|
Directional Stability
Directional stability is stability of a moving body or vehicle about an axis which is perpendicular to its direction of motion. Stability of a vehicle concerns itself with the tendency of a vehicle to return to its original direction in relation to the oncoming medium (water, air, road surface, etc.) when disturbed (rotated) away from that original direction. If a vehicle is directionally stable, a restoring moment is produced which is in a direction ''opposite'' to the rotational disturbance. This "pushes" the vehicle (in rotation) so as to return it to the original orientation, thus tending to keep the vehicle oriented in the original direction. Directional stability is frequently called "weather vaning" because a directionally stable vehicle free to rotate about its center of mass is similar to a weather vane rotating about its (vertical) pivot. With the exception of spacecraft, vehicles generally have a recognisable front and rear and are designed so that the front points m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Torque
In physics and mechanics, torque is the rotational equivalent of linear force. It is also referred to as the moment of force (also abbreviated to moment). It represents the capability of a force to produce change in the rotational motion of the body. The concept originated with the studies by Archimedes of the usage of levers, which is reflected in his famous quote: "''Give me a lever and a place to stand and I will move the Earth''". Just as a linear force is a push or a pull, a torque can be thought of as a twist to an object around a specific axis. Torque is defined as the product of the magnitude of the perpendicular component of the force and the distance of the line of action of a force from the point around which it is being determined. The law of conservation of energy can also be used to understand torque. The symbol for torque is typically \boldsymbol\tau, the lowercase Greek letter '' tau''. When being referred to as moment of force, it is commonly denoted by . ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Second Order Solutions
The second (symbol: s) is the unit of time in the International System of Units (SI), historically defined as of a day – this factor derived from the division of the day first into 24 hours, then to 60 minutes and finally to 60 seconds each (24 × 60 × 60 = 86400). The current and formal definition in the International System of Units ( SI) is more precise:The second ..is defined by taking the fixed numerical value of the caesium frequency, Δ''ν''Cs, the unperturbed ground-state hyperfine transition frequency of the caesium 133 atom, to be when expressed in the unit Hz, which is equal to s−1. This current definition was adopted in 1967 when it became feasible to define the second based on fundamental properties of nature with caesium clocks. Because the speed of Earth's rotation varies and is slowing ever so slightly, a leap second is added at irregular intervals to civil time to keep clocks in sync with Earth's rotation. Uses Analog clocks and watches often ha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Longitudinal Stability
In flight dynamics, longitudinal stability is the stability of an aircraft in the longitudinal, or pitching, plane. This characteristic is important in determining whether an aircraft pilot will be able to control the aircraft in the pitching plane without requiring excessive attention or excessive strength. The longitudinal stability of an aircraft, also called pitch stability, refers to the aircraft's stability in its plane of symmetry about the lateral axis (the axis along the wingspan). It is an important aspect of the handling qualities of the aircraft, and one of the main factors determining the ease with which the pilot is able to maintain level flight. Longitudinal static stability refers to the aircraft's initial tendency on pitching. Dynamic stability refers to whether oscillations tend to increase, decrease or stay constant. Static stability If an aircraft is longitudinally statically stable, a small increase in angle of attack will create a nose-down pitching mom ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dutch Roll
Dutch roll is a type of aircraft motion consisting of an out-of- phase combination of "tail-wagging" (yaw) and rocking from side to side (roll). This yaw-roll coupling is one of the basic flight dynamic modes (others include phugoid, short period, and spiral divergence). This motion is normally well damped in most light aircraft, though some aircraft with well-damped Dutch roll modes can experience a degradation in damping as airspeed decreases and altitude increases. Dutch roll stability can be artificially increased by the installation of a yaw damper. Wings placed well above the center of gravity, sweepback (swept wings) and dihedral wings tend to increase the roll restoring force, and therefore increase the Dutch roll tendencies; this is why high-winged aircraft often are slightly anhedral, and transport-category swept-wing aircraft are equipped with yaw dampers. A similar phenomenon can happen in a trailer pulled by a car. Stability In aircraft design, Dutch rol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
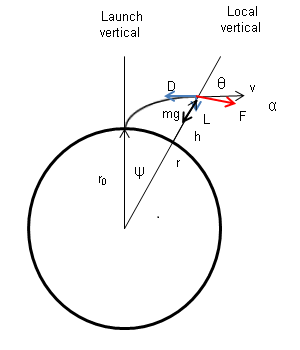
Flight Dynamics
Flight dynamics in aviation and spacecraft, is the study of the performance, stability, and control of vehicles flying through the air or in outer space. It is concerned with how forces acting on the vehicle determine its velocity and attitude with respect to time. For a fixed-wing aircraft, its changing orientation with respect to the local air flow is represented by two critical angles, the angle of attack of the wing ("alpha") and the angle of attack of the vertical tail, known as the sideslip angle ("beta"). A sideslip angle will arise if an aircraft yaws about its centre of gravity and if the aircraft sideslips bodily, i.e. the centre of gravity moves sideways.Flightwise - Volume 2 - Aircraft Stability And Control, Chris Carpenter 1997, Airlife Publishing Ltd., , p.145 These angles are important because they are the principal source of changes in the aerodynamic forces and moments applied to the aircraft. Spacecraft flight dynamics involve three main forces: propulsive ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|