|
Doongul, Queensland
Doongul is a rural locality in the Fraser Coast Region, Queensland, Australia. In the , Doongul had a population of 35 people. Geography Most of the locality is with protected areas. The west of the locality is within the Wongi National Park which extends into neighbouring Golden Fleece to the west. The small Fairlies Knob National Park is immediately south of the Wongi National Park in the south-west of the locality. Apart from the national parks, almost all of the rest of the locality is within the Wongi State Forest, except for the centre and south-east, where the land use is grazing on native vegetation. Doongul has the following mountains, from north to south: * Duckke Benong () * Mount Doongul () * Musket Flat Mountain () * Fairlies Knob () * Cabbage Tree Mountain () The former town of Eliott () is within Doongul on the Old Gayndah Road. History The locality was previously known as Muskat Flat. It presumably takes its present name Doongul from the Doon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
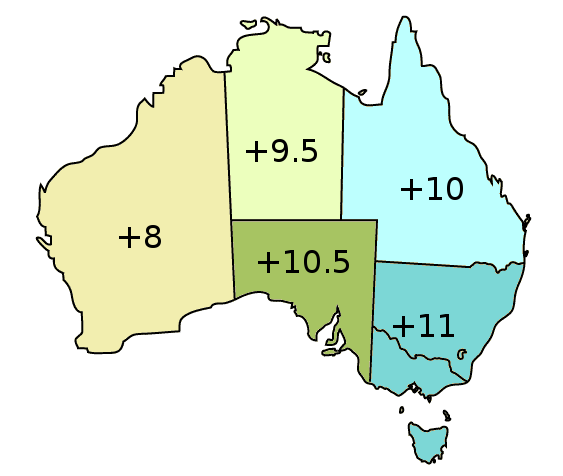
AEST
Australia uses three main time zones: Australian Western Standard Time (AWST; UTC+08:00), Australian Central Standard Time (ACST; UTC+09:30), and Australian Eastern Standard Time (AEST; UTC+10:00). Time is regulated by the individual state governments, some of which observe daylight saving time (DST). Australia's external territories observe different time zones. Standard time was introduced in the 1890s when all of the Australian colonies adopted it. Before the switch to standard time zones, each local city or town was free to determine its local time, called local mean time. Now, Western Australia uses Western Standard Time; South Australia and the Northern Territory use Central Standard Time; while New South Wales, Queensland, Tasmania, Victoria, Jervis Bay Territory, and the Australian Capital Territory use Eastern Standard Time. Daylight saving time (+1 hour) is used in jurisdictions in the south and south-east: South Australia, New South Wales, Victoria, Tasm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Suburbs And Localities (Australia)
Suburbs and localities are the names of geographic subdivisions in Australia, used mainly for address purposes. The term locality is used in rural areas, while the term suburb A suburb (more broadly suburban area) is an area within a metropolitan area, which may include commercial and mixed-use, that is primarily a residential area. A suburb can exist either as part of a larger city/urban area or as a separate ... is used in urban areas. Australian postcodes closely align with the boundaries of localities and suburbs. This Australian usage of the term "suburb" differs from common American and British usage, where it typically means a smaller, frequently separate residential community outside, but close to, a larger city. The Australian usage is closer to the American or British use of "district" or "neighbourhood", and can be used to refer to any portion of a city. Unlike the use in British or American English, this term can include inner-city, outer-metropolitan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Brisbane Courier
''The Courier-Mail'' is an Australian newspaper published in Brisbane. Owned by News Corp Australia, it is published daily from Monday to Saturday in tabloid format. Its editorial offices are located at Bowen Hills, in Brisbane's inner northern suburbs, and it is printed at Murarrie, in Brisbane's eastern suburbs. It is available for purchase throughout Queensland, most regions of Northern New South Wales and parts of the Northern Territory. History The history of ''The Courier-Mail'' is through four mastheads. The ''Moreton Bay Courier'' later became '' The Courier'', then the '' Brisbane Courier'' and, since a merger with the Daily Mail in 1933, ''The Courier-Mail''. The ''Moreton Bay Courier'' was established as a weekly paper in June 1846. Issue frequency increased steadily to bi-weekly in January 1858, tri-weekly in December 1859, then daily under the editorship of Theophilus Parsons Pugh from 14 May 1861. The recognised founder and first editor was Arthur Sidney Lyo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Maryborough Chronicle, Wide Bay And Burnett Advertiser
The ''Fraser Coast Chronicle'' is an online newspaper serving the Fraser Coast area in Queensland, Australia. It was started as the Maryborough Chronicle, Wide Bay and Burnett Advertiser. History Charles Hardie Buzacott first published the ''Maryborough Chronicle, Wide Bay and Burnett Advertiser'' in Maryborough as a four-page tabloid, in his slab hut in Lennox Street in November 1860. It sold for sixpence and was read from Gayndah in the west and Childers in the north to Gympie in the south. In 1863, Buzacott sold his interests to William Swain Roberts and Joseph Robinson, who set out to "reflect the community's wants and opinions while boldly and distinctly enunciating our own views". As the rough river town turned into a respectable city, its newspaper became a bi-weekly in 1864, a tri-weekly in 1868 and a daily in 1882. In 1867, Roberts became sole proprietor and managing editor. A Scot, Andrew Dunn from Toowoomba, joined the ''Chronicle'' in 1885, beginning a long ass ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Queensland Government
The Queensland Government is the democratic administrative authority of the Australian state of Queensland. The Government of Queensland, a parliamentary constitutional monarchy was formed in 1859 as prescribed in its Constitution, as amended from time to time. Since the Federation of Australia in 1901, Queensland has been a State of Australia, with the Constitution of Australia regulating the relationships between all state and territory governments and the Australian Government. Under the Australian Constitution, all states and territories (including Queensland) ceded powers relating to certain matters to the federal government. The government is influenced by the Westminster system and Australia's federal system of government. The Governor of Queensland, as the representative of Charles III, King of Australia, holds nominal executive power, although in practice only performs ceremonial duties. In practice executive power lies with the Premier and Cabinet. The Cabinet ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pastoralism
Pastoralism is a form of animal husbandry where domesticated animals (known as " livestock") are released onto large vegetated outdoor lands ( pastures) for grazing, historically by nomadic people who moved around with their herds. The animal species involved include cattle, camels, goats, yaks, llamas, reindeer, horses and sheep. Pastoralism occurs in many variations throughout the world, generally where environmental characteristics such as aridity, poor soils, cold or hot temperatures, and lack of water make crop-growing difficult or impossible. Operating in more extreme environments with more marginal lands means that pastoral communities are very vulnerable to the effects of global warming. Pastoralism remains a way of life in many geographic areas, including Africa, the Tibetan plateau, the Eurasian steppes, the Andes, Patagonia, the Pampas, Australia and many other places. , between 200 million and 500 million people globally practised pastora ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wongi State Forest
''Manilkara kauki'' is a plant in the subfamily Sapotoideae, and the tribe Sapoteae of the family Sapotaceae; and is the type species for the genus ''Manilkara''. It occurs in tropical Asia from Indo-China ( Cambodia, Myanmar, Thailand and Vietnam) to Malesia ( Indonesia, Malaysia and Papua New Guinea); and also in northern Queensland in Australia. In Java, the plant is called ''sawo kacik'', and is associated with the royal Javanese ritual. In India, the fruit is called ''adão (Adam’s fruit)'' in Konkani. Throughout the world it is known generally by the name ''caqui'', but in Australia it is called ''wongi''. Description The leaves are rigid, blunt-tipped, dark-green on the upper leaf face, and pale and silky below. The edible, orange-red fruit is 3–4 cm long. Uses For reforestation purposes, ''M. kauki'' is a useful graft stock for ''M. zapota'', and parts of the plant are used in herbal medicine Herbal medicine (also herbalism) is the study of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fairlies Knob National Park
Fairlies Knob is a national park in Queensland, Australia, 231 km north of Brisbane. The estimated elevation of the terrain is 259 meters. Wildlife The park is home to 165 species of animals and 250 species of plants. References See also * Protected areas of Queensland Queensland is the second largest state in Australia. It contains around 500 separate protected areas. In 2020, it was estimated a total of 14.2 million hectares or 8.25% of Queensland's landmass was protected. List of terrestrial protected a ... National parks of Queensland Wide Bay–Burnett Protected areas established in 1910 1910 establishments in Australia {{Queensland-national-park-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wongi National Park
''Manilkara kauki'' is a plant in the subfamily Sapotoideae, and the tribe Sapoteae of the family Sapotaceae; and is the type species for the genus ''Manilkara''. It occurs in tropical Asia from Indo-China (Cambodia, Myanmar, Thailand and Vietnam) to Malesia (Indonesia, Malaysia and Papua New Guinea); and also in northern Queensland in Australia. In Java, the plant is called ''sawo kacik'', and is associated with the royal Javanese ritual. In India, the fruit is called ''adão (Adam’s fruit)'' in Konkani. Throughout the world it is known generally by the name ''caqui'', but in Australia it is called ''wongi''. Description The leaves are rigid, blunt-tipped, dark-green on the upper leaf face, and pale and silky below. The edible, orange-red fruit is 3–4 cm long. Uses For reforestation purposes, ''M. kauki'' is a useful graft stock for ''M. zapota'', and parts of the plant are used in herbal medicine. The fruit is reported to be very tasty, and is traditionally ea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Queensland
) , nickname = Sunshine State , image_map = Queensland in Australia.svg , map_caption = Location of Queensland in Australia , subdivision_type = Country , subdivision_name = Australia , established_title = Before federation , established_date = Colony of Queensland , established_title2 = Separation from New South Wales , established_date2 = 6 June 1859 , established_title3 = Federation of Australia, Federation , established_date3 = 1 January 1901 , named_for = Queen Victoria , demonym = , capital = Brisbane , largest_city = capital , coordinates = , admin_center_type = Administration , admin_center = Local government areas of Queensland, 77 local government areas , leader_title1 = Monarchy of Australia, Monarch , leader_name1 = Charles III , leader_title2 = Governor of Queensland, Governor , leader_name2 = Jeannette Young , leader_title3 = Premier of Queensland, Premier , leader_name3 = Annastacia Palaszczuk (Australian Labor Party (Queensland Branch), AL ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fraser Coast Region
The Fraser Coast Region is a local government area in the Wide Bay–Burnett region of Queensland, Australia, about north of Brisbane, the state capital. It is centred on the twin cities of Hervey Bay and Maryborough and also contains Fraser Island. It was created in 2008 from a merger of the Cities of Maryborough and Hervey Bay and the Shires of Woocoo and most of Tiaro. In June 2018 it had a population of 105,463. The 2021-2022 budget of the Fraser Coast Regional Council is A$387 million. History Butchulla (also known as Batjala, Badtjala, Badjela and Badjala) is the language of the Fraser Coast region, including Fraser Island. Butchulla language region includes the landscape within the local government boundaries of the Fraser Coast Regional Council, particularly the towns of Maryborough and Hervey Bay extending south towards Noosa and north to Howard. Prior to the 2008 amalgamation, the Fraser Coast Region existed as four distinct local government areas: * the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kullogum, Queensland
Kullogum is a rural locality in the Bundaberg Region, Queensland, Australia. In the , Kullogum had a population of 120 people. Geography Most of the centre, east, and south of the locality is within the Wongi State Forest. The land use in the rest of the locality is predominantly grazing on native vegetation. The Isis Highway enters the locaity from the north ( Childers) and exits to the north-west ( Eureka). Palmers Hill is in the centre of the locality () and rises to above sea level. History In 1877, of land was resumed from the Kullugum pastoral run to establish smaller farms. The land was offered for selection on 17 April 1877. Demographics In the , Kullogum had a population of 118 people. In the , Kullogum had a population of 120 people. Education There are no schools in Kullogum. The nearest government primary schools are Childers State School in neighbouring Childers to the north and Dallarnil State School in Dallarnil to the west. The nearest governmen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.jpg)

