Tamang language on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
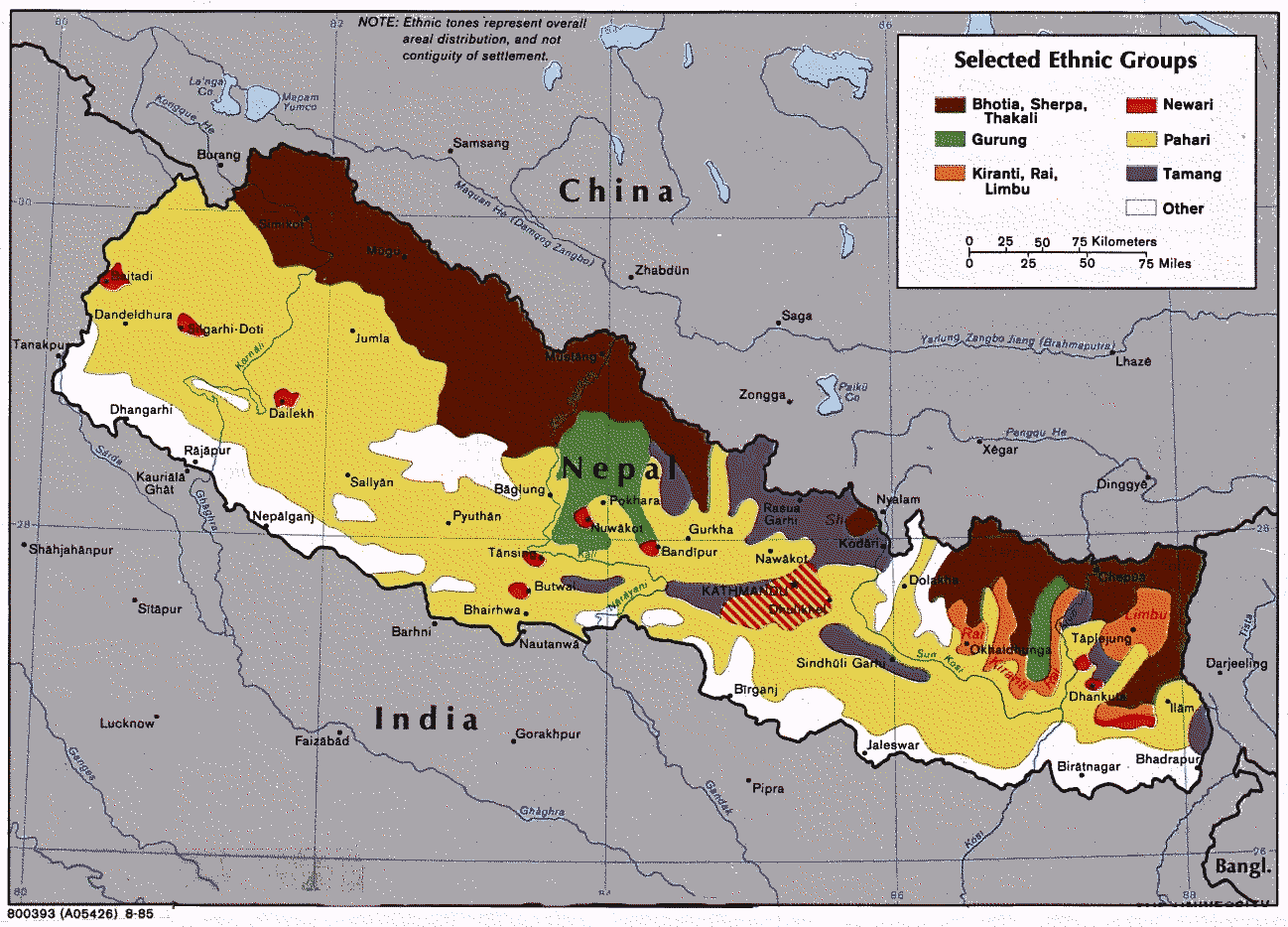 Tamangic language is spoken mainly in Tamangsaling Land in
Tamangic language is spoken mainly in Tamangsaling Land in
Counting in Tamang
*ELAR archive o
Tamang
{{Languages of Northeast India Languages of Nepal Tamangic languages Languages of Sikkim Languages of Bhutan Subject–object–verb languages Languages of Bagmati Province Languages of Koshi Province Languages of Madhesh Province Languages of Gandaki Province Languages written in Devanagari
 Tamangic language is spoken mainly in Tamangsaling Land in
Tamangic language is spoken mainly in Tamangsaling Land in Nepal
Nepal, officially the Federal Democratic Republic of Nepal, is a landlocked country in South Asia. It is mainly situated in the Himalayas, but also includes parts of the Indo-Gangetic Plain. It borders the Tibet Autonomous Region of China Ch ...
, Sikkim
Sikkim ( ; ) is a States and union territories of India, state in northeastern India. It borders the Tibet Autonomous Region of China in the north and northeast, Bhutan in the east, Koshi Province of Nepal in the west, and West Bengal in the ...
, West Bengal
West Bengal (; Bengali language, Bengali: , , abbr. WB) is a States and union territories of India, state in the East India, eastern portion of India. It is situated along the Bay of Bengal, along with a population of over 91 million inhabi ...
(Darjeeling
Darjeeling (, , ) is a city in the northernmost region of the States and union territories of India, Indian state of West Bengal. Located in the Eastern Himalayas, it has an average elevation of . To the west of Darjeeling lies the Koshi Pr ...
) and North-Eastern India. It comprises Eastern Tamang, Northwestern Tamang, Southwestern Tamang, Eastern Gorkha Tamang, and Western Tamang. Lexical similarity
In linguistics, lexical similarity is a measure of the degree to which the word sets of two given languages are similar. A lexical similarity of 1 (or 100%) would mean a total overlap between vocabularies, whereas 0 means there are no common words. ...
between Eastern Tamang (which is regarded as the most prominent) and other Tamang languages varies between 81% and 63%. For comparison, the lexical similarity between Spanish and Portuguese is estimated at 89%. Ethnologue report for Spanish
Dialects
''Ethnologue
''Ethnologue: Languages of the World'' is an annual reference publication in print and online that provides statistics and other information on the living languages of the world. It is the world's most comprehensive catalogue of languages. It w ...
'' divides Tamang into the following varieties due to mutual unintelligibility.
*Eastern Tamang: 759,000 in Nepal (2000 WCD). Population total all countries: 773,000. Sub-dialects are as follows.
**Outer-Eastern Tamang (Sailung Tamang)
**Central-Eastern Tamang (Temal Tamang)
**Southwestern Tamang (Kath-Bhotiya, Lama Bhote, Murmi, Rongba, Sain, Tamang Gyoi, Tamang Gyot, Tamang Lengmo, Tamang Tam)
*Western Tamang: 323,000 (2000 WCD). Sub-dialects are as follows.
**Trisuli (Nuwakot)
**Rasuwa
**Northwestern dialect of Western Tamang (Dhading) — was having separate ISO code tmk, merged with tdg in 2023. Population 55,000 (1991 census). Spoken in the central mountainous strip of Nuwakot District
Nuwakot District (), a part of Bagmati Province, is one of the List of districts of Nepal, seventy-seven districts of Nepal. The district, with Bidur as its district headquarters, covers an area of and had a population of 288,478 in 2001 and 277 ...
, Bagmati Province
Bagmati Province (, ''Bāgmatī pradēśa'') is one of the seven Provinces of Nepal, provinces of Nepal established by the constitution of Nepal. Bagmati is Nepal's second-most populous province and fifth largest province by area. It is bordered ...
.
**Southwestern dialect of Western Tamang
*Eastern Gorkha Tamang: 4,000 (2000 WCD). Sub-dialects are as follows.
**Kasigaon
**Kerounja
The Tamang language is the most widely spoken Sino-Tibetan language in Nepal.
Geographical distribution
''Ethnologue
''Ethnologue: Languages of the World'' is an annual reference publication in print and online that provides statistics and other information on the living languages of the world. It is the world's most comprehensive catalogue of languages. It w ...
'' gives the following location information for the varieties of Tamang.
Eastern Tamang
*Bagmati Province
Bagmati Province (, ''Bāgmatī pradēśa'') is one of the seven Provinces of Nepal, provinces of Nepal established by the constitution of Nepal. Bagmati is Nepal's second-most populous province and fifth largest province by area. It is bordered ...
: Bhaktapur District, Chitwan District, Dolkha District, Kathmandu District
Kathmandu District (; Nepal Bhasa: ये: जिल्ला) is a district located in Kathmandu Valley, Bagmati Province of Nepal. It is one of the seventy-seven districts of Nepal, covers an area of , and is the most densely populated dist ...
, Kavrepalanchok District, Lalitpur District, Makwanpur District, eastern Nuwakot District
Nuwakot District (), a part of Bagmati Province, is one of the List of districts of Nepal, seventy-seven districts of Nepal. The district, with Bidur as its district headquarters, covers an area of and had a population of 288,478 in 2001 and 277 ...
, Ramechhap District, Sindhuli District and western Sindhupalchowk District
Sindhupalchok District (or Sindhupalchok, ) is a part of Bagmati Province and one of the seventy-seven districts of Nepal, with an area of . The district's headquarters is in Chautara. In 2006, 336,478 people resided in 79 village development ...
* Province No. 1: Okhaldhunga District, western Khotang District, and Udayapur District
Southwestern Tamang
*Bagmati Province
Bagmati Province (, ''Bāgmatī pradēśa'') is one of the seven Provinces of Nepal, provinces of Nepal established by the constitution of Nepal. Bagmati is Nepal's second-most populous province and fifth largest province by area. It is bordered ...
: Chitwan District, southern Dhading District
Dhading District ( ), a part of Bagmati Province, is one of the seventy-seven districts of Nepal. The district, with Dhading Besi as its district headquarters, covers an area of , had a population of 338,658 in 2001 and 336,067 in 2011.
Geogr ...
, western and northwestern Kathmandu District
Kathmandu District (; Nepal Bhasa: ये: जिल्ला) is a district located in Kathmandu Valley, Bagmati Province of Nepal. It is one of the seventy-seven districts of Nepal, covers an area of , and is the most densely populated dist ...
area and northwestern Makwanpur District
* Province No. 2: Bara District, Parsa District and Rautahat District
Western Tamang
*Bagmati Province
Bagmati Province (, ''Bāgmatī pradēśa'') is one of the seven Provinces of Nepal, provinces of Nepal established by the constitution of Nepal. Bagmati is Nepal's second-most populous province and fifth largest province by area. It is bordered ...
: western Nuwakot District
Nuwakot District (), a part of Bagmati Province, is one of the List of districts of Nepal, seventy-seven districts of Nepal. The district, with Bidur as its district headquarters, covers an area of and had a population of 288,478 in 2001 and 277 ...
, Rasuwa District, and Dhading District
Dhading District ( ), a part of Bagmati Province, is one of the seventy-seven districts of Nepal. The district, with Dhading Besi as its district headquarters, covers an area of , had a population of 338,658 in 2001 and 336,067 in 2011.
Geogr ...
*central mountainous strip of Nuwakot District
Nuwakot District (), a part of Bagmati Province, is one of the List of districts of Nepal, seventy-seven districts of Nepal. The district, with Bidur as its district headquarters, covers an area of and had a population of 288,478 in 2001 and 277 ...
, Bagmati Province
Bagmati Province (, ''Bāgmatī pradēśa'') is one of the seven Provinces of Nepal, provinces of Nepal established by the constitution of Nepal. Bagmati is Nepal's second-most populous province and fifth largest province by area. It is bordered ...
(''Northwestern Tamang'')
*northeastern Sindhupalchok District
Sindhupalchok District (or Sindhupalchok, ) is a part of Bagmati Province and one of the List of districts of Nepal, seventy-seven districts of Nepal, with an area of . The district's headquarters is in Chautara. In 2006, 336,478 people resided ...
, Bagmati Province
Bagmati Province (, ''Bāgmatī pradēśa'') is one of the seven Provinces of Nepal, provinces of Nepal established by the constitution of Nepal. Bagmati is Nepal's second-most populous province and fifth largest province by area. It is bordered ...
: Bhote Namlan, and Bhote Chaur, on Trishuli river west bank toward Budhi Gandaki river
*northwestern Makwanpur District, Bagmati Province
Bagmati Province (, ''Bāgmatī pradēśa'') is one of the seven Provinces of Nepal, provinces of Nepal established by the constitution of Nepal. Bagmati is Nepal's second-most populous province and fifth largest province by area. It is bordered ...
: Phakel, Chakhel, Khulekhani, Markhu, Tistung, and Palung
*northern Kathmandu District
Kathmandu District (; Nepal Bhasa: ये: जिल्ला) is a district located in Kathmandu Valley, Bagmati Province of Nepal. It is one of the seventy-seven districts of Nepal, covers an area of , and is the most densely populated dist ...
, Bagmati Province
Bagmati Province (, ''Bāgmatī pradēśa'') is one of the seven Provinces of Nepal, provinces of Nepal established by the constitution of Nepal. Bagmati is Nepal's second-most populous province and fifth largest province by area. It is bordered ...
: Jhor, Thoka, and Gagal Phedi
Eastern Tamang
*south and east of Jagat, northern Gorkha District
Gorkha District (), a part of Gandaki Province, is one of seventy-seven districts of Nepal, and the fourth largest district of the country in terms of area. It is historically linked with the creation of modern Nepal and the name of the legenda ...
, Gandaki Province
Gandaki Province ( ) ), is one of the seven federal provinces established by the current constitution of Nepal which was promulgated on 20 September 2015. Pokhara is the province's capital city. It borders the Tibet Autonomous Region in Southw ...
Grammar
Some grammatical features of the Tamang languages include: *A canonical word order of SOV *Use ofpostposition
Adpositions are a class of words used to express spatial or temporal relations (''in, under, towards, behind, ago'', etc.) or mark various semantic roles (''of, for''). The most common adpositions are prepositions (which precede their complemen ...
s;
*The genitive
In grammar, the genitive case ( abbreviated ) is the grammatical case that marks a word, usually a noun, as modifying another word, also usually a noun—thus indicating an attributive relationship of one noun to the other noun. A genitive can ...
s follow noun
In grammar, a noun is a word that represents a concrete or abstract thing, like living creatures, places, actions, qualities, states of existence, and ideas. A noun may serve as an Object (grammar), object or Subject (grammar), subject within a p ...
s;
*question
A question is an utterance which serves as a request for information. Questions are sometimes distinguished from interrogatives, which are the grammar, grammatical forms, typically used to express them. Rhetorical questions, for instance, are i ...
word medial;
*It is an ergative–absolutive language;
*CV, CVC, CCV, V, CCVC;
Phonetically Tamang languages are tonal.
Phonology
Consonants
Vowels
Nasality only marginally occurs, and is typically transcribed with a mark.Tones
Four tones occur as high falling , mid-high level , mid-low level , very low .Mazaudon (2003)Writing system
Tamang language is written inprakriti
Prakriti ( ) is "the original or natural form or condition of anything, original or primary substance". It is a key concept in Hinduism, formulated by the ''Samkhya'' school, where it does not refer merely to matter or nature, but includes all cog ...
.
References
Bibliography
* Perumalsamy, P. 2009 “ Tamang Language ” in Linguistic Survey of India: Sikkim volume I, New Delhi: Office of Registrar General India, pp: 388-455 https://censusindia.gov.in/census.website/data/LSI *External links
Counting in Tamang
*ELAR archive o
Tamang
{{Languages of Northeast India Languages of Nepal Tamangic languages Languages of Sikkim Languages of Bhutan Subject–object–verb languages Languages of Bagmati Province Languages of Koshi Province Languages of Madhesh Province Languages of Gandaki Province Languages written in Devanagari