|
Dichroism
In optics, a dichroic material is either one which causes visible light to be split up into distinct beams of different wavelengths (colours) (not to be confused with Dispersion (optics), dispersion), or one in which light rays having different Polarization (waves), polarizations are absorbed by different amounts. In beam splitters The original meaning of ''dichroic'', from the Greek language, Greek ''dikhroos'', two-coloured, refers to any optical device which can split a beam of light into two beams with differing wavelengths. Such devices include mirrors and dichroic filter, filters, usually treated with optical coatings, which are designed to reflect light over a certain range of wavelengths and transmit light which is outside that range. An example is the dichroic prism, used in some camcorders, which uses several coatings to split light into red, green and blue components for recording on separate charge-coupled device, CCD arrays, however it is now more common to have a Ba ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Circular Dichroism
Circular dichroism (CD) is dichroism involving circular polarization, circularly polarized light, i.e., the differential Absorption (electromagnetic radiation), absorption of left- and right-handed light. Left-hand circular (LHC) and right-hand circular (RHC) polarized light represent two possible spin angular momentum of light, spin angular momentum states for a photon, and so circular dichroism is also referred to as dichroism for spin angular momentum. This phenomenon was discovered by Jean-Baptiste Biot, Augustin Fresnel, and Aimé Cotton in the first half of the 19th century. Circular dichroism and optical rotation, circular birefringence are manifestations of optical activity. It is exhibited in the absorption (electromagnetic radiation), absorption bands of optical activity, optically active chirality (chemistry), chiral molecules. CD spectroscopy has a wide range of applications in many different fields. Most notably, Ultraviolet, far-UV CD is used to investigate the second ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dichroic Filter
In optics, a dichroic material is either one which causes visible light to be split up into distinct beams of different wavelengths (colours) (not to be confused with dispersion), or one in which light rays having different polarizations are absorbed by different amounts. In beam splitters The original meaning of ''dichroic'', from the Greek ''dikhroos'', two-coloured, refers to any optical device which can split a beam of light into two beams with differing wavelengths. Such devices include mirrors and filters, usually treated with optical coatings, which are designed to reflect light over a certain range of wavelengths and transmit light which is outside that range. An example is the dichroic prism, used in some camcorders, which uses several coatings to split light into red, green and blue components for recording on separate CCD arrays, however it is now more common to have a Bayer filter to filter individual pixels on a single CCD array. This kind of dichroic device doe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Optical Anisotropy
Birefringence, also called double refraction, is the optical property of a material having a refractive index that depends on the polarization and propagation direction of light. These optically anisotropic materials are described as birefringent or birefractive. The birefringence is often quantified as the maximum difference between refractive indices exhibited by the material. Crystals with non-cubic crystal structures are often birefringent, as are plastics under mechanical stress. Birefringence is responsible for the phenomenon of double refraction whereby a ray of light, when incident upon a birefringent material, is split by polarization into two rays taking slightly different paths. This effect was first described by Danish scientist Rasmus Bartholin in 1669, who observed it in Iceland spar (calcite) crystals which have one of the strongest birefringences. In the 19th century Augustin-Jean Fresnel described the phenomenon in terms of polarization, understanding light a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polaroid (polarizer)
Polaroid is a type of synthetic plastic sheet which is used as a polarizer or polarizing filter. A trademark of the Polaroid Corporation, the term has since entered common use. Patent The original material, patented in 1929 and further developed in 1932 by Edwin H. Land, consists of many microscopic crystals of iodoquinine sulphate (herapathite) embedded in a transparent nitrocellulose polymer film. The needle-like crystals are aligned during the manufacture of the film by stretching or by applying electric or magnetic fields. With the crystals aligned, the sheet is dichroic: it tends to absorb light which is polarized parallel to the direction of crystal alignment but to transmit light which is polarized perpendicular to it. The resultant electric field of an electromagnetic wave (such as light) determines its polarization. If the wave interacts with a line of crystals as in a sheet of polaroid, any varying electric field in the direction parallel to the line of the crystals wi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tourmaline
Tourmaline ( ) is a crystalline silicate mineral, silicate mineral group in which boron is chemical compound, compounded with chemical element, elements such as aluminium, iron, magnesium, sodium, lithium, or potassium. This gemstone comes in a wide variety of colors. The name is derived from the Sinhala language, Sinhalese (), which refers to the carnelian gemstones. History Brightly colored Ceylonese gem tourmalines were brought to Europe in great quantities by the Dutch East India Company to satisfy a demand for curiosities and gems. Tourmaline was sometimes called the "Ceylonese Magnet" because it could attract and then repel hot ashes due to its Pyroelectricity, pyroelectric properties. Tourmalines were used by chemists in the 19th century to Polarization (waves), polarize light by shining rays onto a cut and polished surface of the gem. Species and varieties Commonly encountered species and varieties of tourmaline include the following: * Schorl species ** Brownish ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dichroic Prism
A dichroic prism is a prism (optics), prism that splits light into two beams of differing wavelength, wavelengths (colour). A trichroic prism assembly combines two dichroic prisms to split an image into 3 colours, typically as red, green and blue of the RGB colour model. They are usually constructed of one or more glass prisms with dichroism, dichroic optical coatings that selectively reflect or transmit light depending on the light's wavelength. That is, certain surfaces within the prism act as dichroic filters. These are used as beam splitters in many optical instruments. (See: Dichroism, for the etymology of the term.) Applications in camcorders or digital cameras One common application of dichroic prisms is in some camcorders and high-quality digital cameras. A ''trichroic prism assembly'' is a combination of two dichroic prisms which are used to split an image into red, green, and blue components, which can be separately detected on three charge-coupled device, CCD arrays. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Circular Polarization
In electrodynamics, circular polarization of an electromagnetic wave is a polarization state in which, at each point, the electromagnetic field of the wave has a constant magnitude and is rotating at a constant rate in a plane perpendicular to the direction of the wave. In electrodynamics, the strength and direction of an electric field is defined by its electric field vector. In the case of a circularly polarized wave, the tip of the electric field vector, at a given point in space, relates to the phase of the light as it travels through time and space. At any instant of time, the electric field vector of the wave indicates a point on a helix oriented along the direction of propagation. A circularly polarized wave can rotate in one of two possible senses: ''right-handed circular polarization (RHCP)'' in which the electric field vector rotates in a right-hand sense with respect to the direction of propagation, and ''left-handed circular polarization (LHCP)'' in which the vecto ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polarization (waves)
, or , is a property of transverse waves which specifies the geometrical orientation of the oscillations. In a transverse wave, the direction of the oscillation is perpendicular to the direction of motion of the wave. One example of a polarized transverse wave is vibrations traveling along a taut string, for example, in a musical instrument like a guitar string. Depending on how the string is plucked, the vibrations can be in a vertical direction, horizontal direction, or at any angle perpendicular to the string. In contrast, in longitudinal waves, such as sound waves in a liquid or gas, the displacement of the particles in the oscillation is always in the direction of propagation, so these waves do not exhibit polarization. Transverse waves that exhibit polarization include electromagnetic waves such as light and radio waves, gravitational waves, and transverse sound waves ( shear waves) in solids. An electromagnetic wave such as light consists of a coupled oscillating el ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Greek Language
Greek (, ; , ) is an Indo-European languages, Indo-European language, constituting an independent Hellenic languages, Hellenic branch within the Indo-European language family. It is native to Greece, Cyprus, Italy (in Calabria and Salento), southern Albania, and other regions of the Balkans, Caucasus, the Black Sea coast, Asia Minor, and the Eastern Mediterranean. It has the list of languages by first written accounts, longest documented history of any Indo-European language, spanning at least 3,400 years of written records. Its writing system is the Greek alphabet, which has been used for approximately 2,800 years; previously, Greek was recorded in writing systems such as Linear B and the Cypriot syllabary. The Greek language holds a very important place in the history of the Western world. Beginning with the epics of Homer, ancient Greek literature includes many works of lasting importance in the European canon. Greek is also the language in which many of the foundational texts ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quantum Mechanics
Quantum mechanics is the fundamental physical Scientific theory, theory that describes the behavior of matter and of light; its unusual characteristics typically occur at and below the scale of atoms. Reprinted, Addison-Wesley, 1989, It is the foundation of all quantum physics, which includes quantum chemistry, quantum field theory, quantum technology, and quantum information science. Quantum mechanics can describe many systems that classical physics cannot. Classical physics can describe many aspects of nature at an ordinary (macroscopic and Microscopic scale, (optical) microscopic) scale, but is not sufficient for describing them at very small submicroscopic (atomic and subatomic) scales. Classical mechanics can be derived from quantum mechanics as an approximation that is valid at ordinary scales. Quantum systems have Bound state, bound states that are Quantization (physics), quantized to Discrete mathematics, discrete values of energy, momentum, angular momentum, and ot ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
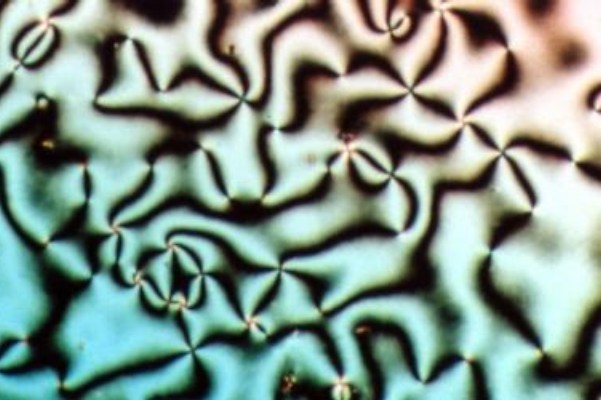
Liquid Crystals
Liquid crystal (LC) is a state of matter whose properties are between those of conventional liquids and those of solid crystals. For example, a liquid crystal can flow like a liquid, but its molecules may be oriented in a common direction as in a solid. There are many types of LC phases, which can be distinguished by their optical properties (such as textures). The contrasting textures arise due to molecules within one area of material ("domain") being oriented in the same direction but different areas having different orientations. An LC material may not always be in an LC state of matter (just as water may be ice or water vapour). Liquid crystals can be divided into three main types: thermotropic, lyotropic, and metallotropic. Thermotropic and lyotropic liquid crystals consist mostly of organic molecules, although a few minerals are also known. Thermotropic LCs exhibit a phase transition into the LC phase as temperature changes. Lyotropic LCs exhibit phase transitions a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Visible Light
Light, visible light, or visible radiation is electromagnetic radiation that can be perceived by the human eye. Visible light spans the visible spectrum and is usually defined as having wavelengths in the range of 400–700 nanometres (nm), corresponding to frequencies of 750–420 terahertz. The visible band sits adjacent to the infrared (with longer wavelengths and lower frequencies) and the ultraviolet (with shorter wavelengths and higher frequencies), called collectively '' optical radiation''. In physics, the term "light" may refer more broadly to electromagnetic radiation of any wavelength, whether visible or not. In this sense, gamma rays, X-rays, microwaves and radio waves are also light. The primary properties of light are intensity, propagation direction, frequency or wavelength spectrum, and polarization. Its speed in vacuum, , is one of the fundamental constants of nature. All electromagnetic radiation exhibits some properties of both particles and waves ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |