|
Eurasiatic Languages
Eurasiatic is a hypothetical and controversial language macrofamily proposal that would include many language families historically spoken in northern, western, and southern Eurasia. The idea of a Eurasiatic superfamily dates back more than 100 years. Joseph Greenberg's proposal, dating to the 1990s, is the most widely discussed version. In 2013, Mark Pagel and three colleagues published what they believe to be statistical evidence for a Eurasiatic language family. The branches of Eurasiatic vary between proposals, but typically include the highly controversial Altaic macrofamily (composed in part of Mongolic, Tungusic and Turkic), Chukchi-Kamchatkan, Eskimo–Aleut, Indo-European, and Uralic—although Greenberg uses the controversial Uralic-Yukaghir classification instead. Other branches sometimes included are the Kartvelian and Dravidian families, as proposed by Pagel et al., in addition to the language isolates Nivkh, Etruscan and Greenberg's "Korean–Japanese ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Siberia
Siberia ( ; , ) is an extensive geographical region comprising all of North Asia, from the Ural Mountains in the west to the Pacific Ocean in the east. It has formed a part of the sovereign territory of Russia and its predecessor states since the lengthy conquest of Siberia, which began with the fall of the Khanate of Sibir in 1582 and concluded with the annexation of Chukotka in 1778. Siberia is vast and sparsely populated, covering an area of over , but home to roughly a quarter of Russia's population. Novosibirsk, Krasnoyarsk, and Omsk are the largest cities in the area. Because Siberia is a geographic and historic concept and not a political entity, there is no single precise definition of its territorial borders. Traditionally, Siberia spans the entire expanse of land from the Ural Mountains to the Pacific Ocean, with the Ural River usually forming the southernmost portion of its western boundary, and includes most of the drainage basin of the Arctic Ocean. I ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Macrofamily
A macrofamily (also called a superfamily or superphylum) is a term often used in historical linguistics to refer to a hypothetical higher order grouping of languages. Metonymically, the term became associated with the practice of trying to group together various languages and language families (including isolates) in a larger scale classification. Campbell, Lyle and Mixco, Mauricio J. (2007), ''A Glossary of Historical Linguistics'', University of Utah Press/Edinburgh University Press. However, some scholars Campbell, Lyle (2004), ''Historical Linguistics: An Introduction'', Edinburgh University Press. view this term as superfluous if not outright redundant as there is no real tangible linguistic divide the same way there is between a linguistic isolate and a language family proper. Lyle Campbell, professor at the University of Hawaiʻi at Mānoa, had famously said that he is preferring to use the terms "language family" for those classifications for which there is consensus an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nostratic
Nostratic is a hypothetical language macrofamily including many of the language families of northern Eurasia first proposed in 1903. Though a historically important proposal, it is now generally considered a fringe theory. Its exact composition varies based on proponent; it typically includes the Kartvelian, Indo-European, and Uralic languages; some languages from the similarly controversial Altaic family, the Afroasiatic languages, and the Dravidian languages (also referred to as Elamo-Dravidian). The Nostratic hypothesis originates with Holger Pedersen in the early 20th century. The name "Nostratic" is due to Pedersen (1903), derived from the Latin '' nostrates'' "fellow countrymen". The hypothesis was significantly expanded in the 1960s by Soviet linguists, notably Vladislav Illich-Svitych and Aharon Dolgopolsky. The hypothesis has fallen out of favour since the latter half of the 20th century and has limited degrees of acceptance, predominantly among a minority of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Etruscan Language
Etruscan ( ) was the language of the Etruscan civilization in the ancient region of Etruria, in Etruria Padana and Etruria Campana in what is now Italy. Etruscan influenced Latin but was eventually superseded by it. Around 13,000 Etruscan epigraphy, inscriptions have been found so far, only a small minority of which are of significant length; some bilingual inscriptions with texts also in Latin, Ancient Greek, Greek, or Phoenician language, Phoenician; and a few dozen purported loanwords. Attested from 700 BC to AD 50, the relation of Etruscan to other languages has been a source of long-running speculation and study. Nowadays, it is generally agreed to be in the Tyrsenian language family, but before it gained currency as one of the Tyrsenian languages, it was commonly treated as an Language isolate, isolate, although there were also a number of other less well-known hypotheses. The consensus among linguists and Etruscologists is that Etruscan was a Pre-Indo-European languages, Pre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Language Isolate
A language isolate is a language that has no demonstrable genetic relationship with any other languages. Basque in Europe, Ainu and Burushaski in Asia, Sandawe in Africa, Haida and Zuni in North America, Kanoê in South America, and Tiwi in Oceania are all examples of such languages. The exact number of language isolates is yet unknown due to insufficient data on several languages. One explanation for the existence of language isolates is that they might be the last remaining member of a larger language family. Such languages might have had relatives in the past that have since disappeared without being documented, leaving them an orphaned language. One example is the Ket language spoken in central Siberia, which belongs to the wider Yeniseian language family; had it been discovered in recent times independently from its now extinct relatives, such as Yugh and Kott, it would have been classified as an isolate. Another explanation for language isolates is that they aro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
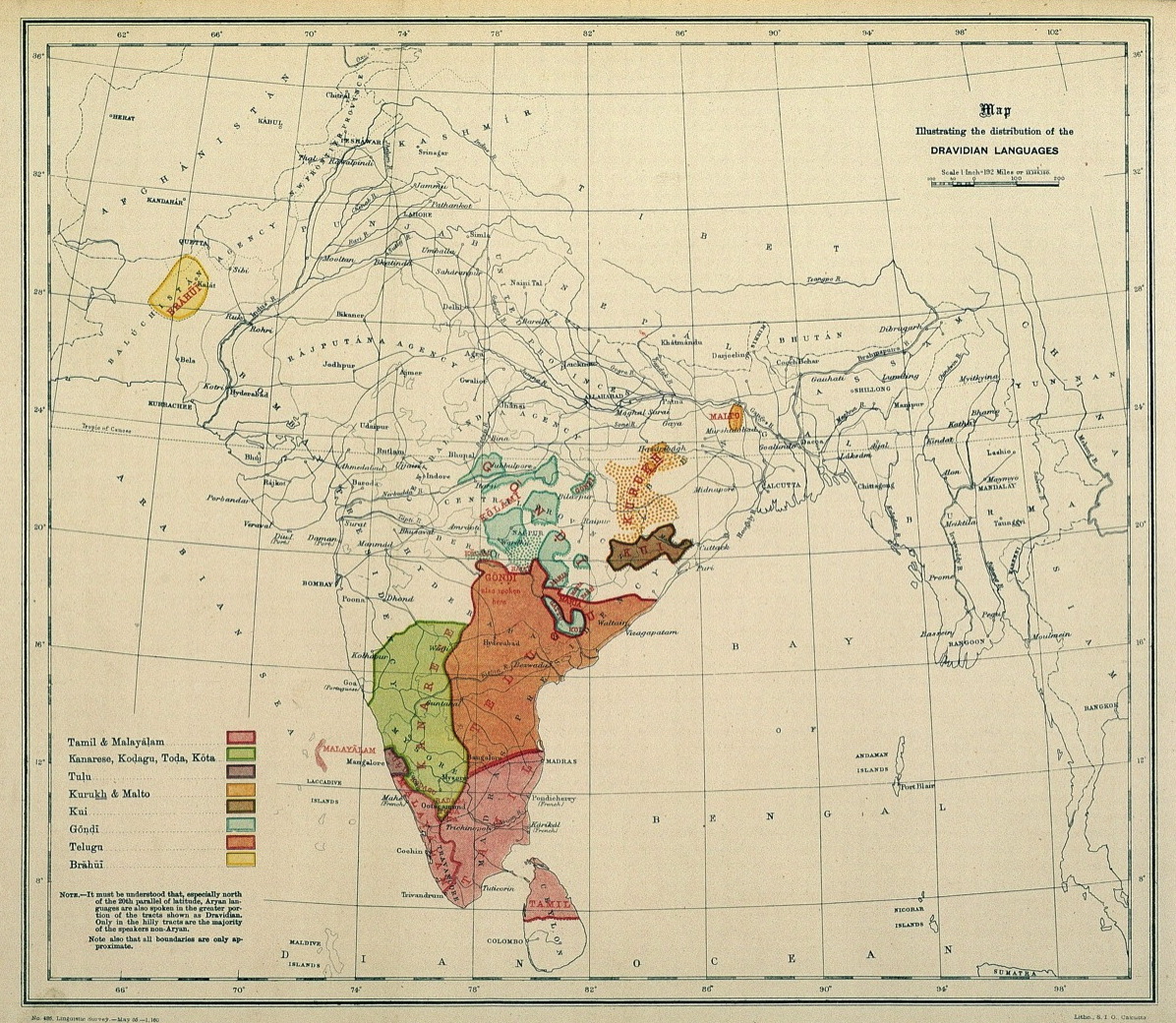
Dravidian Languages
The Dravidian languages are a language family, family of languages spoken by 250 million people, primarily in South India, north-east Sri Lanka, and south-west Pakistan, with pockets elsewhere in South Asia. The most commonly spoken Dravidian languages are (in descending order) Telugu language, Telugu, Tamil language, Tamil, Kannada, and Malayalam, all of which Classical languages of India, have long literary traditions. Smaller literary languages are Tulu language, Tulu and Kodava language, Kodava. Together with several smaller languages such as Gondi language, Gondi, these languages cover the southern part of India and the northeast of Sri Lanka, and account for the overwhelming majority of speakers of Dravidian languages. Malto language, Malto and Kurukh language, Kurukh are spoken in isolated pockets in eastern India. Kurukh is also spoken in parts of Nepal, Bhutan and Bangladesh. Brahui language, Brahui is mostly spoken in the Balochistan region of Pakistan, Sistan and Baluc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kartvelian Languages
The Kartvelian languages ( ; ka, ქართველური ენები, tr; also known as South Caucasian or Kartvelic languages Boeder (2002), p. 3) are a language family indigenous to the South Caucasus and spoken primarily in Georgia. There are approximately 5 million Georgian language speakers worldwide, with large groups in Russia, Iran, the United States, the European Union, Israel, and northeastern Turkey. The Kartvelian family has no known relation to any other language family, making it one of the world's primary language families. The most widely spoken of these languages is Georgian. The earliest literary source in any Kartvelian language is the Old Georgian Bir el Qutt inscriptions, written in ancient Georgian Asomtavruli script at the once-existing Georgian monastery near Bethlehem,Lang (1966), p. 154 dated to . Georgian scripts are used to write all Kartvelian languages. Status Georgian is the official language of Georgia (spoken by 90% of the p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Uralic Languages
The Uralic languages ( ), sometimes called the Uralian languages ( ), are spoken predominantly in Europe and North Asia. The Uralic languages with the most native speakers are Hungarian, Finnish, and Estonian. Other languages with speakers above 100,000 are Erzya, Moksha, Mari, Udmurt and Komi spoken in the European parts of the Russian Federation. Still smaller minority languages are Sámi languages of the northern Fennoscandia; other members of the Finnic languages, ranging from Livonian in northern Latvia to Karelian in northwesternmost Russia; the Samoyedic languages and the others of members of the Ugric languages, Mansi and Khanty spoken in Western Siberia. The name ''Uralic'' derives from the family's purported "original homeland" (''Urheimat'') hypothesized to have been somewhere in the vicinity of the Ural Mountains, and was first proposed by Julius Klaproth in ''Asia Polyglotta'' (1823). Finno-Ugric is sometimes used as a synonym for Uralic but more accu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eskimo–Aleut
The Eskaleut ( ), Eskimo–Aleut or Inuit–Yupik–Unangan languages are a language family native to the northern portions of the North American continent, and a small part of northeastern Asia. Languages in the family are indigenous to parts of what are now the United States (Alaska); Canada (Inuit Nunangat) including Nunavut, Northwest Territories (principally in the Inuvialuit Settlement Region), northern Quebec (Nunavik), and northern Labrador (Nunatsiavut); Greenland; and the Russian Far East (Chukchi Peninsula). The language family is also known as ''Eskaleutian'', or ''Eskaleutic.'' The Eskaleut language family is divided into two branches: Eskimoan and Aleut. The Aleut branch consists of a single language, Aleut, spoken in the Aleutian Islands and the Pribilof Islands. Aleut is divided into several dialects. The Eskimoan languages are divided into two branches: the Yupik languages, spoken in western and southwestern Alaska and in Chukotka, and the Inuit languages, spoke ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chukchi-Kamchatkan
The Chukotko-Kamchatkan or Chukchi–Kamchatkan languages are a language family of extreme northeastern Siberia. Its speakers traditionally were indigenous hunter-gatherers and reindeer-herders. Chukotko-Kamchatkan is endangered. The Kamchatkan branch is moribund, represented only by Western Itelmen, with less than a hundred speakers left. The Chukotkan branch had close to 7,000 speakers left (as of 2010, the majority being speakers of Chukchi), with a reported total ethnic population of 25,000. While the family is sometimes grouped typologically and geographically as Paleosiberian, no external genetic relationship has been widely accepted as proven. The most popular such proposals have been for links with Eskimo–Aleut, either alone or in the context of a wider grouping. Alternative names Less commonly encountered names for the family are Chukchian, Chukotian, Chukotan, Kamchukchee and Kamchukotic. Of these, ''Chukchian'', ''Chukotian'' and ''Chukotan'' are ambiguous, sinc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mark Pagel
Mark David Pagel FRS (born 5 June 1954 in Seattle, Washington) is an evolutionary biologist and professor. He heads the Evolutionary Biology Group at the University of Reading. He is known for comparative studies in evolutionary biology. In 1994, with his spouse, anthropologist Ruth Mace, Pagel pioneered the Comparative Method in Anthropology. Education Pagel was a student educated at the University of Washington where he was awarded a PhD in Mathematics in 1980 for work on ridge regression. Research During the late 1980s, Pagel worked on developing ways to analyse species relatedness, in the zoology department at the University of Oxford. Having met there, in 1994, Pagel and anthropologist Ruth Mace co-authored a paper, "The Comparative Method in Anthropology", that used phylogenetic methods to analyse human cultures, pioneering a new field of science — using evolutionary trees, or phylogenies, in anthropology, to explain human behaviour. Pagel's interests include evolutio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |