|
ETA-10
The ETA10 is a vector supercomputer designed, manufactured, and marketed by ETA Systems, a spin-off division of Control Data Corporation (CDC). The ETA10 was an evolution of the CDC Cyber 205, which can trace its origins back to the CDC STAR-100, one of the first vector supercomputers to be developed. CDC announced it was creating ETA Systems, and a successor to the Cyber 205, on 18 April 1983 at the Frontiers of Supercomputing conference, held at the Los Alamos National Laboratory. It was then referred to tentatively as the Cyber 2XX, and later as the GF-10, before it was named the ETA10. Prototypes were operational in mid-1986, and the first delivery was made in December 1986. The supercomputer was formally announced in April 1987 at an event held at its first customer installation, the Florida State University, Tallahassee's Scientific Computational Research Institute. On 17 April 1989, CDC abruptly closed ETA Systems due to ongoing financial losses, and discontinued pro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vector Processor
In computing, a vector processor or array processor is a central processing unit (CPU) that implements an instruction set where its instructions are designed to operate efficiently and effectively on large one-dimensional arrays of data called ''vectors''. This is in contrast to scalar processors, whose instructions operate on single data items only, and in contrast to some of those same scalar processors having additional single instruction, multiple data (SIMD) or SWAR Arithmetic Units. Vector processors can greatly improve performance on certain workloads, notably numerical simulation and similar tasks. Vector processing techniques also operate in video-game console hardware and in graphics accelerators. Vector machines appeared in the early 1970s and dominated supercomputer design through the 1970s into the 1990s, notably the various Cray platforms. The rapid fall in the price-to-performance ratio of conventional microprocessor designs led to a decline in vector sup ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Control Data Corporation
Control Data Corporation (CDC) was a mainframe and supercomputer firm. CDC was one of the nine major United States computer companies through most of the 1960s; the others were IBM, Burroughs Corporation, DEC, NCR, General Electric, Honeywell, RCA, and UNIVAC. CDC was well-known and highly regarded throughout the industry at the time. For most of the 1960s, Seymour Cray worked at CDC and developed a series of machines that were the fastest computers in the world by far, until Cray left the company to found Cray Research (CRI) in the 1970s. After several years of losses in the early 1980s, in 1988 CDC started to leave the computer manufacturing business and sell the related parts of the company, a process that was completed in 1992 with the creation of Control Data Systems, Inc. The remaining businesses of CDC currently operate as Ceridian. Background and origins: World War II–1957 During World War II the U.S. Navy had built up a classified team of engineers to bu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
CDC 8600
The CDC 8600 was the last of Seymour Cray's supercomputer designs while he worked for Control Data Corporation. As the natural successor to the CDC 6600 and CDC 7600, the 8600 was intended to be about 10 times as fast as the 7600, already the fastest computer on the market. The design was essentially four 7600's, packed into a very small chassis so they could run at higher clock speeds. Development started in 1968, shortly after the release of the 7600, but the project soon started to bog down. The dense packaging of the system led to serious reliability problems and difficulty cooling the individual components. By 1971, CDC was having cash-flow problems and the design was still not coming together, prompting Cray to leave the company in 1972. The 8600 design effort was eventually canceled in 1974, and Control Data moved on to the CDC STAR-100 series instead. Cray revisited the 8600's basic design in his Cray-2 of the early 1980s. The introduction of integrated circuits solv ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
EOS (operating System)
The ETA10 is a vector supercomputer designed, manufactured, and marketed by ETA Systems, a spin-off division of Control Data Corporation (CDC). The ETA10 was an evolution of the CDC Cyber 205, which can trace its origins back to the CDC STAR-100, one of the first vector supercomputers to be developed. CDC announced it was creating ETA Systems, and a successor to the Cyber 205, on 18 April 1983 at the Frontiers of Supercomputing conference, held at the Los Alamos National Laboratory. It was then referred to tentatively as the Cyber 2XX, and later as the GF-10, before it was named the ETA10. Prototypes were operational in mid-1986, and the first delivery was made in December 1986. The supercomputer was formally announced in April 1987 at an event held at its first customer installation, the Florida State University, Tallahassee's Scientific Computational Research Institute. On 17 April 1989, CDC abruptly closed ETA Systems due to ongoing financial losses, and discontinued pro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Virtual Memory
In computing, virtual memory, or virtual storage is a memory management technique that provides an "idealized abstraction of the storage resources that are actually available on a given machine" which "creates the illusion to users of a very large (main) memory". The computer's operating system, using a combination of hardware and software, maps memory addresses used by a program, called '' virtual addresses'', into ''physical addresses'' in computer memory. Main storage, as seen by a process or task, appears as a contiguous address space or collection of contiguous segments. The operating system manages virtual address spaces and the assignment of real memory to virtual memory. Address translation hardware in the CPU, often referred to as a memory management unit (MMU), automatically translates virtual addresses to physical addresses. Software within the operating system may extend these capabilities, utilizing, e.g., disk storage, to provide a virtual address space that c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Operating System
An operating system (OS) is system software that manages computer hardware, software resources, and provides common daemon (computing), services for computer programs. Time-sharing operating systems scheduler (computing), schedule tasks for efficient use of the system and may also include accounting software for cost allocation of Scheduling (computing), processor time, mass storage, printing, and other resources. For hardware functions such as input and output and memory allocation, the operating system acts as an intermediary between programs and the computer hardware, although the application code is usually executed directly by the hardware and frequently makes system calls to an OS function or is interrupted by it. Operating systems are found on many devices that contain a computer from cellular phones and video game consoles to web servers and supercomputers. The dominant general-purpose personal computer operating system is Microsoft Windows with a market share of aroun ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Unix
Unix (; trademarked as UNIX) is a family of multitasking, multiuser computer operating systems that derive from the original AT&T Unix, whose development started in 1969 at the Bell Labs research center by Ken Thompson, Dennis Ritchie, and others. Initially intended for use inside the Bell System, AT&T licensed Unix to outside parties in the late 1970s, leading to a variety of both academic and commercial Unix variants from vendors including University of California, Berkeley ( BSD), Microsoft ( Xenix), Sun Microsystems (SunOS/ Solaris), HP/ HPE (HP-UX), and IBM ( AIX). In the early 1990s, AT&T sold its rights in Unix to Novell, which then sold the UNIX trademark to The Open Group, an industry consortium founded in 1996. The Open Group allows the use of the mark for certified operating systems that comply with the Single UNIX Specification (SUS). Unix systems are characterized by a modular design that is sometimes called the " Unix philosophy". According to this p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
System V
Unix System V (pronounced: "System Five") is one of the first commercial versions of the Unix operating system. It was originally developed by AT&T and first released in 1983. Four major versions of System V were released, numbered 1, 2, 3, and 4. System V Release 4 (SVR4) was commercially the most successful version, being the result of an effort, marketed as ''Unix System Unification'', which solicited the collaboration of the major Unix vendors. It was the source of several common commercial Unix features. System V is sometimes abbreviated to SysV. , the AT&T-derived Unix market is divided between four System V variants: IBM's AIX, Hewlett Packard Enterprise's HP-UX and Oracle's Solaris, plus the free-software illumos forked from OpenSolaris. Overview Introduction System V was the successor to 1982's UNIX System III. While AT&T developed and sold hardware that ran System V, most customers ran a version from a reseller, based on AT&T's reference implementation. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
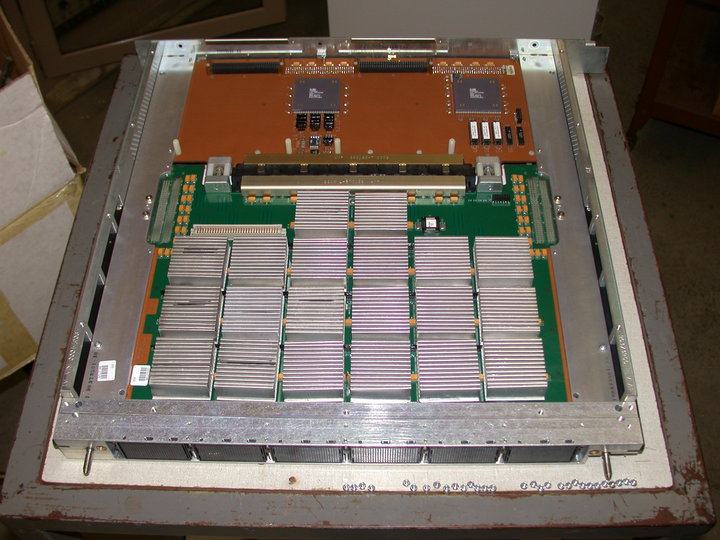
ETA Systems ETA10 Supercomputer (1987-1989) Where CPU Is Mounted In A Liquid Nitrogen Tank For Liquid Cooling (End Of An ERA) - Computer History Museum, 2010-01-21 15
Eta (uppercase , lowercase ; grc, ἦτα ''ē̂ta'' or ell, ήτα ''ita'' ) is the seventh letter of the Greek alphabet, representing the close front unrounded vowel . Originally denoting the voiceless glottal fricative in most dialects, its sound value in the classical Attic dialect of Ancient Greek was a long open-mid front unrounded vowel , raised to in hellenistic Greek, a process known as iotacism or itacism. In the ancient Attic number system (Herodianic or acrophonic numbers), the number 100 was represented by "", because it was the initial of , the ancient spelling of = "one hundred". In the later system of (Classical) Greek numerals eta represents 8. Eta was derived from the Phoenician letter heth . Letters that arose from eta include the Latin H and the Cyrillic letter И and Й. History Consonant h The letter shape 'H' was originally used in most Greek dialects to represent the voiceless glottal fricative . In this function, it was borrowed in th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Livermore Time Sharing System
The Livermore Time Sharing System (LTSS) was a supercomputer operating system originally developed by the Lawrence Livermore Laboratories for the Control Data Corporation 6600 and 7600 series of supercomputers. LTSS resulted in the Cray Time Sharing System and then the Network Livermore Timesharing System (NLTSS).''Virtualization with Xen'' by David E. Williams 2007 page /ref> See also *UNICOS UNICOS is a range of Unix and after it Linux operating system (OS) variants developed by Cray for its supercomputers. UNICOS is the successor of the Cray Operating System (COS). It provides network clustering and source code compatibility la ... References {{Compu-network-stub Discontinued operating systems Time-sharing operating systems Supercomputer operating systems ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cybil (programming Language)
Cybil (short for the Cyber Implementation Language of the Control Data Network Operating System) was a Pascal-like language developed at Control Data Corporation for the Cyber computer family. Cybil was used as the implementation language for the NOS/VE operating system based on a CDC NOS/VE information leaflet on the CDC Cyber series and was also used to write the eOS operating system for the ETA10 supercomputer in the 1980s. References [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |