|
Epipophyses
Epipophyses are bony projections of the cervical vertebrae found in archosauromorphs, particularly dinosaurs (including some basal birds). These paired processes sit above the postzygapophyses on the rear of the vertebral neural arch. Their morphology is variable and ranges from small, simple, hill-like elevations to large, complex, winglike projections. Epipophyses provided large attachment areas for several neck muscles; large epipophyses are therefore indicative of a strong neck musculature. The presence of epipophyses is a synapomorphy (distinguishing feature) of the group Dinosauria. Epipophyses were present in the basal-most dinosaurs, but absent in the closest relatives of the group, such as ''Marasuchus'' and '' Silesaurus''. They were typical for most dinosaur lineages; however, they became lost in several derived theropod lineages in the wake of an increasingly S-shaped curvature of the neck. Several scientific papers have observed that epipophyses were present in v ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dinosaur
Dinosaurs are a diverse group of reptiles of the clade Dinosauria. They first appeared during the Triassic Geological period, period, between 243 and 233.23 million years ago (mya), although the exact origin and timing of the #Evolutionary history, evolution of dinosaurs is a subject of active research. They became the dominant terrestrial vertebrates after the Triassic–Jurassic extinction event 201.3 mya and their dominance continued throughout the Jurassic and Cretaceous periods. The fossil record shows that birds are feathered dinosaurs, Evolution of birds, having evolved from earlier Theropoda, theropods during the Late Jurassic epoch, and are the only dinosaur lineage known to have survived the Cretaceous–Paleogene extinction event approximately 66 mya. Dinosaurs can therefore be divided into avian dinosaurs—birds—and the extinct non-avian dinosaurs, which are all dinosaurs other than birds. Dinosaurs are varied from taxonomy (biology), taxonomic, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
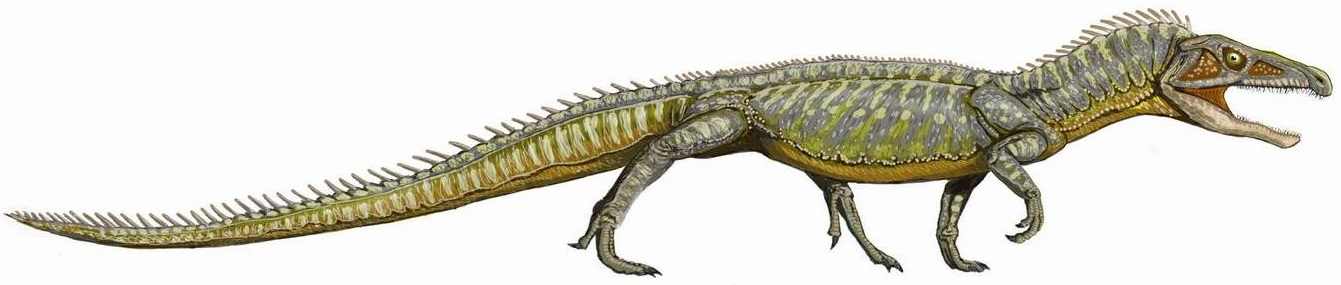
Carnotaurus LA
''Carnotaurus'' (; ) is a genus of theropod dinosaur that lived in South America during the Late Cretaceous period, probably sometime between 72 and 69 million years ago. The only species is ''Carnotaurus sastrei''. Known from a single well-preserved skeleton, it is one of the best-understood theropods from the Southern Hemisphere. The skeleton, found in 1984, was uncovered in the Chubut Province of Argentina from rocks of the La Colonia Formation. ''Carnotaurus'' is a derived member of the Abelisauridae, a group of large theropods that occupied the large predatorial niche in the southern landmasses of Gondwana during the late Cretaceous. Within the Abelisauridae, the genus is often considered a member of the Brachyrostra, a clade of short-snouted forms restricted to South America. ''Carnotaurus'' was a lightly built, bipedal predator, measuring in length and weighing . As a theropod, ''Carnotaurus'' was highly specialized and distinctive. It had two thick horns above the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Xilousuchus
''Xilousuchus'' is an extinct genus of poposauroid from lower Triassic (Olenekian stage) deposits of Fugu County of northeastern Shanxi Province, China. Xilousuchus is one of the oldest archosaurs known to date. Discovery and naming It is known from the holotype, IVPP V 6026, a single well-preserved partial skeleton including the skull. It was found from the Heshanggou Formation of the Ordos Basin, Hazhen commune. It was first named by Xiao-Chun Wu in 1981 and the type species is ''Xilousuchus sapingensis''. Wu (1981) referred ''Xilousuchus'' to the Proterosuchia. Gower and Sennikov (1996) found it to be an erythrosuchian based strictly on the braincase. A more detailed re-description of the genus was provided by Nesbitt ''et al.'' (2010) and found poposauroid affinities. In his massive revision of archosaurs which included a large cladistic analysis, Sterling J. Nesbitt (2011) found ''Xilousuchus'' to be a poposauroid which is most closely related to '' Arizonas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Michael P
Michael may refer to: People * Michael (given name), a given name * he He ..., a given name * Michael (surname), including a list of people with the surname Michael Given name * Michael (bishop elect)">Michael (surname)">he He ..., a given name * Michael (surname), including a list of people with the surname Michael Given name * Michael (bishop elect), English 13th-century Bishop of Hereford elect * Michael (Khoroshy) (1885–1977), cleric of the Ukrainian Orthodox Church of Canada * Michael Donnellan (fashion designer), Michael Donnellan (1915–1985), Irish-born London fashion designer, often referred to simply as "Michael" * Michael (footballer, born 1982), Brazilian footballer * Michael (footballer, born 1983), Brazilian footballer * Michael (footballer, born 1993), Brazilian footballer * Michael (footballer, born February 1996), Brazilian footballer * Michael (footballer, born March 1996), Brazilian footballer * Michael (footballer, born 1999), Brazilian football ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Allokotosauria
Allokotosauria is a clade of early archosauromorph reptiles from the Middle to Late Triassic known from Asia, Africa, North America and Europe. Allokotosauria was first described and named when a new monophyletic grouping of specialized herbivorous archosauromorphs was recovered by Sterling J. Nesbitt, John J. Flynn, Adam C. Pritchard, J. Michael Parrish, Lovasoa Ranivoharimanana and André R. Wyss in 2015. The name Allokotosauria is derived from Greek meaning "strange reptiles" in reference to unexpected grouping of early archosauromorph with a high disparity of features typically associated with herbivory. History Nesbitt ''et al.'' (2015) defined the group as a stem-based taxon containing '' Azendohsaurus madagaskarensis'' and '' Trilophosaurus buettneri'' and all taxa more closely related to them than to ''Tanystropheus longobardicus'', '' Proterosuchus fergusi'', ''Protorosaurus speneri'' or '' Rhynchosaurus articeps''. Therefore, Allokotosauria includes the families Aze ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tanystropheidae
Tanystropheidae is an extinct family (biology), family of archosauromorph reptiles that lived throughout the Triassic Period, often considered to be "protorosaurs". They are characterized by their long, stiff necks formed from elongated cervical vertebrae with very long cervical ribs. Members of the group include both terrestrial and aquatic forms. While some tanystropheids were small lizard-like animals, other tanystropheids such as ''Tanystropheus'' were large animals that had necks that were several meters long, longer than the rest of their bodies. Tanystropheids are known from Europe, Asia (Russia, China, and Saudi Arabia), North America and probably South America (Brazil). The presence of tanystropheids in Europe and China indicate that they lived along much of the coastline of the Tethys Ocean. However, species in western North America are found in terrestrial deposits, suggesting that as a group, tanystropheids were ecologically diverse. Relationships among tanystropheid ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rhynchosaur
Rhynchosaurs are a group of extinct herbivorous Triassic archosauromorph reptiles, belonging to the order Rhynchosauria. Members of the group are distinguished by their triangular skulls and elongated, beak like premaxillary bones. Rhynchosaurs first appeared in the Early Triassic, reaching their broadest abundance and a global distribution during the Carnian stage of the Late Triassic. Description Rhynchosaurs were herbivores, and at times abundant (in some fossil localities accounting for 40 to 60% of specimens found), with stocky bodies and a powerful beak. Early primitive forms, like '' Mesosuchus'' and '' Howesia'', were generally small, typically lizard-like in build, and had skulls rather similar to the early diapsid ''Youngina'', except for the beak and a few other features. Later and more advanced genera grew to up to two meters in length. The skull in these forms were short, broad, and triangular, becoming much wider than long in the most advanced forms like '' Hype ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Halazhaisuchus
''Halazhaisuchus'' is an extinct genus of archosauriform from the Early Triassic of China. It is known from a single species, ''Halazhaisuchus qiaoensis'', which was named in 1982 from the lower Ermaying Formation in Shaanxi. It was assigned to the family Euparkeriidae as a close relative of the genus '' Euparkeria'' from South Africa. ''Halazhaisuchus'' is known from a single holotype specimen called V6027, which was discovered in 1977 and includes a portion of the vertebral column, some ribs, two scapulae and two humeri, the right radius and ulna, and a left coracoid. Two rows of plate-like bones called osteoderm Osteoderms are bony deposits forming scales, plates, or other structures based in the dermis. Osteoderms are found in many groups of extant and extinct reptiles and amphibians, including lizards, crocodilians, frogs, temnospondyls (extinct amph ...s run along the length of the vertebrae. When it was first described in 1982, ''Halazhaisuchus'' was considered a c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vancleavea
''Vancleavea'' is a genus of extinct, armoured, non-archosaurian archosauriforms from the Late Triassic of western North America. The type species, type and only known species is ''V. campi'', named by Robert Long & Phillip A Murry in 1995 in paleontology, 1995. At that time, the genus was only known from fragmentary bones including osteoderms and vertebrae. However, since then many more fossils have been found, including a pair of nearly complete skeletons discovered in 2002. These finds have shown that members of the genus were bizarre semiaquatic reptiles. ''Vancleavea'' individuals had short snouts with large, fang-like teeth, and long bodies with small limbs. They were completely covered with bony plates known as osteoderms, which came in several different varieties distributed around the body. Phylogenetics, Phylogenetic analyses by professional paleontologists have shown that ''Vancleavea'' was an archosauriform, part of the lineage of reptiles that would lead to archosaurs ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Archosauriformes
Archosauriformes (Ancient Greek, Greek for 'ruling lizards', and Latin for 'form') is a clade of diapsid reptiles encompassing Archosaur, archosaurs and some of their close relatives. It was defined by Jacques Gauthier (1994) as the clade stemming from the Most recent common ancestor, last common ancestor of Proterosuchidae and Archosauria. Phil Senter (2005) defined it as the most exclusive clade containing ''Proterosuchus'' and Archosauria. Gauthier as part of the ''Phylonyms'' (2020) defined the clade as the last common ancestor of ''Chicken, Gallus'', ''Alligator'', and ''Proterosuchus'', and all its descendants. Archosauriforms are a branch of Archosauromorpha, archosauromorphs which originated in the Late Permian (roughly 252 million years ago) and persist to the present day as the two surviving archosaur groups: Crocodilia, crocodilians and Bird, birds. Archosauriforms present several traits historically ascribed to the group Archosauria. These include serrated teeth set in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aphanosauria
Aphanosauria ("hidden lizards") is an extinct group of reptiles distantly related to dinosaurs (including birds). They are at the base of a group known as Avemetatarsalia, one of two main branches of archosaurs. The other main branch, Pseudosuchia, includes modern crocodilians. Aphanosaurs possessed features from both groups, indicating that they are the oldest and most primitive known clade of avemetatarsalians, at least in terms of their position on the archosaur family tree. Other avemetatarsalians include the flying pterosaurs, small bipedal Lagerpetidae, lagerpetids, herbivorous Silesauridae, silesaurids, and the incredibly diverse dinosaurs, which survive to the present day in the form of birds. Aphanosauria is formally defined as the most inclusive clade containing ''Teleocrater, Teleocrater rhadinus'' and ''Yarasuchus, Yarasuchus deccanensis'' but not ''House sparrow, Passer domesticus'' (house sparrow) or ''Nile crocodile, Crocodylus niloticus'' (Nile crocodile). This grou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Avemetatarsalia
Avemetatarsalia (meaning "bird metatarsals") is a clade of diapsid Reptile, reptiles containing all archosaurs more closely related to birds than to crocodilians. The two most successful groups of avemetatarsalians were the dinosaurs and pterosaurs. Dinosaur, Dinosaurs were the largest terrestrial animals for much of the Mesozoic era, Mesozoic Era, and one group of small feathered dinosaurs (Aves, i.e. birds) has survived up to the present day. Pterosaur, Pterosaurs were the first flying vertebrates and persisted through the Mesozoic before dying out at the Cretaceous–Paleogene extinction event, Cretaceous-Paleogene (K-Pg) extinction event. Both dinosaurs and pterosaurs appeared in the Triassic period, Triassic Period, shortly after avemetatarsalians as a whole. The name Avemetatarsalia was first established by British palaeontologist Michael J. Benton, Michael Benton in 1999. An alternate name is Pan-Aves, or "all birds", in reference to its definition containing all animals, li ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |