|
Neon
Neon is a chemical element; it has symbol Ne and atomic number 10. It is the second noble gas in the periodic table. Neon is a colorless, odorless, inert monatomic gas under standard conditions, with approximately two-thirds the density of air. Neon was discovered in 1898 alongside krypton and xenon, identified as one of the three remaining rare inert elements in dry air after the removal of nitrogen, oxygen, argon, and carbon dioxide. Its discovery was marked by the distinctive bright red emission spectrum it exhibited, leading to its immediate recognition as a new element. The name ''neon'' originates from the Greek word , a neuter singular form of (), meaning 'new'. Neon is a chemically inert gas; although neon compounds do exist, they are primarily ionic molecules or fragile molecules held together by van der Waals forces. The synthesis of most neon in the cosmos resulted from the nuclear fusion within stars of oxygen and helium through the alpha-capture proce ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
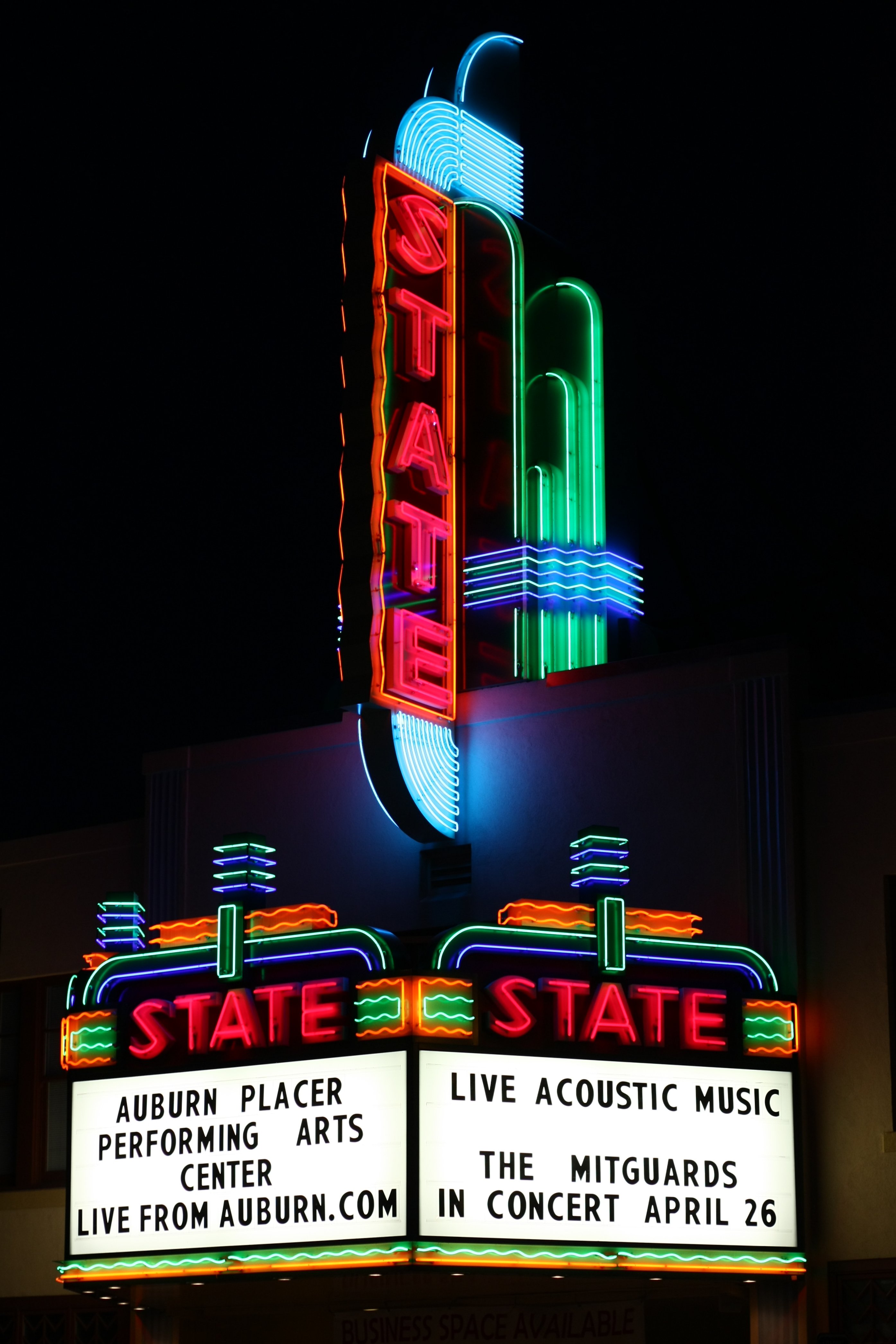
Neon Sign
In the signage industry, neon signs are electric signs lighted by long luminous gas-discharge tubes that contain rarefied neon or other gases. They are the most common use for neon lighting, which was first demonstrated in a modern form in December 1910 by Georges Claude at the Paris Motor Show. While they are used worldwide, neon signs were popular in the United States from about the 1920s to 1950s. The installations in Times Square, many originally designed by Douglas Leigh, were famed, and there were nearly 2,000 small shops producing neon signs by 1940. Pages 221–223 describe Moore tubes. Pages 369–374 describe neon tube lighting. Page 385 discusses Risler's contributions to fluorescent coatings in the 1920s. Pages 388–391 discuss the development of the commercial fluorescent at General Electric in the 1930s. In addition to signage, neon lighting is used frequently by artists and architects, and (in a modified form) in plasma display panels and televisions. Paid acce ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neon Compounds
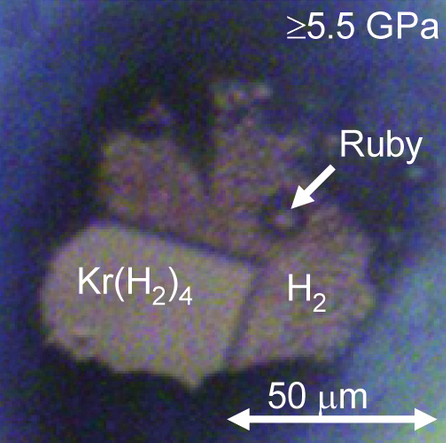
Neon compounds are chemical compounds containing the element neon (Ne) with other molecules or elements from the periodic table. Compounds of the noble gas neon were believed not to exist, but there are now known to be molecular ions containing neon, as well as temporary excited neon-containing molecules called excimers. Several neutral neon molecules have also been predicted to be stable, but are yet to be discovered in nature. Neon has been shown to crystallize with other substances and form clathrates or Van der Waals solids. Neon has a high first ionization potential of 21.564 eV, which is only exceeded by that of helium (24.587 eV), requiring too much energy to make stable ionic compounds. Neon's polarisability of 0.395 Å3 is the second lowest of any element (only helium's is more extreme). Low polarisability means there will be little tendency to link to other atoms. Neon has a Lewis basicity or proton affinity of 2.06 eV. Neon is theoretically less reactive ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
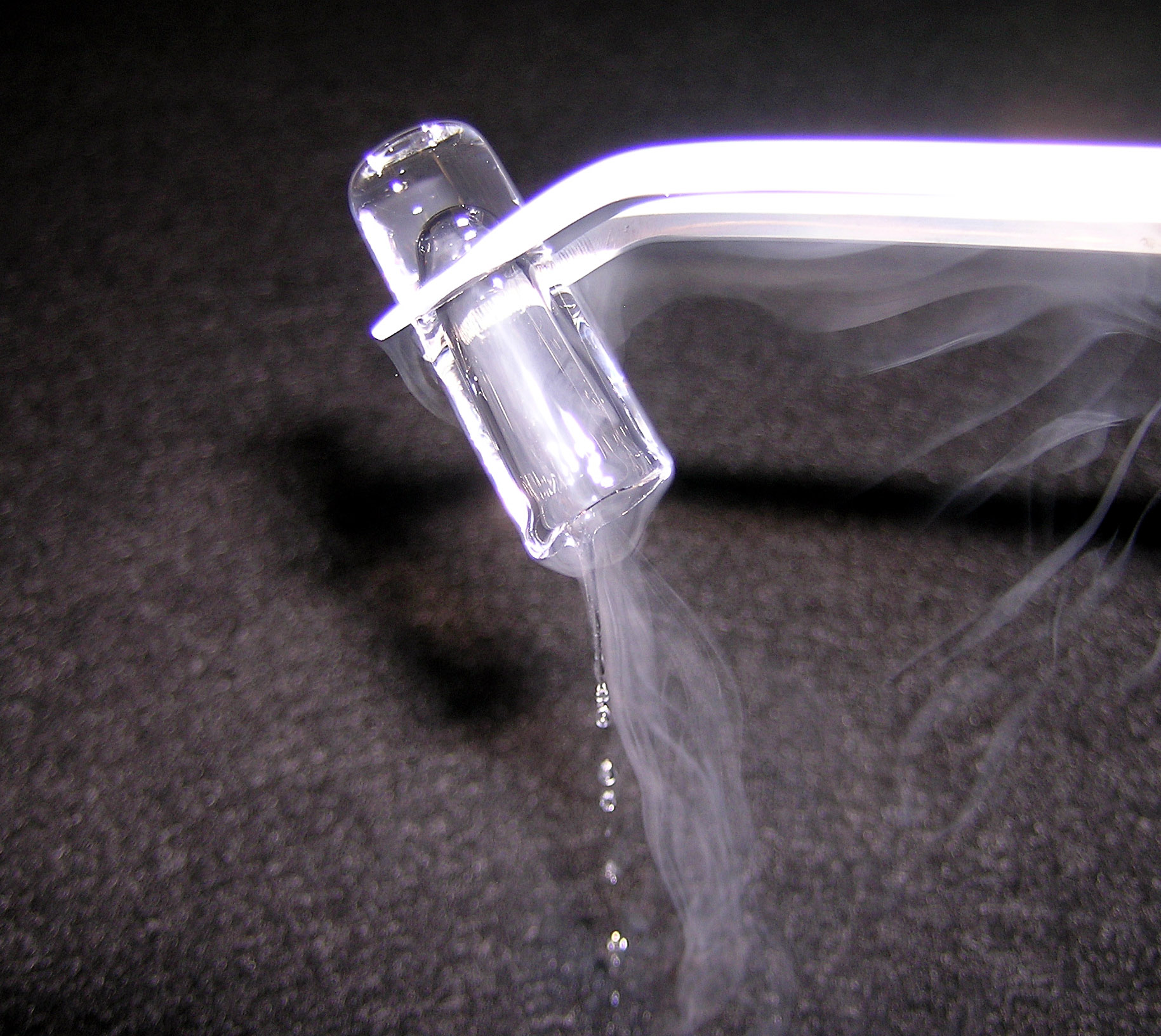
Neon Glow Lamp
A neon lamp (also neon glow lamp) is a miniature gas-discharge lamp. The lamp typically consists of a small glass capsule that contains a mixture of neon and other gases at a low pressure and two electrodes (an anode and a cathode). When sufficient voltage is applied and sufficient current is supplied between the electrodes, the lamp produces an orange glow discharge. The glowing portion in the lamp is a thin region near the cathode; the larger and much longer neon signs are also glow discharges, but they use the positive column which is not present in the ordinary neon lamp. Neon glow lamps were widely used as indicator lamps in the displays of electronic instruments and appliances. They are still sometimes used for their electrical simplicity in high-voltage circuits. History Neon was discovered in 1898 by William Ramsay and Morris Travers. The characteristic, brilliant red color that is emitted by gaseous neon when excited electrically was noted immediately; Travers la ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Noble Gas
The noble gases (historically the inert gases, sometimes referred to as aerogens) are the members of Group (periodic table), group 18 of the periodic table: helium (He), neon (Ne), argon (Ar), krypton (Kr), xenon (Xe), radon (Rn) and, in some cases, oganesson (Og). Under Standard temperature and pressure, standard conditions, the first six of these Chemical element, elements are odorless, colorless, monatomic gases with very low chemical reactivity and cryogenics, cryogenic boiling points. The properties of oganesson are uncertain. The intermolecular force between noble gas atoms is the very weak London dispersion force, so their boiling points are all cryogenic, below . The noble gases' Chemically inert, inertness, or tendency not to Chemical reaction, react with other chemical substances, results from their electron configuration: their Electron shell, outer shell of valence electrons is "full", giving them little tendency to participate in chemical reactions. Only a few hun ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Helium–neon Laser
A helium–neon laser or He–Ne laser is a type of gas laser whose high energetic gain medium consists of a mixture of helium and neon (ratio between 5:1 and 10:1) at a total pressure of approximately 1 Torr (133.322 Pa) inside a small electrical discharge. The best-known and most widely used He-Ne laser operates at a center wavelength of 632.81646 nm (in air), 632.99138 nm (vac), and frequency 473.6122 THz, in the red part of the visible spectrum. Because of the mode structure of the laser cavity, the instantaneous output of a laser can be shifted by up to 500 MHz in either direction from the center. History of He-Ne laser development The first He-Ne lasers emitted infrared at 1150 nm, and were the first gas lasers and the first lasers with continuous wave output. However, a laser that operated at visible wavelengths was much more in demand. A number of other neon transitions were investigated to identify ones in which a population inversion could be achi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Helium
Helium (from ) is a chemical element; it has chemical symbol, symbol He and atomic number 2. It is a colorless, odorless, non-toxic, inert gas, inert, monatomic gas and the first in the noble gas group in the periodic table. Its boiling point is the lowest among all the Chemical element, elements, and it does not have a melting point at standard pressures. It is the second-lightest and second-most Abundance of the chemical elements, abundant element in the observable universe, after hydrogen. It is present at about 24% of the total elemental mass, which is more than 12 times the mass of all the heavier elements combined. Its abundance is similar to this in both the Sun and Jupiter, because of the very high nuclear binding energy (per nucleon) of helium-4 with respect to the next three elements after helium. This helium-4 binding energy also accounts for why it is a product of both nuclear fusion and radioactive decay. The most common isotope of helium in the universe is helium-4, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Xenon
Xenon is a chemical element; it has symbol Xe and atomic number 54. It is a dense, colorless, odorless noble gas found in Earth's atmosphere in trace amounts. Although generally unreactive, it can undergo a few chemical reactions such as the formation of xenon hexafluoroplatinate, the first noble gas compound to be synthesized. Xenon is used in flash lamps and arc lamps, and as a general anesthetic. The first excimer laser design used a xenon dimer molecule (Xe2) as the lasing medium, and the earliest laser designs used xenon flash lamps as pumps. Xenon is also used to search for hypothetical weakly interacting massive particles and as a propellant for ion thrusters in spacecraft. Naturally occurring xenon consists of seven stable isotopes and two long-lived radioactive isotopes. More than 40 unstable xenon isotopes undergo radioactive decay, and the isotope ratios of xenon are an important tool for studying the early history of the Solar System. Radioactive xe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
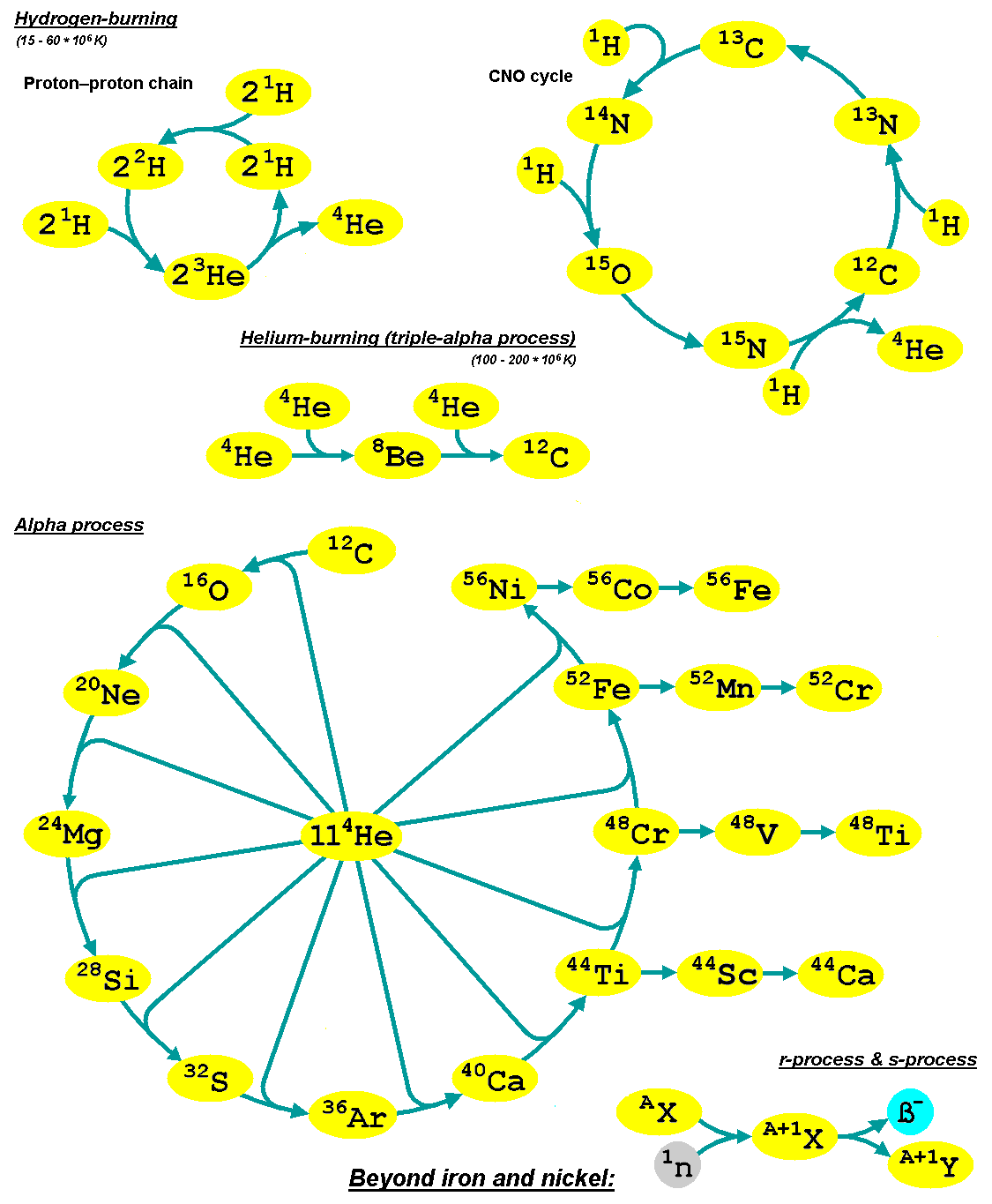
Alpha Process
The alpha process, also known as alpha capture or the alpha ladder, is one of two classes of nuclear fusion reactions by which stars convert helium into heavier elements. The other class is a cycle of reactions called the triple-alpha process, which consumes only helium, and produces carbon. The alpha process most commonly occurs in massive stars and during supernovae. Both processes are preceded by hydrogen fusion, which produces the helium that fuels both the triple-alpha process and the alpha ladder processes. After the triple-alpha process has produced enough carbon, the alpha-ladder begins and fusion reactions of increasingly heavy elements take place, in the order listed below. Each step only consumes the product of the previous reaction and helium. The later-stage reactions which are able to begin in any particular star, do so while the prior stage reactions are still under way in outer layers of the star. :\begin \ce& E=\mathsf \\ \ce& E=\mathsf \\ \ce& E=\mathsf \\ \c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Krypton
Krypton (from 'the hidden one') is a chemical element; it has symbol (chemistry), symbol Kr and atomic number 36. It is a colorless, odorless noble gas that occurs in trace element, trace amounts in the Earth's atmosphere, atmosphere and is often used with other rare gases in fluorescent lamps. Krypton is chemically inert. Krypton, like the other noble gases, is used in lighting and photography. Krypton light has many spectral lines, and krypton Plasma (physics), plasma is useful in bright, high-powered gas lasers (krypton ion laser, ion and excimer laser, excimer lasers), each of which resonates and amplifies a single spectral line. krypton fluoride laser, Krypton fluoride also makes a useful laser medium. From 1960 to 1983, the history of the metre#Krypton standard, official definition of the metre was based on the wavelength of one spectral line of krypton-86, because of the high power and relative ease of operation of krypton discharge tubes. History Krypton was discovere ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geissler Tube
A Geissler tube is a precursor to modern gas discharge tubes, demonstrating the principles of electrical glow discharge, akin to contemporary neon lights, and central to the discovery of the electron. This device was developed in 1857 by Heinrich Geissler, a German physicist and glassblower. A Geissler tube is composed of a sealed glass cylinder of various shapes, which is partially evacuated and equipped with a metal electrode at each end. It contains rarefied gases—such as neon or argon, air, mercury vapor, or other conductive substances, and sometimes ionizable minerals or metals like sodium. When a high voltage is applied between the electrodes, there is an electric current through the tube, causing gas molecules to ionize by shedding electrons. The free electrons reunite with the ions and the resulting energic atoms emit light via fluorescence, with the emitted color characteristic of the contained material. Colorful decorative Geissler tubes were made in many art ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Monatomic Gas
In physics and chemistry, "monatomic" is a combination of the words "mono" and "atomic", and means "single atom". It is usually applied to gases: a monatomic gas is a gas in which atoms are not bound to each other. Examples at standard conditions of temperature and pressure include all the noble gases (helium, neon, argon, krypton, xenon, and radon), though all chemical elements will be monatomic in the gas phase at sufficiently high temperature (or very low pressure). The thermodynamic behavior of a monatomic gas is much simpler when compared to polyatomic gases because it is free of any rotational or vibrational energy. Noble gases The only chemical elements that are stable single atoms (so they are not molecules) at standard temperature and pressure (STP) are the noble gases. These are helium, neon, argon, krypton, xenon, and radon. Noble gases have a full outer valence shell making them rather non-reactive species. While these elements have been described historically as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Argon
Argon is a chemical element; it has symbol Ar and atomic number 18. It is in group 18 of the periodic table and is a noble gas. Argon is the third most abundant gas in Earth's atmosphere, at 0.934% (9340 ppmv). It is more than twice as abundant as water vapor (which averages about 4000 ppmv, but varies greatly), 23 times as abundant as carbon dioxide (400 ppmv), and more than 500 times as abundant as neon (18 ppmv). Argon is the most abundant noble gas in Earth's crust, comprising 0.00015% of the crust. Nearly all argon in Earth's atmosphere is radiogenic argon-40, derived from the decay of potassium-40 in Earth's crust. In the universe, argon-36 is by far the most common argon isotope, as it is the most easily produced by stellar nucleosynthesis in supernovas. The name "argon" is derived from the Greek word , neuter singular form of meaning 'lazy' or 'inactive', as a reference to the fact that the element undergoes almost no chemical reactions. The complete oc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |