|
Cîteaux Abbey
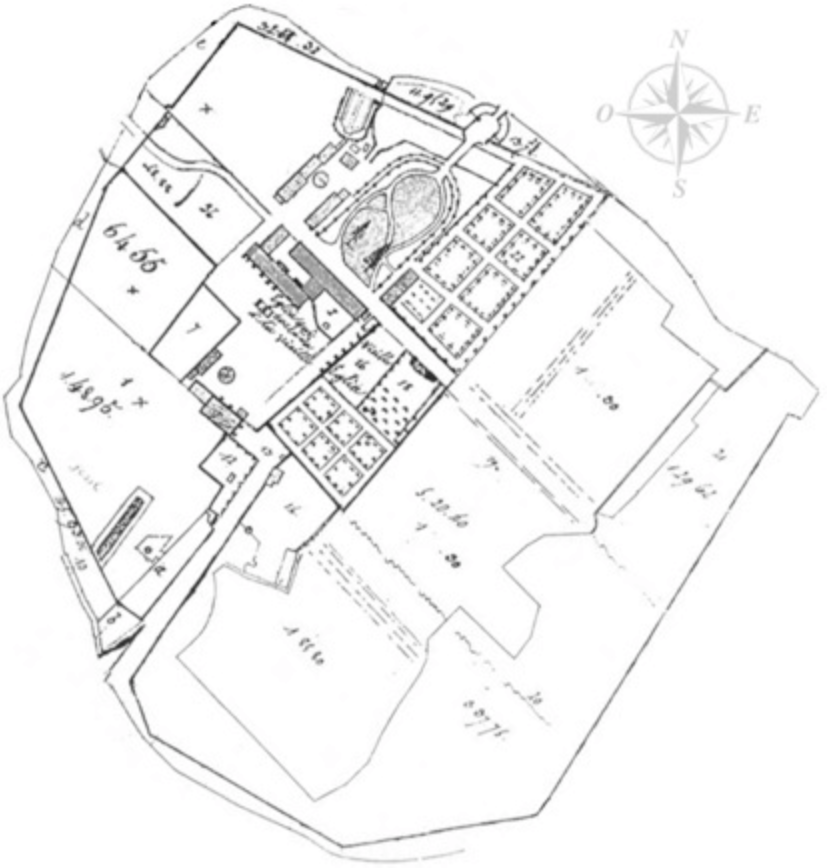
Cîteaux Abbey (french: Abbaye de Cîteaux, links=no ) is a Catholic abbey located in Saint-Nicolas-lès-Cîteaux, south of Dijon, France. It is notable for being the original house of the Cistercian order. Today, it belongs to the Trappists (also called the Cistercians of the Strict Observance). The abbey has about 35 members. The monks produce a cheese branded under the abbey's name, as well as caramels and honey-based candies. History Cîteaux Abbey was founded on Saint Benedict's Day, 21 March 1098, by a group of monks from Molesme Abbey seeking to follow more closely the Rule of St. Benedict. The Abbey was supported by Renaud, Vicomte de Beaune, and Odo I, Duke of Burgundy. They were led by Saint Robert of Molesme, who became the first abbot. The site was wooded and swampy, in a sparsely populated area. The toponym predates the abbey, but its origin is uncertain. Theories include a derivation from ''cis tertium'' 'lapidem miliarium'' "this side of the third ilestone ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Abbaye De Cîteaux La Bibliothèque
An abbey is a type of monastery used by members of a religious order under the governance of an abbot or abbess. Abbeys provide a complex of buildings and land for religious activities, work, and housing of Christian monks and nuns. The concept of the abbey has developed over many centuries from the early monastic ways of religious men and women where they would live isolated from the lay community about them. Religious life in an abbey may be monastic. An abbey may be the home of an enclosed religious order or may be open to visitors. The layout of the church and associated buildings of an abbey often follows a set plan determined by the founding religious order. Abbeys are often self-sufficient while using any abundance of produce or skill to provide care to the poor and needy, refuge to the persecuted, or education to the young. Some abbeys offer accommodation to people who are seeking spiritual retreat. There are many famous abbeys across the Mediterranean Basin and Europe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alberic Of Cîteaux
Alberic of Cîteaux (died 26 January 1109), sometimes known as Aubrey of Cîteaux, was a French monk and abbot, one of the founders of the Cistercian Order. He is now honored as a saint. Life Alberic was a hermit in the forest of Collan in France who, along with five other hermits, invited Abbot Robert of Molesme to begin a new monastery with them that would operate under the Rule of St. Benedict. Robert led these hermits to the forest of Molesme and established a religious settlement there in 1075, Molesme Abbey. Robert served as the first abbot, and Alberic as the prior. However, as the settlement's fame grew, gifts came in and the wealth attracted new monks more lax in their observance of the rule. The Molesme community was divided, and the monks opposed Robert and Alberic. Robert twice left the monastery to live as a hermit, and twice the pope ordered him back to his community. During one of Robert's absences, the brothers imprisoned Alberic so that they might have their ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
French Wars Of Religion
The French Wars of Religion is the term which is used in reference to a period of civil war between French Catholics and Protestants, commonly called Huguenots, which lasted from 1562 to 1598. According to estimates, between two and four million people died from violence, famine or diseases which were directly caused by the conflict; additionally, the conflict severely damaged the power of the French monarchy. The fighting ended in 1598 when Henry of Navarre, who had converted to Catholicism in 1593, was proclaimed Henry IV of France and issued the Edict of Nantes, which granted substantial rights and freedoms to the Huguenots. However, the Catholics continued to have a hostile opinion of Protestants in general and they also continued to have a hostile opinion of him as a person, and his assassination in 1610 triggered a fresh round of Huguenot rebellions in the 1620s. Tensions between the two religions had been building since the 1530s, exacerbating existing regional divisi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Marchenoir
Marchenoir () is a commune in the Loir-et-Cher department of central France. The nearby forest of Marchenoir was the site of L'Aumône Abbey, a Cistercian daughter house of Cîteaux Abbey. The Earl of Buckingham The peerage title Earl of Buckingham was created several times in the Peerage of England. It is not to be confused with the title of Earl of Buckinghamshire. It was first created in 1097 for Walter Giffard, but became extinct in 1164 with the d ... stayed at the Abbey in 1380 whilst his army was quartered in the Forest. History In 1650 Claude Pajon was appointed to be pastor to the Reformed Church at Marchenoir. * The husband and wife comedians Raymond Bussières and Annette Poivre are buried in the Marchenoir cemetery. Population See also *Communes of the Loir-et-Cher department References Communes of Loir-et-Cher {{LoirCher-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
L'Aumône Abbey
L’Aumône Abbey (french: Abbaye Notre-Dame de l’Aumône, la, Eleemosynae; also known as french: Petit-Cîteaux, la, Cistercium minus) is a former Cistercian monastery in the commune of La Colombe, Loir-et-Cher, France, 34 kilometres north of Blois in the Forêt de Cîteaux, part of the Forêt de Marchenoir. History The abbey was founded in 1121, thanks to a gift from Count Theobald IV of Blois, as the seventh daughter house of Cîteaux Abbey. It became the mother house of 29 abbeys, including Waverley Abbey in England (the first Cistercian foundation in the British Isles), Bégard Abbey, Tintern Abbey, Langonnet Abbey and Le Landais Abbey. The abbey suffered greatly during the Hundred Years' War and by 1396 lay mostly in ruins. The subsequent reconstruction and the introduction of commendatory abbots proved a serious burden. The abbey was suppressed in 1791 during the French Revolution. The land was sold in 1818 and the debris from the ruins was used as building materia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thomas Of Woodstock, 1st Duke Of Gloucester
Thomas of Woodstock, 1st Duke of Gloucester (7 January 13558 or 9 September 1397) was the fifth surviving son and youngest child of King Edward III of England and Philippa of Hainault. Early life Thomas was born on 7 January 1355 at Woodstock Palace in Oxfordshire after two short-lived brothers, one of whom had also been baptised Thomas. He married Eleanor de Bohun in 1374, was given Pleshey Castle in Essex, and was appointed Constable of the Realm, a position previously held by the Bohuns. The younger sister of Woodstock's wife, Mary de Bohun, was subsequently married to Henry of Bolingbroke, Earl of Derby, who later became King Henry IV of England. In 1377, at the age of 22, Woodstock was knighted and created Earl of Buckingham. On 22 June 1380 he became Earl of Essex in right of his wife. In 1385, he received the title Duke of Aumale, and at about the same time was created Duke of Gloucester. Campaign in Brittany Thomas of Woodstock was in command of a large campa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hundred Years' War
The Hundred Years' War (; 1337–1453) was a series of armed conflicts between the kingdoms of England and France during the Late Middle Ages. It originated from disputed claims to the French throne between the English House of Plantagenet and the French royal House of Valois. Over time, the war grew into a broader power struggle involving factions from across Western Europe, fuelled by emerging nationalism on both sides. The Hundred Years' War was one of the most significant conflicts of the Middle Ages. For 116 years, interrupted by several truces, five generations of kings from two rival dynasties fought for the throne of the dominant kingdom in Western Europe. The war's effect on European history was lasting. Both sides produced innovations in military technology and tactics, including professional standing armies and artillery, that permanently changed warfare in Europe; chivalry, which had reached its height during the conflict, subsequently declined. Stronge ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Blanche Of Castile
Blanche of Castile ( es, Blanca de Castilla; 4 March 1188 – 27 November 1252) was Queen of France by marriage to Louis VIII. She acted as regent twice during the reign of her son, Louis IX: during his minority from 1226 until 1234, and during his absence from 1248 until 1252. She was born in Palencia, Spain, in 1188, the third daughter of Alfonso VIII, King of Castile, and Eleanor of England, sister of King Richard I of England and King John of England. Early life In her youth, she visited the Abbey of Santa María la Real de Las Huelgas, founded by her parents, several times. In consequence of the Treaty of Le Goulet between Philip Augustus and John of England, Blanche's sister, Urraca, was betrothed to Philip's son, Louis. After meeting the two sisters, their grandmother Eleanor of Aquitaine (who had been a queen consort of France herself) judged that Blanche's personality was more fit to fulfil the role. In the spring of 1200, Eleanor crossed the Pyrenees with her an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Louis IX Of France
Louis IX (25 April 1214 – 25 August 1270), commonly known as Saint Louis or Louis the Saint, was King of France from 1226 to 1270, and the most illustrious of the Direct Capetians. He was crowned in Reims at the age of 12, following the death of his father Louis VIII. His mother, Blanche of Castile, ruled the kingdom as regent until he reached maturity, and then remained his valued adviser until her death. During Louis' childhood, Blanche dealt with the opposition of rebellious vassals and secured Capetian success in the Albigensian Crusade, which had started 20 years earlier. As an adult, Louis IX faced recurring conflicts with some of his realm's most powerful nobles, such as Hugh X of Lusignan and Peter of Dreux. Simultaneously, Henry III of England attempted to restore the Angevin continental possessions, but was promptly routed at the Battle of Taillebourg. Louis annexed several provinces, notably parts of Aquitaine, Maine and Provence. Louis IX enjoyed immense pre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dukes Of Burgundy
Duke of Burgundy (french: duc de Bourgogne) was a title used by the rulers of the Duchy of Burgundy, from its establishment in 843 to its annexation by France in 1477, and later by Holy Roman Emperors and Kings of Spain from the House of Habsburg who claimed Burgundy proper and ruled the Burgundian inheritance in the Low Countries. The Duchy of Burgundy was a small portion of the traditional lands of the Burgundians west of the river Saône which, in 843, was allotted to Charles the Bald's kingdom of West Franks. Under the Ancien Régime, the Duke of Burgundy was the premier lay peer of the kingdom of France. Beginning with Robert II of France, the title was held by the Capetians, the French royal family. It was granted to Robert's younger son, Robert, who founded the House of Burgundy. When the senior line of the House of Burgundy became extinct, it was inherited by John II of France through proximity of blood. John granted the duchy to his younger son, Philip the Bold. The Va ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Clairvaux Abbey
Clairvaux Abbey (, ; la, Clara Vallis) was a Cistercian monastery in Ville-sous-la-Ferté, from Bar-sur-Aube. The original building, founded in 1115 by St. Bernard, is now in ruins; the present structure dates from 1708. Clairvaux Abbey was a good example of the general layout of a Cistercian monastery. The abbey has been listed since 1926 as a historical monument by the French Ministry of Culture. The grounds are now occupied and used by Clairvaux Prison, a high-security prison. History In 1115 Bernard, a Benedictine monk of the Abbaye de Saint-Nicolas-lès-Cîteaux, was sent with a group of twelve other monks to found a new house at Vallée d'Absinthe. Hughes I, Count of Troyes, donated this valley to the colony of Cistercians.Gildas, Marie. "Abbey of Clairvaux." The Catholic Encyclopedia [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Doctor Of The Church
Doctor of the Church (Latin: ''doctor'' "teacher"), also referred to as Doctor of the Universal Church (Latin: ''Doctor Ecclesiae Universalis''), is a title given by the Catholic Church to saints recognized as having made a significant contribution to theology or doctrine through their research, study, or writing. , the Catholic Church has named 37 Doctors of the Church. Of these, the 18 who died before the Great Schism of 1054 are also held in high esteem by the Eastern Orthodox Church, although it does not use the formal title "Doctor of the Church". Among the 37 recognised Doctors, 28 are from the West and nine from the East; four are women and thirty-three are men; one abbess, three nuns, one tertiary associated with a religious order; 19 bishops, twelve priests, one deacon; 27 from Europe, three from Africa, and seven from Asia. More Doctors (twelve) lived in the fourth century than any other; eminent Christian writers of the first, second, and third centuries are usually ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |