|
ESP32-S2
ESP32 is a family of low-cost, energy-efficient microcontrollers that integrate both Wi-Fi and Bluetooth capabilities. These chips feature a variety of processing options, including the Tensilica Xtensa LX6 microprocessor available in both dual-core and single-core variants, the Xtensa LX7 dual-core processor, or a single-core RISC-V microprocessor. In addition, the ESP32 incorporates components essential for wireless data communication such as built-in antenna switches, an RF balun, power amplifiers, low-noise receivers, filters, and power-management modules. Typically, the ESP32 is embedded on device-specific printed circuit boards or offered as part of development kits that include a variety of GPIO pins and connectors, with configurations varying by model and manufacturer. The ESP32 was designed by Espressif Systems and is manufactured by TSMC using their 40 nm process. It is a successor to the ESP8266 microcontroller. Features Features of the ESP32 include the foll ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
RISC-V
RISC-V (pronounced "risk-five") is an open standard instruction set architecture (ISA) based on established reduced instruction set computer (RISC) principles. The project commenced in 2010 at the University of California, Berkeley. It transferred to the RISC-V Foundation in 2015, and from there to RISC-V International, a Swiss non-profit entity, in November 2019. Similar to several other RISC ISAs, e.g. Amber (processor), Amber (ARMv2)(2001), SuperH#J_Core, J-Core(2015), OpenRISC(2000), or OpenSPARC(2005), RISC-V is offered under royalty-free open-source licenses. The documents defining the RISC-V instruction set architecture (ISA) are offered under a Creative Commons license or a BSD licenses, BSD License. Mainline support for RISC-V was added to the Linux 5.17 kernel in 2022, along with its toolchain. In July 2023, RISC-V, in its 64-bit computing, 64-bit variant called riscv64, was included as an official architecture of Linux distribution Debian, in its Debian version histor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Espressif Systems
Espressif Systems (Shanghai) Co., Ltd. (Espressif; ) is a publicly listed Chinese semiconductor company headquartered in Shanghai. It focuses on developing and selling wireless microcontroller unit communication chips and modules that are used in internet of things (IoT). History In 2008, Espressif was founded in China by Singaporean national, Teo Swee Ann. Teo who graduated from National University of Singapore with degrees in electrical engineering had worked for Montage Technology as an engineering director. Espressif initially started as one-man consulting firm which later expanded. However due to small quantity of chips commissioned by Espressif, foundries tended to reject it. However TSMC who had heard of Teo's work at Montage Technology gave Espressif a chance and became its supplier. On 22 July 2019, Espressif had its initial public offering and became a listed company on the Shanghai Stock Exchange STAR Market. The offering raised 1.2 billion yuan. In March ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Delta-sigma Modulator
Delta-sigma (ΔΣ; or sigma-delta, ΣΔ) modulation is an oversampling method for encoding signals into low bit depth digital signals at a very high sample-frequency as part of the process of delta-sigma analog-to-digital converters (ADCs) and digital-to-analog converters (DACs). Delta-sigma modulation achieves high quality by utilizing a negative feedback loop during quantization to the lower bit depth that continuously corrects quantization errors and moves quantization noise to higher frequencies well above the original signal's bandwidth. Subsequent low-pass filtering for demodulation easily removes this high frequency noise and time averages to achieve high accuracy in amplitude, which can be ultimately encoded as pulse-code modulation (PCM). Both ADCs and DACs can employ delta-sigma modulation. A delta-sigma ADC (e.g. Figure 1 top) encodes an analog signal using high-frequency delta-sigma modulation and then applies a digital filter to demodulate it to a high ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wi-Fi Protected Access
Wi-Fi Protected Access (WPA) (Wireless Protected Access), Wi-Fi Protected Access 2 (WPA2), and Wi-Fi Protected Access 3 (WPA3) are the three security certification programs developed after 2000 by the Wi-Fi Alliance to secure wireless computer networks. The Alliance defined these in response to serious weaknesses researchers had found in the previous system, Wired Equivalent Privacy (WEP). WPA (sometimes referred to as the TKIP standard) became available in 2003. The Wi-Fi Alliance intended it as an intermediate measure in anticipation of the availability of the more secure and complex WPA2, which became available in 2004 and is a common shorthand for the full IEEE 802.11i (or IEEE 802.11i-2004) standard. In January 2018, the Wi-Fi Alliance announced the release of WPA3, which has several security improvements over WPA2. As of 2023, most computers that connect to a wireless network have support for using WPA, WPA2, or WPA3. All versions thereof, at least as implemented throu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
CAN Bus
A controller area network bus (CAN bus) is a vehicle bus standard designed to enable efficient communication primarily between electronic control units (ECUs). Originally developed to reduce the complexity and cost of electrical wiring in automobiles through multiplexing, the CAN bus protocol has since been adopted in various other contexts. This Broadcasting (networking), broadcast-based, Message passing, message-oriented protocol ensures data integrity and prioritization through a process called Arbiter (electronics), arbitration, allowing the highest priority device to continue transmitting if multiple devices attempt to send data simultaneously, while others back off. Its reliability is enhanced by Differential signalling, differential signaling, which mitigates electrical noise. Common versions of the CAN protocol include CAN 2.0, CAN FD, and CAN XL which vary in their data rate capabilities and maximum data payload sizes. History Development of the CAN Bus (computing), ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
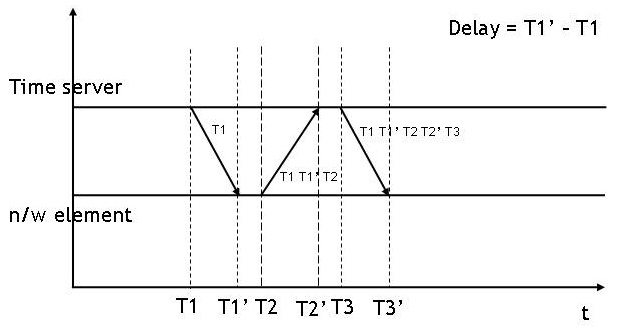
Precision Time Protocol
The Precision Time Protocol (PTP) is a protocol for clock synchronization throughout a computer network with relatively high precision and therefore ''potentially'' high accuracy. In a local area network (LAN), accuracy can be sub-microsecond making it suitable for measurement and control systems. PTP is used to synchronize financial transactions, mobile phone tower transmissions, sub-sea acoustic arrays, and networks that require precise timing but lack access to satellite navigation signals. The first version of PTP, IEEE 1588-2002, was published in 2002. IEEE 1588-2008, also known as PTP Version 2, is not backward compatible with the 2002 version. IEEE 1588-2019 was published in November 2019 and includes backward-compatible improvements to the 2008 publication. IEEE 1588-2008 includes a ''profile'' concept defining PTP operating parameters and options. Several profiles have been defined for applications including telecommunications, electric power distribution and aud ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ethernet
Ethernet ( ) is a family of wired computer networking technologies commonly used in local area networks (LAN), metropolitan area networks (MAN) and wide area networks (WAN). It was commercially introduced in 1980 and first standardized in 1983 as IEEE 802.3. Ethernet has since been refined to support higher bit rates, a greater number of nodes, and longer link distances, but retains much backward compatibility. Over time, Ethernet has largely replaced competing wired LAN technologies such as Token Ring, FDDI and ARCNET. The original 10BASE5 Ethernet uses a thick coaxial cable as a shared medium. This was largely superseded by 10BASE2, which used a thinner and more flexible cable that was both less expensive and easier to use. More modern Ethernet variants use Ethernet over twisted pair, twisted pair and fiber optic links in conjunction with Network switch, switches. Over the course of its history, Ethernet data transfer rates have been increased from the original to the lates ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
MultiMediaCard
MultiMediaCard, officially abbreviated as MMC, is a memory card standard used for solid-state storage. Unveiled in 1997 by SanDisk and Siemens, MMC is based on a surface-contact low-pin-count serial interface using a single memory stack substrate assembly, and is therefore much smaller than earlier systems based on high-pin-count parallel interfaces using traditional surface-mount assembly such as CompactFlash. Both products were initially introduced using SanDisk NOR-based flash technology. MMC is about the size of a postage stamp: 32 mm × 24 mm × 1.4 mm. MMC originally used a 1- bit serial interface, but newer versions of the specification allow transfers of 4 or 8 bits at a time. MMC can be used in many devices that can use Secure Digital (SD) cards. MMCs may be available in sizes up to 16 gigabytes (GB). They are used in almost every context in which memory cards are used, like cellular phones, digital audio players, digital cameras, and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
CE-ATA
Consumer Electronics ATA (CE-ATA) is an interface standard for the connection of storage devices and hosts in consumer electronic device such as mobile and handheld devices. One of the primary goals is to standardize connections for small form factor hard disk drives such as 1-inch Microdrives. The standard is maintained by the CE-ATA Workgroup. History The CE-ATA Specification was developed in 2005. Interface MMC CE-ATA is electrically and physically compatible with MMC specification. CE-ATA uses MMC connector on host devices and matching flex cable or circuit connection on CE-ATA hard disk drives. Pin Assignment {, class="wikitable" border="1" style="text-align: center;" , - ! Pin # ! Signal - x4 Data Lines ! Signal - x8 Data Lines , - , 1 , , Vss , , Vss , - , 2 , , DAT2 , , DAT2 , - , 3 , , DAT3 , , DAT3 , - , 4 , , Supply Voltage , , Vss , - , 5 , , CMD , , DAT4 , - , 6 , , Interface Voltage , , DAT5 , - , 7 , , CLK , , Supply Voltage , - , ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Secure Digital
Secure Digital (SD) is a proprietary, non-volatile, flash memory card format developed by the SD Association (SDA). Owing to their compact size, SD cards have been widely adopted in a variety of portable consumer electronics, including digital cameras, camcorders, video game consoles, mobile phones, action cameras, and camera drones. The SD format was introduced in August 1999 by SanDisk, Panasonic (then known as Matsushita), and Kioxia (then part of Toshiba). It was designed as a successor to the MultiMediaCard (MMC) format, introducing several improvements aimed at enhancing usability, durability, and performance, which contributed to its rapid emergence as an industry standard. To manage the licensing and intellectual property rights related to the format, the three companies established SD-3C, LLC. In January 2000, they also founded the SDA, a non-profit organization dedicated to developing and promoting SD card standards. As of 2023, the SDA includes approximatel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Universal Asynchronous Receiver-transmitter
A universal asynchronous receiver-transmitter (UART ) is a peripheral device for asynchronous serial communication in which the data format and transmission speeds are configurable. It sends data bits one by one, from the least significant to the most significant, framed by start and stop bits so that precise timing is handled by the communication channel. The electric signaling levels are handled by a driver circuit external to the UART. Common signal levels are RS-232, RS-485, and raw TTL for short debugging links. Early teletypewriters used current loops. It was one of the earliest computer communication devices, used to attach teletypewriters for an operator console. It was also an early hardware system for the Internet. A UART is usually implemented in an integrated circuit (IC) and used for serial communications over a computer or peripheral device serial port. One or more UART peripherals are commonly integrated in microcontroller chips. Specialised UARTs are use ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
I²C
I2C (Inter-Integrated Circuit; pronounced as "" or ""), alternatively known as I2C and IIC, is a synchronous, multi-master/multi-slave, single-ended, serial communication bus invented in 1980 by Philips Semiconductors (now NXP Semiconductors). It is widely used for attaching lower-speed peripheral integrated circuits (ICs) to processors and microcontrollers in short-distance, intra-board communication. The I2C bus can be found in a wide range of electronics applications where simplicity and low manufacturing cost are more important than speed. PC components and systems which involve I2C include serial presence detect (SPD) EEPROMs on dual in-line memory modules (DIMMs) and Extended Display Identification Data (EDID) for monitors via VGA, DVI, and HDMI connectors. Common I2C applications include reading hardware monitors, sensors, real-time clocks, controlling actuators, accessing low-speed DACs and ADCs, controlling simple LCD or OLED displays, changing computer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |