|
Damak
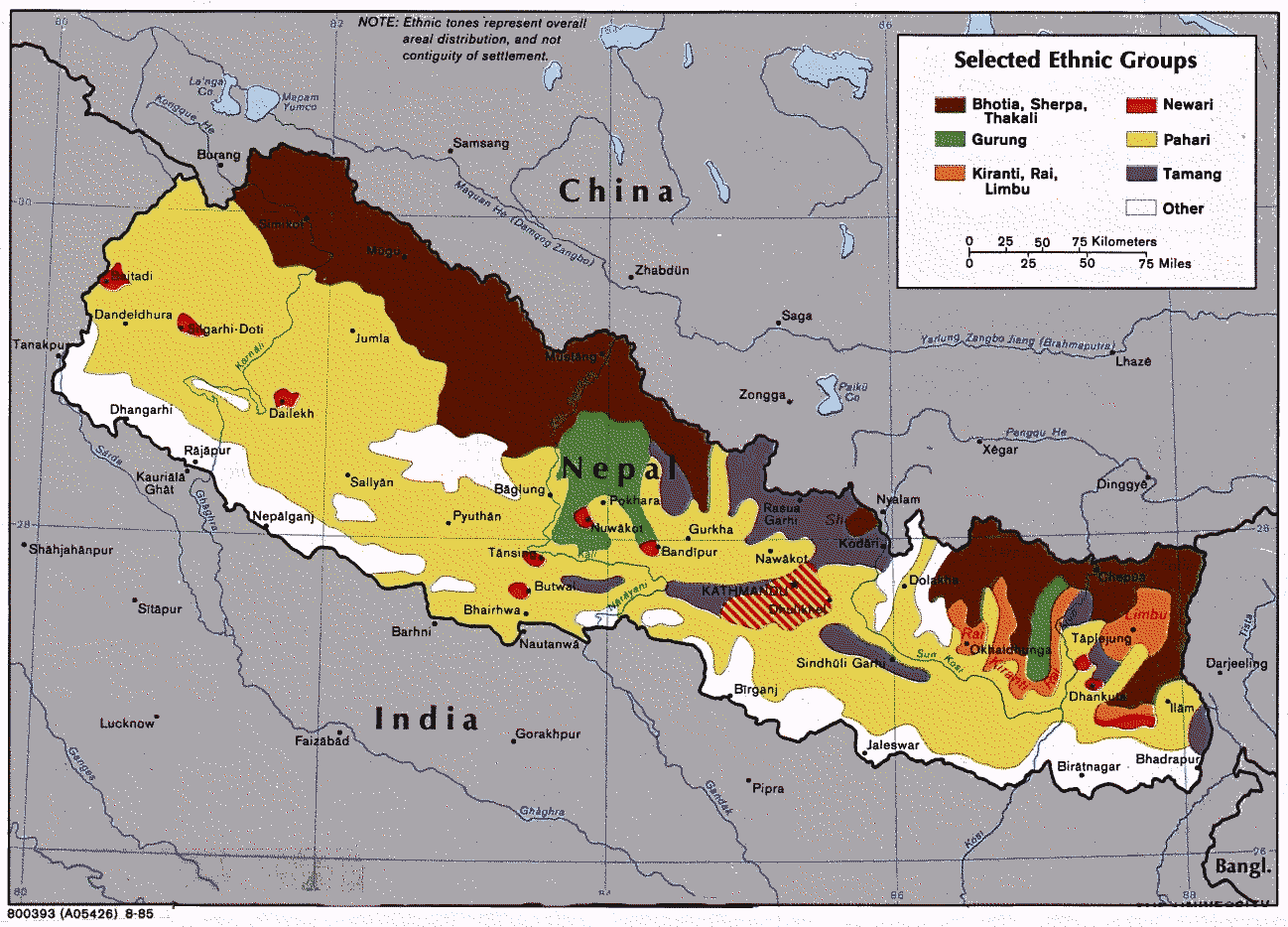
Damak ( Nepali: दमक) is one of the oldest municipalities in Jhapa District of Koshi Province in eastern Nepal. It is situated between the Ratuwa River in the east and the Maawa River in the west. It has Sivalik Hills in its north and ends with the intersection of Ratuwa River and Maawa River in the south. Mahendra Highway, the longest highway of Nepal, bisects the municipality .It is the largest city in Jhapa District with a population of 107,410 in 2021. Demographics At the time of the 2011 Nepal census, Damak Municipality had a population of 75,743. Of these, 65.0% spoke Nepali, 19.2% Limbu, 11.3% Maithili, 4.6% Dhimal, 4.1% Rai, 2.9% Newar, 2.5% Tamang, 1.5% Magar, 0.9% Hindi, 0.8% Rajbanshi, 0.7% Urdu, 0.5% Gurung, 0.4% Bengali, 0.4% Bantawa, 0.4% Tharu, 0.3% Bhojpuri, 0.3% Majhi, 0.3% Rajasthani, 0.3% Santali, 0.3% Sunwar, 0.2% Kisan, 0.2% Kumal, 0.1% Bhujel, 0.1% Chamling, 0.1% Sherpa, 0.1% Tajpuriya, 0.1% Thulung, 0.1% Uranw/Urau, 0.1% Yakkha and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Koshi Province
Koshi Province () is an autonomous Provinces of Nepal, province of Nepal adopted by the Constitution of Nepal on 20 September 2015. It covers an area of , about 17.5% of the country's total area. With the industrial city of Biratnagar as its capital, the province includes the towns of Birtamod, Sundar Haraincha, Damak, Dharan, Itahari, Triyuga Municipality and Mechinagar, and Mount Everest, Kangchenjunga and Ama Dablam. Koshi River, the largest river of the nation, forms the province's western boundary. Under the First-past-the-post voting system issued by the Constituency Delimitation Commission, Nepal, the province hosts 28 parliamentary seats and 56 provincial assembly seats. The province is bordered by the Tibet Autonomous Region of China to the north, the Indian states of Sikkim and West Bengal to the east, Bihar to the south, and Bagmati Province and Madhesh Province to the west. According to the 2021 Nepal census, there are around five million people in the province, with a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ratua Khola
The Ratuwa River ( Nepali: रतुवा खोला) is a perennial river located in eastern Nepal. Originating from the Chure Pahad, it flows southward through the Terai region, forming the eastern boundary of Damak Municipality, before crossing into India, where it merges with the Kankai River in Bihar. The river plays a significant role in the region's ecosystem, agriculture, and urban life but faces challenges related to environmental degradation and flood risks. Geographical Features The Ratuwa River basin covers parts of Ilam, Jhapa Jhapa District (; ) is a district of Koshi Province in eastern Nepal named after a Rajbanshi Surjapuri language word "Jhapa", meaning "to cover" (verb). The 2021 Nepal Census, puts the total population of the district at 994,090. The total a ..., and Morang districts. It has a total catchment area of 400.66 km², with significant portions in the Chure-Bhawar range, the Terai plains, and a small section in the Mahabharat range ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mahendra Highway
Mahendra Highway or NH01 (previously: H01) (), also called East-West Highway (), runs across the Terai geographical region of Nepal, from Mechinagar in the east to Bhim Datta in the west, cutting across the entire width of the country. It is the longest highway in Nepal and was constructed in cooperation with various countries. The highway is named after King Mahendra Shah. Overview The highway is mostly a single-lane road in each direction. It is a major infrastructure element because east–west travel was previously limited to the Hulaki Highway built during the Rana regime, expensive and limited air travel, or Nepalese trains and buses. The highway crosses the Terai from east to west for over . It connects Nepal from Kakarbhitta ( Mechinagar Municipality) to West Mahendra Nagar in the east. Bharatpur city and Chitwan Valley are located towards the central part of this highway. The major destinations along and around the highway are Mechinagar, Bhadrapur, Itahari, J ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dhimal Language
Dhimal is a Sino-Tibetan languages, Sino-Tibetan language of Nepal spoken by about 20,000 people, mainly in the Terai of Koshi Province. There is an eastern and western dialect, which are separated by the Kankai River. Most people transcribe Dhimal into Devanagari and there are standard conventions for extra phonological distinctions. Distribution and status Dhimal is spoken in the southern Terai of eastern Nepal, specifically in the districts of Morang District, Morang, Jhapa District, Jhapa and Sunsari District, Sunsari. In the region the Dhimal make up slightly more than 1% of the population. The eastern and western dialects are separated by the Kankai River in Jhapa District. The main areas of concentration for the western dialect is between the towns of Belbari Municipality, Belbari and Damak Municipality, Damak, while the eastern dialect is concentrated along the Mechi River bordering India. Until the early 20th century, the Terai was considered a hostile environment for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jhapa District
Jhapa District (; ) is a district of Koshi Province in eastern Nepal named after a Rajbanshi Surjapuri language word "Jhapa", meaning "to cover" (verb). The 2021 Nepal Census, puts the total population of the district at 994,090. The total area of the district is 1,606 square kilometres. History The lowlands of Limbuwan (present-day terai lands of Sunsari, Morang, and Jhapa) were collectively known as Morang since the time of King Mawrong of 7th century. In the beginning of 1400 AD, Morang Kingdom patriated from Kingdom of Ilam and Kingdom of Mikluk Bodhey (Choubise) and started ruling on its own. Location Jhapa is the easternmost district of Nepal and lies in the fertile Terai plains. It is part of the Outer Terai. Jhapa borders with Ilam in the north, Morang in the west, the Indian state of Bihar in the south and the Indian state of West Bengal to the southeast and east. Geographically, it covers an area of and lies on 87°39’ east to 88°12’ east longitude and 2 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Cities In Nepal
Cities and towns in Nepal are incorporated under municipality. A municipality in Nepal is a sub-unit of a district. The Government of Nepal has set-out a minimum criteria for municipalities. These criteria include a certain population, infrastructure and revenues. Presently, there are 293 municipalities in Nepal among which 6 are metropolis, 11 are sub-metropolis and 276 are municipal councils. Other than that there are 460 rural municipalities totaling 753 local level government within Nepal. Kathmandu, the capital, is also the largest city. In terms of area, Pokhara is the largest metropolitan city covering a subtotal of 464.28 km2 while Lalitpur is the smallest, with an area of 36.12 km2. Ghorahi is the largest sub-metropolitan city with an area of 522.21 km2 where as Dhangadhi is the largest sub-metropolitan city by a population of 204,788. Budhanilkantha with a population of 179,688 is the largest municipality followed by Birendranagar with a population ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kiranti Languages
The Kiranti languages are a major family of Sino-Tibetan languages spoken in Nepal and India (notably Sikkim, Darjeeling, Kalimpong, and Bhutan) by the Kirati people. External relationships George van Driem had formerly proposed that the Kiranti languages were part of a Mahakiranti family, although specialists are not completely certain of either the existence of a Kiranti subgroup or its precise membership. LaPolla (2003), though, proposes that Kiranti may be part of a larger " Rung" group. Classification There are about two dozen Kiranti languages. Among the better known are Limbu, Sunuwar, Bantawa, Chamling, Khaling, Bahing, Yakkha, Wayu, Dungmali, Lohorung, and Kulung. Kiranti verbs are not easily segmentable, due in large part to the presence of portmanteau morphemes, crowded affix strings, and extensive (and often nonintuitive) allomorphy. Thus their relationship to each other has been a subject of debate. Overall, Kiranti languages are classified: ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
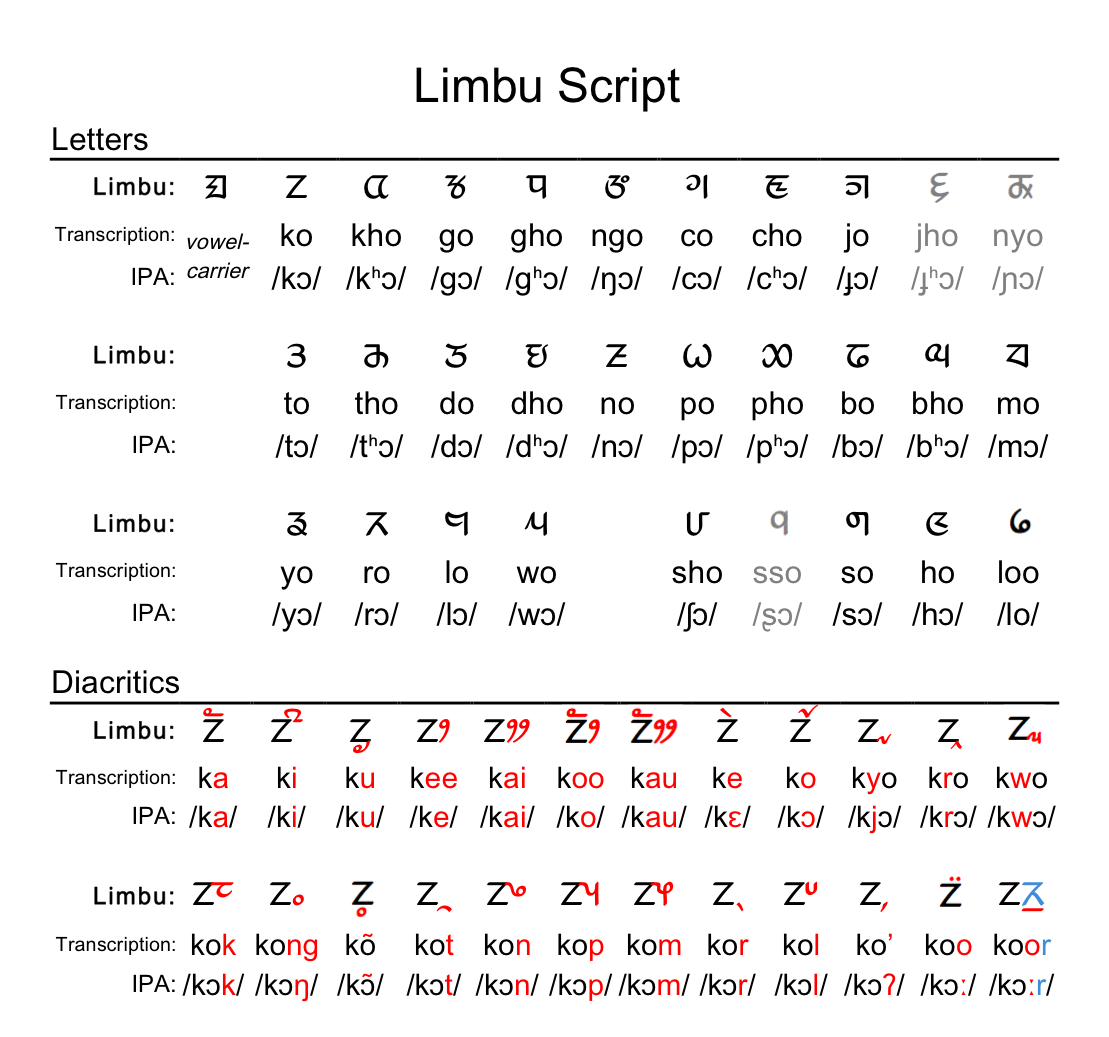
Limbu Language
Limbu (Limbu: , ''yakthuṅ pan'') is a Sino-Tibetan language spoken by the Limbu people of Nepal and Northeastern India (particularly West Bengal, Sikkim, Assam and Nagaland) as well as expatriate communities in Bhutan. The Limbu refer to themselves as ''Yakthung'' and their language as ''Yakthungpan.'' Yakthungpan has four main dialects: Phedape, Chhathare, Tambarkhole and Panthare dialects.A Grammar of Limbu By George van Driem 1987 Among four dialects, the Phedape dialect is widely spoken and well understood by most Yakthungpan speakers. However, as there are some dominant Panthare scholars who have role to create knowledge and control knowledge in the Limbu communities, Panthare dialect is being popularised as a "standard" Limbu language. As Panthare Yakthungs are much more engaged in central political position and administrative positions, they are trying to introduce Panthare dialect as a Standard Yakthungpan. Yakthungpan (Limbu language) is one of the major languages ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Maithili Language
Maithili ( , ) is an Indo-Aryan language spoken in parts of India and Nepal. It is native to the Mithila region, which encompasses parts of the eastern Indian states of Bihar and Jharkhand as well as Nepal's Koshi Province, Koshi and Madhesh Provinces. It is one of the 22 scheduled languages of India. It is the second most commonly spoken native languages of Nepal, Nepalese language constitutionally registered as one of the fourteen provincial official languages of Nepal. It is spoken by 21.7 million people. Of those, 3.2 million are Nepalis, Nepalese speakers. The language is predominantly written in Devanagari, but the historical Tirhuta script, Tirhuta and Kaithi scripts retained some use until today. Official status In 2003, Maithili was included in the 8th Schedule, Eighth Schedule of the Indian Constitution as a recognised language of India, Indian language, which allows it to be used in education, government, and other official contexts in India. The Maithili language i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Magar Language
Magar Dhut (, ) is a Sino-Tibetan language spoken mainly in Nepal, southern Bhutan, and in Darjeeling, Assam and Sikkim, India, by the Magar people. It is divided into two groups (Eastern and Western) and further dialect divisions give distinct tribal identity. In Nepal 810,000 people speak the language. While the government of Nepal developed Magar language curricula, as provisioned by the constitution, the teaching materials have never successfully reached Magar schools, where most school instruction is in the Nepali language. It is not unusual for groups with their own language to feel that the "mother-tongue" is an essential part of identity. The Dhut Magar language is sometimes lumped with the Magar Kham language spoken further west in Bheri, Dhaulagiri, and Rapti zones. Although the two languages share many common words, they have major structural differences and are not mutually intelligible. Geographical distribution Western Magar Western Magar (dialects: ''Pal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Newar Language
Newar (; , ) is a Sino-Tibetan languages, Sino-Tibetan language spoken by the Newar people, the indigenous inhabitants of Nepal Mandala, which consists of the Kathmandu Valley and surrounding regions in Nepal. The language is known officially in Nepal as Nepal Bhasa, a name that has been historically used for the language. The term "Newari" is also used to refer to the language, although the Indic ''-i'' suffix is considered inappropriate by some Newar speakers. The language served as the official language of Nepal during the Malla dynasty (Nepal), Malla dynasty since the 14th century till the end of dynasty in 1769 during which the language was referred as "Nepal Bhasa", a term which literally means "Nepalese Language". However, the language is not the same as Nepali language, Nepali, an Indo-Aryan languages, Indo-Aryan language and the current official language of Nepal, which only got the name Nepali in the 1930s. Newar literature, Literature in Newar is one of the oldest i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tamang Language
Tamangic language is spoken mainly in Tamangsaling Land in Nepal, Sikkim, West Bengal (Darjeeling) and North-Eastern India. It comprises Eastern Tamang, Northwestern Tamang, Southwestern Tamang, Eastern Gorkha Tamang, and Western Tamang. Lexical similarity between Eastern Tamang (which is regarded as the most prominent) and other Tamang languages varies between 81% and 63%. For comparison, the lexical similarity between Spanish and Portuguese is estimated at 89%. Ethnologue report for Spanish Dialects ''Ethnologue'' divides Tamang into the following varieties due to mutual unintelligibility. *Eastern Tamang: 759,000 in Nepal (2000 WCD). Population total all countries: 773,000. Sub-dialects are as follows. **Outer-Eastern Tamang (Sailung Tamang) **Central-Eastern Tamang (Temal Tamang) **Southwestern Tamang (Kath-Bhotiya, Lama Bhote, Murmi, Rongba, Sain, Tamang Gyoi, Tamang Gyot, Tamang Lengmo, Tamang Tam) *Western Tamang: 323,000 (2000 WCD). Sub-dialects are as follows. ** ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |