|
El (deity)
El is a Northwest Semitic word meaning 'god' or 'deity', or referring (as a proper name) to any one of multiple major ancient Near Eastern deities. A rarer form, ''ila'', represents the predicate form in the Old Akkadian and Amorite languages. The word is derived from the Proto-Semitic *ʔil-. Originally a Canaanite deity known as ''El'', ''Al'' or ''Il'' the supreme god of the ancient Canaanite religion and the supreme god of East Semitic speakers in Early Dynastic Period of Mesopotamia. Among the Hittites, El was known as Elkunirša ( ). Although El gained different appearances and meanings in different languages over time, it continues to exist as ''El-'', ''-il'' or ''-el'' in compound proper noun phrases such as Elizabeth, Ishmael, Israel, Samuel, Daniel, Michael, Gabriel (Arabic: Jibra'il), and Bethel. Linguistic forms and meanings Cognate forms of El are found throughout the Semitic languages. They include Ugaritic , pl. ; Phoenician pl. ; Hebrew , pl. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Adonai
Judaism has different names given to God in Judaism, God, which are considered sacred: (), (''Adonai'' ), (''El (deity), El'' ), ( ), (''El Shaddai, Shaddai'' ), and ( ); some also include I Am that I Am.This is the formulation of Joseph Karo (SA YD 276:9). Maimonides (MT Yesodei haTorah 6:2), Jacob ben Asher (AT YD 276), and Isaac Alfasi (HK Menachot 3b) also included I Am that I Am, as do many later authorities, including Moses Isserles (SA YD 276:9). The original lists are found in y. Megillah 1:9 and b. Shavuot 35a, with some MSs agreeing with each authority. Maimonides and followers give the number of names as seven; however, manuscript inconsistency makes it difficult to judge which are included. Authorities including Asher ben Jehiel (''Responsa'' 3:15), the Tosafot, Tosafists (b. Sotah 10a), Yechiel of Paris (cited ''Birkei Yosef, Oraḥ Hayyim'' 85:8), Simeon ben Zemah Duran, Yaakov ben Moshe Levi Moelin, and Moses Isserles (SA YD 276:13), include the term Shalom ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yam (god)
Yam (sometimes Yamm; ; “sea”) was a god representing the sea and other sources of water worshiped in various locations on the eastern Mediterranean coast, as well as further inland in modern Syria. He is best known from the Ugaritic texts. While he was a minor deity in Ugaritic religion, he is nonetheless attested as a recipient of offerings, and a number of theophoric names invoking him have been identified. He also played a role in Ugaritic mythology. In the '' Baal Cycle'' he is portrayed as an enemy of the weather god, Baal. Their struggle revolves around attaining the rank of the king of the gods. The narrative portrays Yam as the candidate favored by the senior god El, though ultimately it is Baal who emerges victorious. Yam nonetheless continues to be referenced through the story after his defeat. In texts from other archaeological sites in Syria, attestations of Yam are largely limited to theophoric names. In Emar he was among the many deities venerated during a l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Proto-Semitic
Proto-Semitic is the reconstructed common ancestor of the Semitic languages. There is no consensus regarding the location of the linguistic homeland for Proto-Semitic: scholars hypothesize that it may have originated in the Levant, the Sahara, the Horn of Africa, the Arabian Peninsula, or northern Africa. The Semitic language family is considered part of the broader macro-family of Afroasiatic languages. Dating The earliest attestations of any Semitic language are in Akkadian, dating to around the 24th to 23rd centuries BC (see Sargon of Akkad) and the Eblaite language, but earlier evidence of Akkadian comes from personal names in Sumerian texts from the first half of the third millennium BC. One of the earliest known Akkadian inscriptions was found on a bowl at Ur, addressed to the very early pre-Sargonic king Meskiagnunna of Ur (–2450 BC) by his queen Gan-saman, who is thought to have been from Akkad. The earliest text fragments of West Semitic are snake spells in Egyp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amorite Language
Amorite is an extinct early Semitic language, formerly spoken during the Bronze Age by the Amorite tribes prominent in ancient Near Eastern history. It is known from Ugaritic, which is classed by some as its westernmost dialect, and from non- Akkadian proper names recorded by Akkadian scribes during periods of Amorite rule in Babylonia (the end of the 3rd and the beginning of the 2nd millennium BC), notably from Mari and to a lesser extent Alalakh, Tell Harmal and Khafajah. Occasionally, such names are also found in early Egyptian texts; and one place name, "Sənīr" (שְׂנִיר) for Mount Hermon, is known from the Bible (Book of Deuteronomy, ). Amorite is considered an archaic Northwest Semitic language. Notable characteristics include the following: * The usual Northwest Semitic imperfective-perfective distinction is found: ''Yantin-Dagan'', 'Dagon gives' (''ntn''); ''Raṣa-Dagan'', 'Dagon was pleased' (rṣy). It included a 3rd-person suffix -''a'' (unlike Akkadian o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
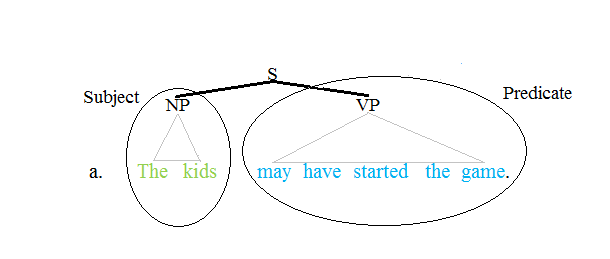
Predicate (grammar)
The term predicate is used in two ways in linguistics and its subfields. The first defines a predicate as everything in a standard declarative sentence except the subject (grammar), subject, and the other defines it as only the main content verb or associated predicative expression of a clause. Thus, by the first definition, the predicate of the sentence ''Frank likes cake'' is ''likes cake'', while by the second definition, it is only the content verb ''likes'', and ''Frank'' and ''cake'' are the argument (linguistics), arguments of this predicate. The conflict between these two definitions can lead to confusion. Syntax Traditional grammar The notion of a predicate in traditional grammar traces back to Aristotelian logic. A predicate is seen as a property that a subject has or is characterized by. A predicate is therefore an expression that can be ''true of'' something. Thus, the expression "is moving" is true of anything that is moving. This classical understanding of pred ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Religions Of The Ancient Near East
The religions of the ancient Near East were mostly polytheistic, with some examples of monolatry (for example, Yahwism and Atenism). Some scholars believe that the similarities between these religions indicate that the religions are related, a belief known as patternism. Many religions of the ancient near East and their offshoots can be traced to Proto-Semitic religion. Other religions in the ancient Near East include the ancient Egyptian religion, the Luwian and Hittite religions of Asia Minor and the Sumerian religion of ancient Mesopotamia. Offshoots of Proto-Semitic religion include Canaanite religion and Arabian religion. Judaism is a development of Canaanite religion, both Indo-European and Semitic religions influenced the ancient Greek religion, and Zoroastrianism was a product of ancient Indo-Iranian religion primarily the ancient Iranian religion. In turn these religious traditions strongly influenced the later monotheistic religions of Christianity, Mandaeism, Gno ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Deity
A deity or god is a supernatural being considered to be sacred and worthy of worship due to having authority over some aspect of the universe and/or life. The ''Oxford Dictionary of English'' defines ''deity'' as a God (male deity), god or goddess, or anything revered as divine. C. Scott Littleton defines a deity as "a being with powers greater than those of ordinary humans, but who interacts with humans, positively or negatively, in ways that carry humans to new Higher consciousness, levels of consciousness, beyond the grounded preoccupations of ordinary life". Religions can be categorized by how many deities they worship. Monotheism, Monotheistic religions accept only one deity (predominantly referred to as "God"), whereas Polytheism, polytheistic religions accept multiple deities. Henotheism, Henotheistic religions accept one God, supreme deity without denying other deities, considering them as aspects of the same divine principle. Nontheistic religions deny any supreme eter ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Northwest Semitic
Northwest Semitic is a division of the Semitic languages comprising the indigenous languages of the Levant. It emerged from Proto-Semitic language, Proto-Semitic in the Early Bronze Age. It is first attested in proper names identified as Amorite language, Amorite in the Middle Bronze Age. The oldest coherent texts are in Ugaritic language, Ugaritic, dating to the Late Bronze Age, which by the time of the Bronze Age collapse are joined by Old Aramaic, and by the Iron Age by Sutean language, Sutean and the Canaanite languages (Hebrew language, Hebrew, Phoenician language, Phoenician/Punic language, Punic, Edomite language, Edomite and Moabite language, Moabite). The term was coined by Carl Brockelmann in 1908,-ṣṭ- in the Dt stem in Hebrew (hiṣṭaddēḳ ‘he declared himself righteous’) suggests backing rather than glottalization. The same assimilation is attested in Aramaic (yiṣṭabba ‘he will be moistened’). Grammar Nouns Three cases can be reconstructed for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ʾilāh
' (; plural: ') is an Arabic term meaning "god". In Arabic, ilah refers to anyone or anything that is worshipped. The feminine is ' (, meaning "goddess"); with the article, it appears as ' (). The Arabic word for God (') is thought to be derived from it (in a proposed earlier form ''al-Lāh'') though this is disputed. is cognate to Northwest Semitic '' '' and Akkadian ''ilum''. The word is from a Proto-Semitic archaic biliteral ' meaning "god" (possibly with a wider meaning of "strong"), which was extended to a regular triliteral by the addition of a '' h'' (as in Hebrew '' , ''). The word is spelled either with an optional diacritic alif to mark the ' only in Qur'anic texts or (more rarely) with a full alif, . The term is used throughout the Quran in passages discussing the existence of God or the beliefs in other divinities by non-Muslims. Notably, the first statement of the ' (the Muslim confession of faith) is "There is no god (') except the God (')." See also * Arabian ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Saturn (mythology)
Saturn ( ) was a god in Religion in ancient Rome, ancient Roman religion, and a character in Roman mythology. He was described as a god of time, generation, dissolution, abundance, wealth, agriculture, periodic renewal and liberation. Saturn's mythological reign was depicted as a Golden Age of abundance and peace. After the Roman conquest of Greece, he was conflated with the Greek Titan Cronus. Saturn's consort was his sister Ops, with whom he fathered Jupiter (mythology), Jupiter, Neptune (mythology), Neptune, Pluto (mythology), Pluto, Juno (mythology), Juno, Ceres (Roman mythology), Ceres and Vesta (mythology), Vesta. Saturn was especially celebrated during the festival of Saturnalia each December, perhaps the most famous of the Roman festivals, a time of feasting, role reversals, free speech, gift-giving and revelry. The Temple of Saturn in the Forum Romanum, Roman Forum housed the state treasury and archives (''aerarium'') of the Roman Republic and the early Roman Empire. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kumarbi
Kumarbi, also known as Kumurwe, Kumarwi and Kumarma, was a Hurrian god. He held a senior position in the Hurrian pantheon, and was described as the "father of gods". He was portrayed as an old, deposed king of the gods, though this most likely did not reflect factual loss of the position of the head of the pantheon in Hurrian religion, but only a mythological narrative. It is often assumed that he was an agricultural deity, though this view is not universally accepted and the evidence is limited. He was also associated with prosperity. It was believed that he resided in the underworld. Multiple Hurrian deities were regarded as Kumarbi's children, including Teshub, whom he conceived after biting off the genitals of Anu. They were regarded as enemies. In myths dealing with the conflict between them Kumarbi fathers various enemies meant to supplant the weather god, such as the stone giant Ullikummi. Kumarbi was also closely associated with other deities who were regarded as the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Enlil
Enlil, later known as Elil and Ellil, is an List of Mesopotamian deities, ancient Mesopotamian god associated with wind, air, earth, and storms. He is first attested as the chief deity of the Sumerian pantheon, but he was later worshipped by the Akkadian Empire, Akkadians, Babylonian Empire, Babylonians, Assyrian Empire, Assyrians, and Hurrians. Enlil's primary center of worship was the Ekur temple in the city of Nippur, which was believed to have been built by Enlil himself and was regarded as the "mooring-rope" of heaven and earth. He is also sometimes referred to in Sumerian texts as Nunamnir. According to one Sumerian hymn, Enlil himself was so holy that not even the other gods could look upon him. Enlil rose to prominence during the twenty-fourth century BC with the rise of Nippur. His Cult (religious practice), cult fell into decline after Nippur was sacked by the Elamites in 1230 BC and he was eventually supplanted as the chief god of the Mesopotamian pantheon by the Baby ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |