|
Tai Chi
is a Chinese martial art. Initially developed for combat and self-defense, for most practitioners it has evolved into a sport and form of exercise. As an exercise, tai chi is performed as gentle, low-impact movement in which practitioners perform a series of deliberate, flowing motions while focusing on deep, slow breaths. Often referred to as " meditation in motion", tai chi aims to concentrate and balance the body's purported (vital energy), providing benefits to mental and physical health. Many forms of tai chi are practiced, both traditional and modern. While the precise origins are not known, the earliest documented practice is from Chen Village and Zhabao Village in Henan on the North China Plain, a region where centuries of rebellions, invasions, and adverse economic and social conditions nurtured the development of a wide range of martial arts, including those of the Shaolin Monastery on Mount Song at the western edge of the plain. Most modern styles trace th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dantian
Dantian is a concept in traditional Chinese medicine loosely translated as "elixir field", "sea of '' qi''", or simply "energy center." Dantian are the "''qi'' focus flow centers," important focal points for meditative and exercise techniques such as qigong, martial arts such as tai chi, and in traditional Chinese medicine. Dantian is also now commonly understood to refer to the diaphragm in various Qigong practices and breath control techniques, such as diaphragmatic breathing for singing and speaking. Along with '' jing'' and '' shen'', it is considered one of the Three Treasures of traditional Chinese medicine. Overview Historically the first detailed description of the lower Dantian is in the '' Laozi zhongjing'' from the 3rd century CE, which refers to the elixir-of-life field where "essence" and "spirit" are stored; it is related to regeneration and sexual energy, menstruation and semen.Laozi zhongjing (Central Scripture of Laozi), sec. 17. Translation published in Fabri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yang Luchan
Yang Luchan ( zh, c=杨露禅, w=Yang Lu-ch'an, p=Yáng Lùchán), also known as Yang Fukui (1799–1872), was an influential Chinese practitioner and teacher of the internal style tai chi martial art. He is known as the founder of Yang-style tai chi, the most popular and widely practised tai chi style in the world today. History Yang Luchan's family was a poor farming/worker class from Hebei Province, Guangping Prefecture, Yongnian County. Yang would follow his father in planting the fields and, as a teenager, held temporary jobs. One period of temporary work was spent doing odd jobs at the Taihetang Chinese pharmacy located in the west part of Yongnian City, opened by Chen Dehu of the Chen Village in Huaiqing Prefecture, Wen County, Henan. As a child, Yang liked martial arts and studied Changquan, gaining a certain level of skill. One day Yang reportedly witnessed one of the partners of the pharmacy utilizing a style of martial art that he had never before seen to easily ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Henan
Henan; alternatively Honan is a province in Central China. Henan is home to many heritage sites, including Yinxu, the ruins of the final capital of the Shang dynasty () and the Shaolin Temple. Four of the historical capitals of China, Luoyang, Anyang, Kaifeng and Zhengzhou, are in Henan. While the province's name means 'south of the river', approximately a quarter of the province lies north of the Yellow River. With an area of , Henan covers a large part of the fertile and densely populated North China Plain. Its neighboring provinces are Shaanxi, Shanxi, Hebei, Shandong, Anhui, and Hubei. Henan is China's third-most populous province and the most populous among inland provinces, with a population of over 99 million as of 2020. It is also the world's seventh-most populous administrative division; if it were a country by itself, Henan would be the 17th-most populous in the world, behind Egypt and Vietnam. People from Henan often suffer from regional discrimination ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zhaobao Tai Chi
Zhaobao tai chi ( zh, c=趙堡太極拳, p=Zhàobǎo tàijíquán) is a style of tai chi that is often considered to be a modern style transmitted from Chen Qingping, but actually has a strong documented lineage that confirms its authenticity as an ancient style of tai chi and as a true transmission from Wang Zongyue. Form and Characteristics The main set of Zhaobao tai chi, or Zhaobao Jia, consists of 108 movements in the big frame and 75 refined movements in the small frame progressing in difficulty. Great emphasis is placed on ''Yi'' (mind/intent) in Zhaobao training. Like many other styles, Zhaobao Jia can be practiced at three heights, each providing a different degree of complexity. Generally students begin with the Middle Frame (Renpan Jia), progress to the Low Frame (Pangong Jia) and end with the High Frame (Daili Jia). Zhaobao tai chi's practical applications rely heavily on spiral uprooting techniques controlled through the use of '' Qinna'', often followed with the us ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chen-style Tai Chi
The Chen-style tai chi ( zh, s=陳氏太极拳, p=Chén shì tàijíquán) is a Northern Wushu (sport), Chinese martial art and the original form of tai chi. Chen (surname), Chen-style is characterized by silk reeling, alternating fast and slow motions, and bursts of power (''fa jin''). Traditionally, tai chi is practiced as a martial art but has expanded into other domains of practice such as health or performances. Some argue that Chen-style tai chi has preserved and emphasized the martial efficacy to a greater extent. History Origin theories It is not clear how the Chen family actually came to practise their unique martial style and contradictory "histories" abound. What is known is that the other four tai chi styles (Yang, Sun, Wu and Wu (Hao)) trace their teachings back to Chen village in the early 1800s. The Chen family were originally from Hongtong County in Shanxi. In the 13th or 14th century, later documents claim that the head of the Chen family, Chen Bu (), migra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Meditation
Meditation is a practice in which an individual uses a technique to train attention and awareness and detach from reflexive, "discursive thinking", achieving a mentally clear and emotionally calm and stable state, while not judging the meditation process itself. Techniques are broadly classified into focused (or concentrative) and open monitoring methods. Focused methods involve attention to specific objects like breath or mantras, while open monitoring includes mindfulness and awareness of mental events. Meditation is practiced in numerous religious traditions, though it is also practised independently from any religious or spiritual influences for its health benefits. The earliest records of meditation ('' dhyana'') are found in the Upanishads, and meditation plays a salient role in the contemplative repertoire of Jainism, Buddhism and Hinduism. Meditation-like techniques are also known in Judaism, Christianity and Islam, in the context of remembrance of and prayer and dev ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Exercise
Exercise or workout is physical activity that enhances or maintains fitness and overall health. It is performed for various reasons, including weight loss or maintenance, to aid growth and improve strength, develop muscles and the cardiovascular system, prevent injuries, hone athletic skills, improve health, or simply for enjoyment. Many people choose to exercise outdoors where they can congregate in groups, socialize, and improve well-being as well as mental health. In terms of health benefits, usually, 150 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise per week is recommended for reducing the risk of health problems. At the same time, even doing a small amount of exercise is healthier than doing none. Only doing an hour and a quarter (11 minutes/day) of exercise could reduce the risk of early death, cardiovascular disease, stroke, and cancer. Classification Physical exercises are generally grouped into three types, depending on the overall effect they have on the hum ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chinese Martial Art
Chinese martial arts, commonly referred to with umbrella terms Kung fu (term), kung fu (; ), kuoshu () or wushu (sport), wushu (), are Styles of Chinese martial arts, multiple fighting styles that have developed over the centuries in Greater China. These fighting styles are often classified according to common traits, identified as "families" of martial arts. Examples of such traits include ''Shaolin kung fu, Shaolinquan'' () physical exercises involving Five Animals, All Other Animals () mimicry or training methods inspired by Chinese philosophies, Old Chinese philosophies, religions and legends. Styles that focus on qi manipulation are called ''Internal martial arts, internal'' (; ), while others that concentrate on improving muscle and cardiovascular fitness are called ''Styles of Chinese martial arts#External styles, external'' (; ). Geographical associations, as in ''northern'' (; ) and ''Nanquan (martial art), southern'' (; ), is another popular classification method. Ter ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
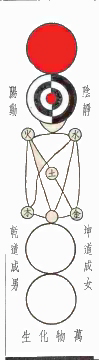
Taiji (philosophy)
In Chinese philosophy, ''taiji'' () is a cosmological state of the universe and its affairs on all levels—including the mutually reinforcing interactions between the two opposing forces of yin and yang (a dualistic monism), as well as that among the Three Treasures, the four cardinal directions, and the Five Elements—which together ultimately bring about the myriad things, each with their own nature. The concept of ''taiji'' has reappeared throughout the technological, religious, and philosophical history of the Sinosphere, finding concrete application in techniques developed in acupuncture and traditional Chinese medicine. Etymology ''Taiji'' () is a compound of ''tai'' ( 'great', 'supreme') and ''ji'' ( 'pole', 'extremity'). Used together, ''taiji'' may be understood as 'source of the world'. Common English translations of ''taiji'' in the cosmological sense include "Supreme Ultimate", "Supreme Pole", and "Great Absolute". Core concept Scholars Zhang and Ryden e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Demonstration Sport
A demonstration sport, or exhibition sport, is a sport which is played to promote it, rather than as part of standard medal competition. This occurs commonly during the Olympic Games but may also occur at other sporting events. Demonstration sports were officially introduced in the 1924 Summer Olympics, though some scholars consider unofficial sports prior to 1924 to also be demonstrations. Most organizing committees then decided to include at least one demonstration sport at each edition of the Games, usually some typical or popular sport in the host country, like baseball at the 1984 Los Angeles Olympic Games and taekwondo at the 1988 Seoul Olympic Games. From 1924 to 1992, only two Summer Olympics Games did not have demonstration sports on their program. Some demonstration sports eventually gained enough popularity to become an official sport in a subsequent edition of the Games. Traditionally, the medals awarded for the demonstration events followed the same design as the Ol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sun Lutang
Sun Lutang (1860-1933) was a master of Chinese ''neijia'' (internal) martial arts and was the progenitor of the Syncretism, syncretic art of Sun-style tai chi. He was also considered an accomplished Neo-Confucian and Taoist scholar (especially of the ''I Ching''), and was a distinguished contributor to the theory of internal martial arts through his many published works. Biography He was born in Hebei and was named Sun Fuquan () by his parents. Years later, his ''baguazhang'' teacher Cheng Tinghua gave him the name Sun Lutang. (It was common in old China for people to have multiple Chinese name, names, through various phases of life). He continued to use his original name in some areas, including the publishing of his books. He was also well-versed in two other neijia, internal martial arts: ''xingyiquan'' and ''baguazhang'' before he came to study tai chi. His expertise in these two martial arts were so high that many regarded him as without equal. Sun learned Wu (Hao)-s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wu Yuxiang
Wu Yuxiang (Wu Yu-hsiang, 1812?–1880?) was a Chinese martial artist, teacher and the founder of Wu (Hao)-style tai chi. Wu was a scholar from a wealthy and influential family who became a senior student of Yang Luchan, the founder of Yang-style tai chi. Wu also studied for a brief time with Chen Qingping, a master of Chen-style and Zhaobao-style tai chi. There is a relatively large body of writing attributed to Wu on the subject of tai chi theory, writings that are considered influential by other tai chi styles were the source of what are now known as the tai chi classics. Wu developed his own style of tai chi and shared it with members of his family, who also wrote about the art. He trained with his two older brothers Wu Chengqing (武澄清, 1800-1884)) and Wu Ruqing (武汝清, 1803-1887), and took on two nephews as disciples. One of those nephews Li Yiyu (Li I-yu, 李亦畬, 1832–1892), authored several particularly important works on tai chi. The other nephew, L ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |