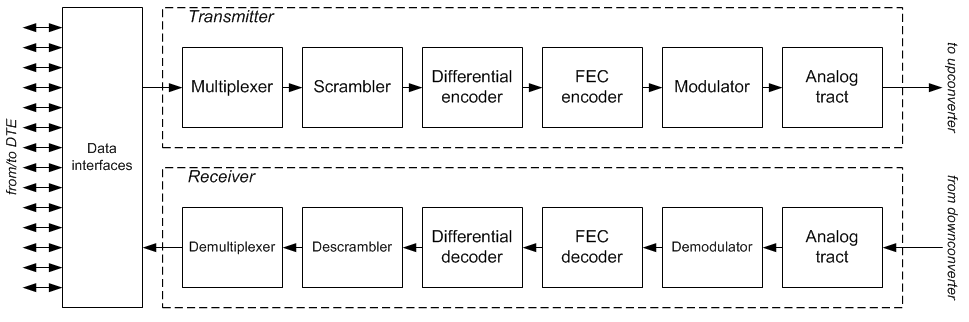
|
DVB-RCS
DVB-RCS (Digital Video Broadcasting - Return Channel via Satellite) provides a method by which the DVB-S platform (and in theory also the DVB-S2 platform) can become a bi-directional, asymmetric data path using wireless between broadcasters and customers. It is a specification for an interactive on-demand multimedia satellite communication system formulated in 1999 by the DVB consortium. Without this method, various degrees of interactivity can be offered, without implying any return channel back from the user to the service provider: Data Carrousel or Electronic Programs Guides ( EPG) are examples of such enhanced TV services which make use of “local interactivity”, without any return path from customer to provider. Chronology The 5th revision of the DVB-RCS standard was completed in 2008. A major update included the very first broadband mobile standardization. This extended version, formally referred to as "ETSI EN 301 790 v 1.5.1" is also known as "DVB-RCS+M". The "+M" ver ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Satellite Modem
A satellite modem or satmodem is a modem used to establish data transfers using a communications satellite as a relay. A satellite modem's main function is to transform an input bitstream to a radio signal and vice versa. There are some devices that include only a demodulator (and no modulator, thus only allowing data to be downloaded by satellite) that are also referred to as "satellite modems." These devices are used in satellite Internet access (in this case uploaded data is transferred through a conventional PSTN modem or an ADSL modem). Satellite link A satellite modem is not the only device needed to establish a communication channel. Other equipment that is essential for creating a satellite link include satellite antennas and frequency converters. Data to be transmitted are transferred to a modem from data terminal equipment (e.g. a computer). The modem usually has intermediate frequency (IF) output (that is, 50-200 MHz), however, sometimes the signal is modulated ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
DVB-S2
Digital Video Broadcasting - Satellite - Second Generation (DVB-S2) is a digital television broadcast standard that has been designed as a successor for the popular DVB-S system. It was developed in 2003 by the Digital Video Broadcasting Project, an international industry consortium, and ratified by ETSI (EN 302307) in March 2005. The standard is based on, and improves upon DVB-S and the electronic news-gathering (or Digital Satellite News Gathering) system, used by mobile units for sending sounds and images from remote locations worldwide back to their home television stations. DVB-S2 is designed for broadcast services including standard and HDTV, interactive services including Internet access, and (professional) data content distribution. The development of DVB-S2 coincided with the introduction of HDTV and H.264 (MPEG-4 AVC) video codecs. Two new key features that were added compared to the DVB-S standard are: * A powerful coding scheme based on a modern LDPC code ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Digital Video Broadcasting
Digital Video Broadcasting (DVB) is a set of international open standards for digital television. DVB standards are maintained by the DVB Project, an international industry consortium, and are published by a Joint Technical Committee (JTC) of the European Telecommunications Standards Institute (ETSI), European Committee for Electrotechnical Standardization (CENELEC) and European Broadcasting Union (EBU). Transmission DVB systems distribute data using a variety of approaches, including: * Satellite: DVB-S, DVB-DSNG, DVB-S2, DVB-S2X and DVB-SH ** DVB-SMATV for distribution via SMATV * Cable: DVB-C, DVB-C2 * Terrestrial television: DVB-T, DVB-T2 ** Digital terrestrial television for handhelds: DVB-H, DVB-SH * Microwave: using DTT ( DVB-MT), the MMDS ( DVB-MC), and/or MVDS standards ( DVB-MS) These standards define the physical layer and data link layer of the distribution system. Devices interact with the physical layer via a synchronous parallel interface ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
DVB-S
Digital Video Broadcasting – Satellite (DVB-S) is the original DVB standard for satellite television and dates from 1995, in its first release, while development lasted from 1993 to 1997. The first commercial applications were by Canal+ in France and Galaxy in Australia, enabling digitally broadcast, satellite-delivered television to the public. According to ETSI, It is used via satellites serving every continent of the world. DVB-S is used in both multiple channel per carrier (MCPC) and single channel per carrier modes for broadcast network feeds as well as for direct-broadcast satellite services like Sky UK and Ireland via Astra in Europe, Dish Network and Globecast in the U.S. and Bell Satellite TV in Canada. While the actual DVB-S standard only specifies physical link characteristics and framing, the overlaid transport stream delivered by DVB-S is mandated as MPEG-2, known as MPEG transport stream (MPEG-TS). Some amateur television Amateur television (ATV) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wireless
Wireless communication (or just wireless, when the context allows) is the transfer of information (''telecommunication'') between two or more points without the use of an electrical conductor, optical fiber or other continuous guided transmission medium, medium for the transfer. The most common wireless technologies use radio waves. With radio waves, intended distances can be short, such as a few meters for Bluetooth, or as far as millions of kilometers for NASA Deep Space Network, deep-space radio communications. It encompasses various types of fixed, mobile, and portable applications, including two-way radios, Mobile phone, cellular telephones, personal digital assistants (PDAs), and wireless networking. Other examples of applications of radio ''wireless technology'' include Global Positioning System, GPS units, garage door openers, wireless Mouse (computing), computer mouse, Keyboard (computing), keyboards and Headset (audio), headsets, headphones, radio receivers, satelli ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Satellite Communication
A communications satellite is an artificial satellite that relays and amplifies radio telecommunication signals via a transponder; it creates a communication channel between a source transmitter and a receiver at different locations on Earth. Communications satellites are used for television, telephone, radio, internet, and military applications. Many communications satellites are in geostationary orbit above the equator, so that the satellite appears stationary at the same point in the sky; therefore the satellite dish antennas of ground stations can be aimed permanently at that spot and do not have to move to track the satellite. Others form satellite constellations in low Earth orbit, where antennas on the ground have to follow the position of the satellites and switch between satellites frequently. The radio waves used for telecommunications links travel by line of sight and so are obstructed by the curve of the Earth. The purpose of communications satellites is to rela ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Burst Transmission
Burst may refer to: *Burst mode (other), a mode of operation where events occur in rapid succession **Burst transmission, a term in telecommunications **Burst switching, a feature of some packet-switched networks **Bursting, a signaling mode of neurons *Burst phase, a feature of the PAL television format *Burst fracture, a type of spinal injury *Burst charge, a component of some fireworks *Burst noise, type of electronic noise that occurs in semiconductors *Burst (coin), a cryptocurrency *Burst finish, a two- or three-color faded effect applied to musical instruments e.g. sunburst (finish) *Burst (village), a village in Erpe-Mere *Burst.com, a software company *Burst Radio, the University of Bristol student radio station *Burst (band), a Swedish progressive metal band **Burst (Burst EP), ''Burst'' (Burst EP) *Burst (UP10TION EP), ''Burst'' (UP10TION EP) * "Burst", a song by Anthrax from ''Sound of White Noise'' {{disambiguation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Round-trip Delay Time
In telecommunications, round-trip delay (RTD) or round-trip time (RTT) is the amount of time it takes for a signal to be sent ''plus'' the amount of time it takes for acknowledgement of that signal having been received. This time delay includes propagation times for the paths between the two communication endpoints. In the context of computer networks, the signal is typically a data packet. RTT is commonly used interchangeably with ping time, which can be determined with the ping command. However, ping time may differ from experienced RTT with other protocols since the payload and priority associated with ICMP messages used by ping may differ from that of other traffic. End-to-end delay is the length of time it takes for a signal to travel in one direction and is often approximated as half the RTT. Protocol design RTT is a measure of the amount of time taken for an entire message to be sent to a destination and for a reply to be sent back to the sender. The time to send the me ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phase-shift Keying
Phase-shift keying (PSK) is a digital modulation process which conveys data by changing (modulating) the phase of a constant frequency carrier wave. The modulation is accomplished by varying the sine and cosine inputs at a precise time. It is widely used for wireless LANs, RFID and Bluetooth communication. Any digital modulation scheme uses a finite number of distinct signals to represent digital data. PSK uses a finite number of phases, each assigned a unique pattern of binary digits. Usually, each phase encodes an equal number of bits. Each pattern of bits forms the symbol that is represented by the particular phase. The demodulator, which is designed specifically for the symbol-set used by the modulator, determines the phase of the received signal and maps it back to the symbol it represents, thus recovering the original data. This requires the receiver to be able to compare the phase of the received signal to a reference signal such a system is termed coherent (an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Time Division Multiple Access
Time-division multiple access (TDMA) is a channel access method for shared-medium networks. It allows several users to share the same frequency channel by dividing the signal into different time slots. The users transmit in rapid succession, one after the other, each using its own time slot. This allows multiple stations to share the same transmission medium (e.g. radio frequency channel) while using only a part of its channel capacity. Dynamic TDMA is a TDMA variant that dynamically reserves a variable number of time slots in each frame to variable bit-rate data streams, based on the traffic demand of each data stream. TDMA is used in digital 2G cellular systems such as Global System for Mobile Communications (GSM), IS-136, Personal Digital Cellular (PDC) and iDEN, in the Maritime Automatic Identification System, and in the Digital Enhanced Cordless Telecommunications (DECT) standard for portable phones. TDMA was first used in satellite communication systems by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |