|
DVB-S2
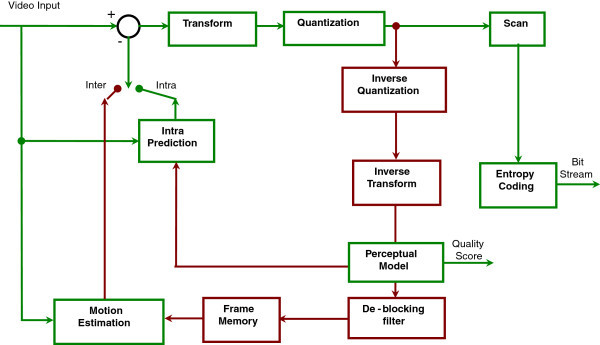
Digital Video Broadcasting - Satellite - Second Generation (DVB-S2) is a digital television broadcast standard that has been designed as a successor for the popular DVB-S system. It was developed in 2003 by the Digital Video Broadcasting Project, an international industry consortium, and ratified by ETSI (EN 302307) in March 2005. The standard is based on, and improves upon DVB-S and the electronic news-gathering (or Digital Satellite News Gathering) system, used by mobile units for sending sounds and images from remote locations worldwide back to their home television stations. DVB-S2 is designed for broadcast services including standard and HDTV, interactive services including Internet access, and (professional) data content distribution. The development of DVB-S2 coincided with the introduction of HDTV and H.264 (MPEG-4 AVC) video codecs. Two new key features that were added compared to the DVB-S standard are: * A powerful coding scheme based on a modern LDPC code ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
DVB-S2X
DVB-S2X is a digital satellite television broadcast standard. DVB-S2X is an extension of DVB-S2 satellite digital broadcasting standard. It was standardized by DVB Project in March 2014 as an optional extension of DVB-S2 standard. It became an ETSI standard. Main features DVB-S2X increased efficiency up to 51% over DVB-S2. Improvements include: *Higher order modulation schemes (64/128/256APSK) *Smaller roll-off factors of 5%, 10% and 15% (though even legacy DVB-S and DVB-S2 receivers can benefit from it) *Improved filtering enabling smaller carrier spacing *Channel bonding in order to combine several carriers, increasing efficiency in 'Direct-To-Home' (DTH) applications Channel bonding helps, particularly for UHDTV services. Statistical multiplexing is often used to allow more television services to fit into a single satellite channel. Statistical multiplexing works best when many television channels can share bandwidth. With UHDTV services, it may be possible to fit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Generic Stream Encapsulation
Generic Stream Encapsulation, or GSE for short, is a Data link layer protocol defined by DVB. GSE provides means to carry packet oriented protocols such as IP on top of uni-directional physical layers such as DVB-S2, DVB-T2 and DVB-C2. GSE provides additional features beyond the pure carriage of IP datagrams that increase the protocol flexibility and applicability. Some key GSE functions/characteristics are: * Support for multi-protocol encapsulation (IPv4, IPv6, MPEG, ATM, Ethernet, 802.1pQ VLANs, etc.) * Transparency to network layer functions, including IP encryption and IP header compression. * Support of several addressing modes. In addition to the 6-byte MAC address (including multicast and unicast), it supports a MAC address-less mode, and an optional 3-byte address mode. * A mechanism for fragmenting IP datagrams or other network layer packets over Base Band frames to support ACM/ VCM. * Support for hardware filtering. * Extensibility: additional link protocols ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Digital Video Broadcasting
Digital Video Broadcasting (DVB) is a set of international open standards for digital television. DVB standards are maintained by the DVB Project, an international industry consortium, and are published by a Joint Technical Committee (JTC) of the European Telecommunications Standards Institute (ETSI), European Committee for Electrotechnical Standardization (CENELEC) and European Broadcasting Union (EBU). Transmission DVB systems distribute data using a variety of approaches, including: * Satellite: DVB-S, DVB-DSNG, DVB-S2, DVB-S2X and DVB-SH ** DVB-SMATV for distribution via SMATV * Cable: DVB-C, DVB-C2 * Terrestrial television: DVB-T, DVB-T2 ** Digital terrestrial television for handhelds: DVB-H, DVB-SH * Microwave: using DTT ( DVB-MT), the MMDS ( DVB-MC), and/or MVDS standards ( DVB-MS) These standards define the physical layer and data link layer of the distribution system. Devices interact with the physical layer via a synchronous parallel interface ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Low-density Parity-check Code
Low-density parity-check (LDPC) codes are a class of error correction codes which (together with the closely-related turbo codes) have gained prominence in coding theory and information theory since the late 1990s. The codes today are widely used in applications ranging from wireless communications to flash-memory storage. Together with turbo codes, they sparked a revolution in coding theory, achieving order-of-magnitude improvements in performance compared to traditional error correction codes. Central to the performance of LDPC codes is their adaptability to the iterative belief propagation decoding algorithm. Under this algorithm, they can be designed to approach theoretical limits (Channel capacity, capacities) of many channels at low computation costs. Theoretically, analysis of LDPC codes focuses on sequences of codes of fixed code rate and increasing block length. These sequences are typically tailored to a set of channels. For appropriately designed sequences, the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Forward Error Correction
In computing, telecommunication, information theory, and coding theory, forward error correction (FEC) or channel coding is a technique used for controlling errors in data transmission over unreliable or noisy communication channels. The central idea is that the sender encodes the message in a redundant way, most often by using an error correction code, or error correcting code (ECC). The redundancy allows the receiver not only to detect errors that may occur anywhere in the message, but often to correct a limited number of errors. Therefore a reverse channel to request re-transmission may not be needed. The cost is a fixed, higher forward channel bandwidth. The American mathematician Richard Hamming pioneered this field in the 1940s and invented the first error-correcting code in 1950: the Hamming (7,4) code. FEC can be applied in situations where re-transmissions are costly or impossible, such as one-way communication links or when transmitting to multiple receivers in m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spectral Efficiency
Spectral efficiency, spectrum efficiency or bandwidth efficiency refers to the information rate that can be transmitted over a given bandwidth in a specific communication system. It is a measure of how efficiently a limited frequency spectrum is utilized by the physical layer protocol, and sometimes by the medium access control (the channel access protocol). Guowang Miao, Jens Zander, Ki Won Sung, and Ben Slimane, Fundamentals of Mobile Data Networks, Cambridge University Press, , 2016. Link spectral efficiency The link spectral efficiency of a digital communication system is measured in '' bit/ s/ Hz'', or, less frequently but unambiguously, in ''(bit/s)/Hz''. It is the net bit rate (useful information rate excluding error-correcting codes) or maximum throughput divided by the bandwidth in hertz of a communication channel or a data link. Alternatively, the spectral efficiency may be measured in ''bit/symbol'', which is equivalent to ''bits per channel use'' (''bpcu''), i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
High-definition Television
High-definition television (HDTV) describes a television or video system which provides a substantially higher image resolution than the previous generation of technologies. The term has been used since at least 1933; in more recent times, it refers to the generation following standard-definition television (SDTV). It is the standard video format used in most broadcasts: Terrestrial television, terrestrial broadcast television, cable television, satellite television. Formats HDTV may be transmitted in various formats: * 720p (): 921,600 pixels * 1080i () interlaced scan: 1,036,800 pixels (≈1.04Mpx). * 1080p () progressive scan: 2,073,600 pixels (≈2.07Mpx). ** Some countries also use a non-standard CTA resolution, such as : 777,600 pixels (≈0.78Mpx) per field or 1,555,200 pixels (≈1.56Mpx) per frame When transmitted at two megapixels per frame, HDTV provides about five times as many pixels as SD (standard-definition television). The increased resolution provides for a cl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
MPEG-4 AVC
Advanced Video Coding (AVC), also referred to as H.264 or MPEG-4 Part 10, is a video compression standard based on block-oriented, motion-compensated coding. It is by far the most commonly used format for the recording, compression, and distribution of video content, used by 84–86% of video industry developers . It supports a maximum resolution of 8K UHD. The intent of the H.264/AVC project was to create a standard capable of providing good video quality at substantially lower bit rates than previous standards (i.e., half or less the bit rate of MPEG-2, H.263, or MPEG-4 Part 2), without increasing the complexity of design so much that it would be impractical or excessively expensive to implement. This was achieved with features such as a reduced-complexity integer discrete cosine transform (integer DCT), variable block-size segmentation, and multi-picture inter-picture prediction. An additional goal was to provide enough flexibility to allow the standard to be appl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amplitude And Phase-shift Keying
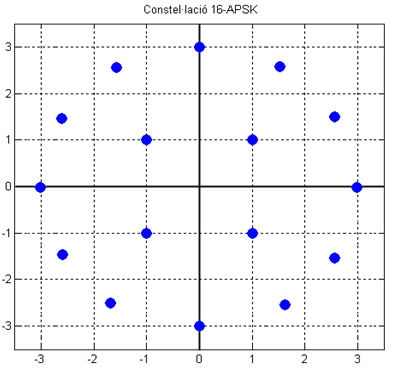
Amplitude and phase-shift keying (APSK) is a digital modulation scheme that conveys data by modulating both the amplitude and the phase of a carrier wave In telecommunications, a carrier wave, carrier signal, or just carrier, is a periodic waveform (usually sinusoidal) that conveys information through a process called ''modulation''. One or more of the wave's properties, such as amplitude or freq .... In other words, it combines both amplitude-shift keying (ASK) and phase-shift keying (PSK). This allows for a lower bit error rate for a given modulation order and signal-to-noise ratio, at the cost of increased complexity, compared to ASK or PSK alone. Quadrature amplitude modulation (QAM) can be considered a subset of APSK because all QAM schemes modulate both the amplitude and phase of the carrier. Conventionally, QAM constellations are rectangular and APSK constellations are circular, however this is not always the case. The distinction between the two is in their production ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
HDTV
High-definition television (HDTV) describes a television or video system which provides a substantially higher image resolution than the previous generation of technologies. The term has been used since at least 1933; in more recent times, it refers to the generation following standard-definition television (SDTV). It is the standard video format used in most broadcasts: Terrestrial television, terrestrial broadcast television, cable television, satellite television. Formats HDTV may be transmitted in various formats: * 720p (): 921,600 pixels * 1080i () interlaced scan: 1,036,800 pixels (≈1.04Mpx). * 1080p () progressive scan: 2,073,600 pixels (≈2.07Mpx). ** Some countries also use a non-standard CTA resolution, such as : 777,600 pixels (≈0.78Mpx) per field or 1,555,200 pixels (≈1.56Mpx) per frame When transmitted at two megapixels per frame, HDTV provides about five times as many pixels as SD (standard-definition television). The increased resolution provides for a cl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Backward Compatibility
In telecommunications and computing, backward compatibility (or backwards compatibility) is a property of an operating system, software, real-world product, or technology that allows for interoperability with an older legacy system, or with Input/output, input designed for such a system. Modifying a system in a way that does not allow backward compatibility is sometimes called "wikt:breaking change, breaking" backward compatibility. Such breaking usually incurs various types of costs, such as Switching barriers, switching cost. A complementary concept is ''forward compatibility''; a design that is forward-compatible usually has a Technology roadmap, roadmap for compatibility with future standards and products. Usage In hardware A simple example of both backward and forward compatibility is the introduction of FM broadcasting, FM radio in stereophonic sound, stereo. FM radio was initially monaural, mono, with only one audio channel represented by one signal (electrical engineerin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |