperial units replaced the Winchester Standards, which were in effect from 1588 to 1825. The system came into official use across the British Empire in 1826. By the late 20th century, most nations of the former empire had officially adopted the metric system as their main system of measurement, but imperial units are still used alongside metric units in the United Kingdom and in some other parts of the former empire, notably Canada. The modern UK legislation defining the imperial system of units is given in the Weights and Measures A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cap Line
In typography, cap height is the height of a capital letter above the baseline for a particular typeface.http://pfaedit.sourceforge.net/glossary.html Glossary of (some) Typographic Terms It specifically is the height of capital letters that are flat—such as H or I—as opposed to round letters such as O, or pointed letters like A, both of which may display overshoot. The height of the small letters is the x-height. See also * Body height (typography) In typography, the body height or point size refers to the height of the space in which a glyph is defined. Originally, in metal typesetting, the body height or the font (or point) size was defined by the height of the lead cuboid ( metal sort) ... References External links Typography {{typ-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Baseline (typography)
In European and West Asian typography and penmanship, the baseline is the line upon which most letters ''sit'' and below which descenders extend. In the example to the right, the letter 'p' has a descender; the other letters sit on the (red) baseline. Most, though not all, typefaces are similar in the following ways as regards the baseline: *capital letters sit on the baseline. The most common exceptions are the J and Q. *All lining figures sit on the baseline: *Some text figures have descenders: *The following lowercase letters have descenders: g j p q y. *Glyphs with rounded lower and upper extents (0 3 6 8 c C G J o O Q) dip very slightly below the baseline (" overshoot") to create the optical illusion that they sit on the baseline, and rise above the x-height or capital height to create the illusion that they have the same height as flat glyphs (such as those for H x X 1 5 7). Peter Karow's ''Digital Typefaces'' suggests that typical overshoot is about 1.5%. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Composition Book
Composition or Compositions may refer to: Arts and literature *Composition (dance), practice and teaching of choreography *Composition (language), in literature and rhetoric, producing a work in spoken tradition and written discourse, to include visuals and digital space *Composition (visual arts), the plan, placement or arrangement of the elements of art in a work * ''Composition'' (Peeters), a 1921 painting by Jozef Peeters *Composition studies, the professional field of writing instruction * ''Compositions'' (album), an album by Anita Baker *Digital compositing, the practice of digitally piecing together a still image or video *Musical composition, an original piece of music, or the process of creating a new piece Computer science *Compose key, a key on a computer keyboard *Compositing window manager a component of a computer's graphical user interface that draws windows and/or their borders *Function composition (computer science), an act or mechanism to combine simple functi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
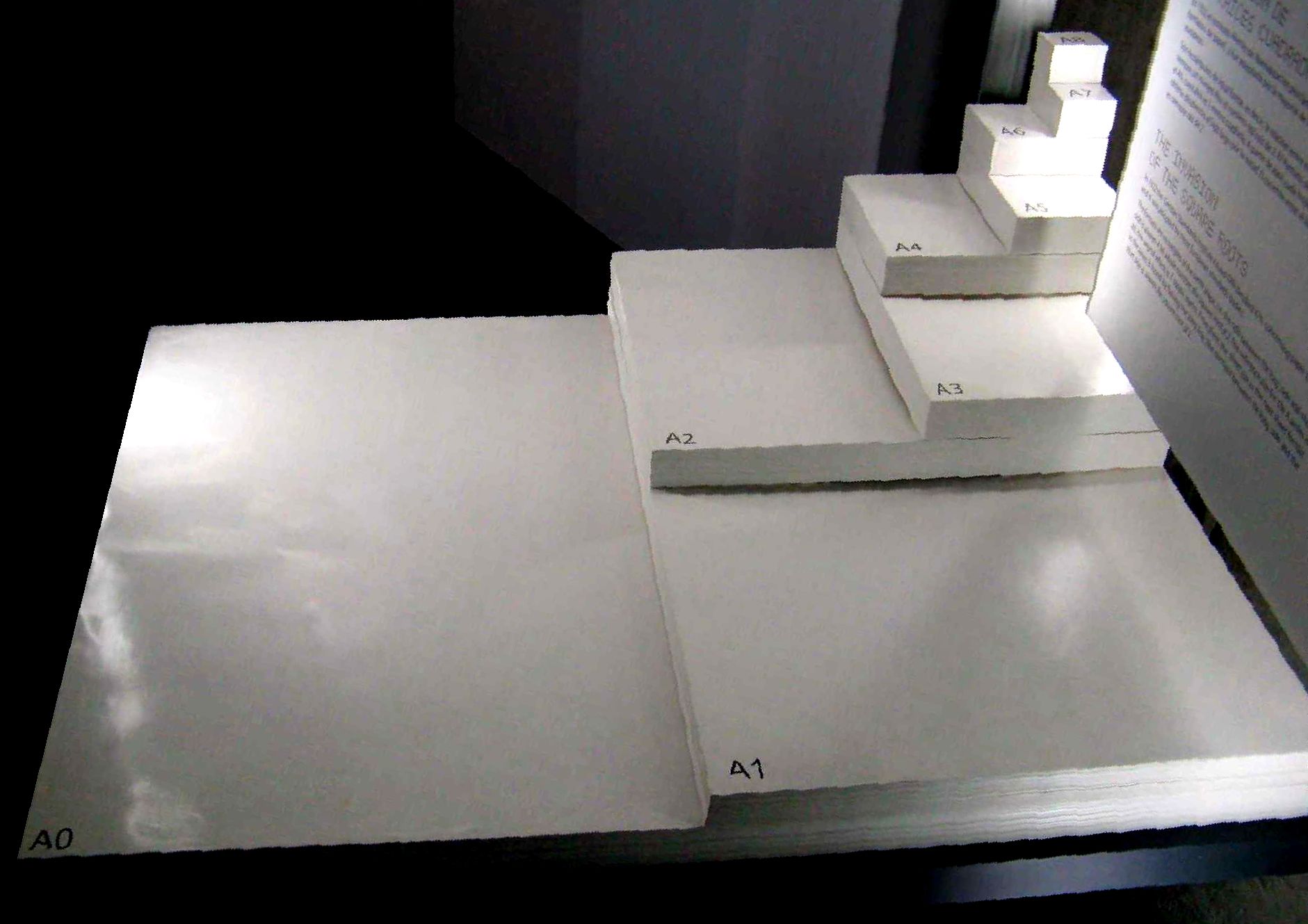
ISO 216
ISO 216 is an international standard for paper sizes, used around the world except in North America and parts of Latin America. The standard defines the "A", "B" and "C" series of paper sizes, which includes the A4, the most commonly available paper size worldwide. Two supplementary standards, ISO 217 and ISO 269, define related paper sizes; the ISO 269 "C" series is commonly listed alongside the A and B sizes. All ISO 216, ISO 217 and ISO 269 paper sizes (except some envelopes) have the same aspect ratio, , within rounding to millimetres. This ratio has the unique property that when cut or folded in half widthways, the halves also have the same aspect ratio. Each ISO paper size is one half of the area of the next larger size in the same series. Dimensions of A, B and C series History The oldest known mention of the advantages of basing a paper size on an aspect ratio of \sqrt is found in a letter written on 25 October 1786 by the German scientist Georg Christoph ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arithmetic
Arithmetic is an elementary branch of mathematics that deals with numerical operations like addition, subtraction, multiplication, and division. In a wider sense, it also includes exponentiation, extraction of roots, and taking logarithms. Arithmetic systems can be distinguished based on the type of numbers they operate on. Integer arithmetic is about calculations with positive and negative integers. Rational number arithmetic involves operations on fractions of integers. Real number arithmetic is about calculations with real numbers, which include both rational and irrational numbers. Another distinction is based on the numeral system employed to perform calculations. Decimal arithmetic is the most common. It uses the basic numerals from 0 to 9 and their combinations to express numbers. Binary arithmetic, by contrast, is used by most computers and represents numbers as combinations of the basic numerals 0 and 1. Computer arithmetic deals with the specificities of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |