|
Curtiss Model 17
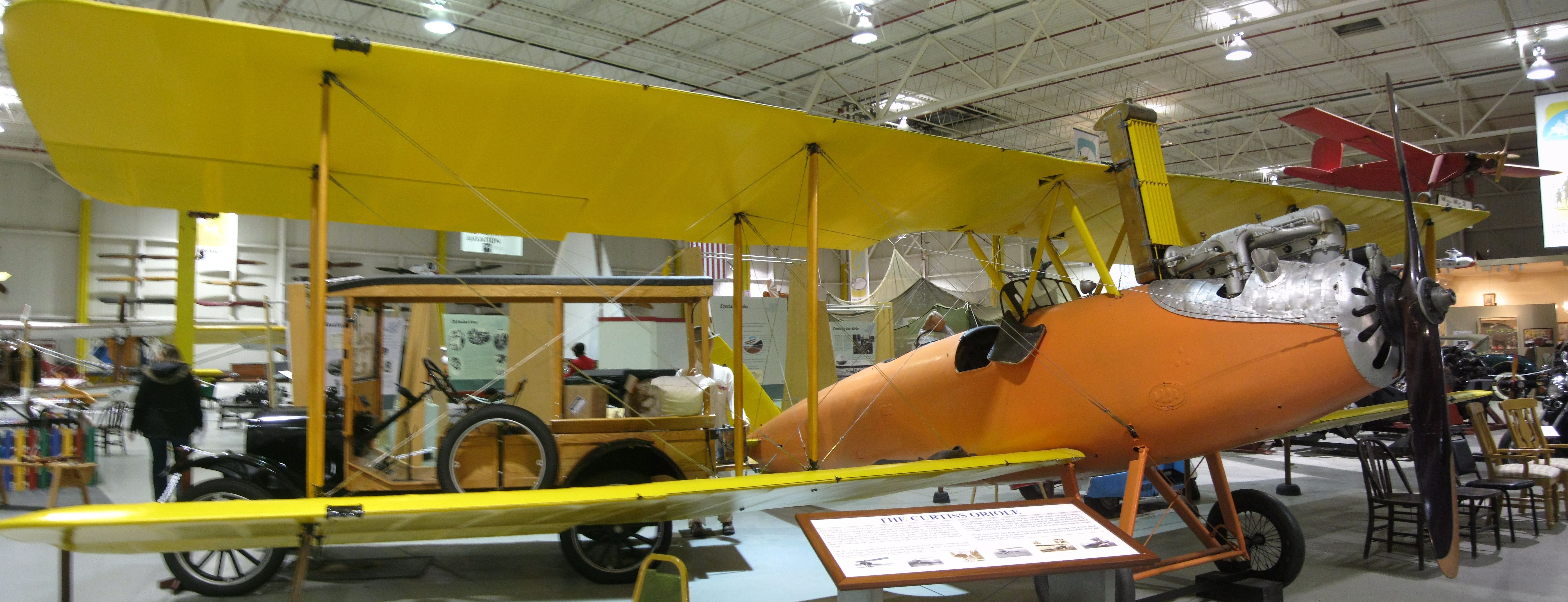
The Curtiss Oriole (Curtiss Model 17) was an American three-seat general-purpose biplane. Design The Oriole fuselage was constructed using laminated wood to form a monocoque body and was powered by either the Curtiss OX-5 V-8 or the Curtiss K-6 engine. The aircraft featured a self-starter and a tall thin radiator in the pilot's field of view. Operational history Surplus Curtiss Oriole wings were sold to Harold Pitcairn to manufacture the first production Pitcairn aircraft, the Pitcairn PA-3 Orowing. Northwest Airlines was founded on August 1, 1926, flying a Curtiss Oriole and a Thomas Morse Biplane on the CAM-9 Airmail route from Minneapolis to Chicago. Admiral Byrd selected a Curtiss Oriole as second aircraft for his 1926 Arctic Expedition to the North Pole with a Fokker F.VII. The Oriole was planned to be used for photography and rescue work. The New York times reported (falsely) that the Oriole was shipped on the steamer Chantier in case the Fokker was unavailable. However ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
WikiProject Aircraft
A WikiProject, or Wikiproject, is an affinity group for contributors with shared goals within the Wikimedia movement. WikiProjects are prevalent within the largest wiki, Wikipedia, and exist to varying degrees within Wikimedia project, sibling projects such as Wiktionary, Wikiquote, Wikidata, and Wikisource. They also exist in different languages, and translation of articles is a form of their collaboration. During the COVID-19 pandemic, CBS News noted the role of Wikipedia's WikiProject Medicine in maintaining the accuracy of articles related to the disease. Another WikiProject that has drawn attention is WikiProject Women Scientists, which was profiled by ''Smithsonian Magazine, Smithsonian'' for its efforts to improve coverage of women scientists which the profile noted had "helped increase the number of female scientists on Wikipedia from around 1,600 to over 5,000". On Wikipedia Some Wikipedia WikiProjects are substantial enough to engage in cooperative activities with outsi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Curtiss Museum Oriole
The Curtiss Aeroplane and Motor Company (1909–1929) was an American aircraft manufacturer originally founded by Glenn Hammond Curtiss and Augustus Moore Herring in Hammondsport, New York. After significant commercial success in its first decades, it merged with the Wright Aeronautical to form Curtiss-Wright Corporation. History Origin In 1907, Glenn Curtiss was recruited by the scientist Dr. Alexander Graham Bell as a founding member of Bell's Aerial Experiment Association (AEA), with the intent of establishing an aeronautical research and development organization. According to Bell, it was a "co-operative scientific association, not for gain but for the love of the art and doing what we can to help one another."Milberry 1979, p 13. In 1909, shortly before the AEA was disbanded, Curtiss partnered with Augustus Moore Herring to form the Herring-Curtiss Company.Gunston 1993, p. 87. It was renamed the Curtiss Aeroplane Company in 1910 and reorganized in 1912 after being ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Curtiss Aircraft
The Curtiss Aeroplane and Motor Company (1909–1929) was an American aircraft manufacturer originally founded by Glenn Hammond Curtiss and Augustus Moore Herring in Hammondsport, New York. After significant commercial success in its first decades, it merged with the Wright Aeronautical to form Curtiss-Wright Corporation. History Origin In 1907, Glenn Curtiss was recruited by the scientist Dr. Alexander Graham Bell as a founding member of Bell's Aerial Experiment Association (AEA), with the intent of establishing an aeronautical research and development organization. According to Bell, it was a "co-operative scientific association, not for gain but for the love of the art and doing what we can to help one another."Milberry 1979, p 13. In 1909, shortly before the AEA was disbanded, Curtiss partnered with Augustus Moore Herring to form the Herring-Curtiss Company.Gunston 1993, p. 87. It was renamed the Curtiss Aeroplane Company in 1910 and reorganized in 1912 after being ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1920s United States Civil Utility Aircraft
Nineteen or 19 may refer to: * 19 (number) * One of the years 19 BC, AD 19, 1919, 2019 Films * ''19'' (film), a 2001 Japanese film * ''Nineteen'' (1987 film), a 1987 science fiction film * '' 19-Nineteen'', a 2009 South Korean film * '' Diciannove'', a 2024 Italian drama film informally referred to as "Nineteen" in some sources Science * Potassium, an alkali metal * 19 Fortuna, an asteroid Music * 19 (band), a Japanese pop music duo Albums * ''19'' (Adele album), 2008 * ''19'', a 2003 album by Alsou * ''19'', a 2006 album by Evan Yo * ''19'', a 2018 album by MHD * ''19'', one half of the double album '' 63/19'' by Kool A.D. * ''Number Nineteen'', a 1971 album by American jazz pianist Mal Waldron * ''XIX'' (EP), a 2019 EP by 1the9 Songs * "19" (song), a 1985 song by British musician Paul Hardcastle * "Stone in Focus", officially "#19", a composition by Aphex Twin * "Nineteen", a song from the 1992 album ''Refugee'' by Bad4Good * "Nineteen", a song from the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Air Enthusiast
''Air Enthusiast'' was a British, bi-monthly, aviation magazine, published by the Key Publishing group. Initially begun in 1974 as ''Air Enthusiast Quarterly'', the magazine was conceived as a historical adjunct to ''Air International'' magazine. ''Air International'' was (and remains) involved with current aviation topics and the ''Quarterly'' concerned itself with historical matters. Each issue contained 80 pages; as a result certain articles were divided and each part appeared over a number of issues. ''Air Enthusiast'' was illustrated with colour and black-and-white photos, diagrams, profiles and three-view drawings. Earlier issues featured cutaway drawings, but these were dropped. The articles provided detail for varieties of aircraft and events. The magazine was published by three publishing companies and changed editors once, with William Green and Gordon Swanborough as joint editors for 16 years and Ken Ellis as the sole editor for the final 16 years. The magazine ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
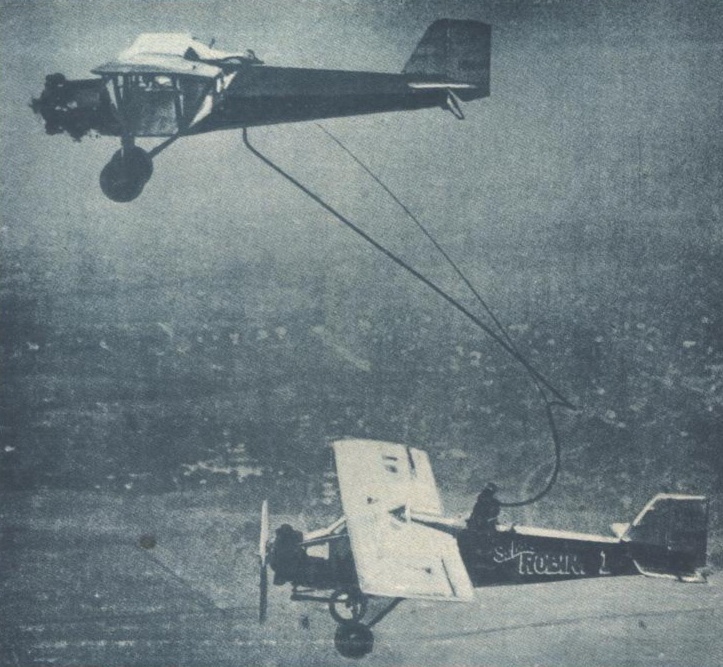
Curtiss Robin
The Curtiss Robin, introduced in 1928, is an American high-wing monoplane built by the Curtiss-Robertson Airplane Manufacturing Company. The J-1 version was flown by Wrong Way Corrigan who crossed the Atlantic after being refused permission to do so. Design The Robin, a workmanlike cabin monoplane, had a wooden wing and steel tubing fuselage. The cabin accommodated three persons; two passengers were seated side-by-side behind the pilot. Early Robins were distinguished by large flat fairings over the parallel diagonal wing bracing struts; the fairings were abandoned on later versions, having been found to be ineffective in creating lift. The original landing gear had bungee rubber cord shock absorbers, later replaced by an oleo-pneumatic system; a number of Robins had twin floats added. Variants of the Robin were fitted with engines which developed . Operational history A single modified Robin (with a Warner R-420-1) was used by the United States Army Air Corps, and designat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Curtiss JN Jenny
The Curtiss JN "Jenny" is a series of biplanes built by the Glenn Curtiss Aeroplane Company of Hammondsport, New York, later the Curtiss Aeroplane and Motor Company. Although the Curtiss JN series was originally produced as a training aircraft for the US Army, the "Jenny" (the common nickname derived from "JN") continued after World War I as a civilian aircraft, becoming the "backbone of American postwar [civil] aviation". Thousands of surplus Jennys were sold at bargain prices to private owners in the years after the war, and became central to the barnstorming era that helped awaken the US to civil aviation through much of the 1920s. Design and development Curtiss combined the best features of the Curtiss Model J, model J and Curtiss Model N, model N Training aircraft, trainers, built for the United States Army, US Army and United States Navy, US Navy, and began producing the JN or "Jenny" series of aircraft in 1915. Curtiss built only a limited number of the JN-1 and JN-2 bipl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
V-8 Engine
A V8 engine is an eight-cylinder (engine), cylinder piston engine in which two banks of four cylinders share a common crankshaft and are arranged in a V engine, V configuration. Origins The first known V8 was the Antoinette (manufacturer)#Private engine-building venture, Antoinette, designed by Léon Levavasseur, and built in 1904 by the French Antoinette (manufacturer)#Private engine-building venture, Antoinette company for use in speedboat racing, cars, and later, airplanes. Also in 1904, V8 engines began small-scale production by Renault and Buchet for use in race cars. Design V-angle Most engines use a V-angle (the angle between the two banks of cylinders) of 90 degrees. This angle results in good engine balance, which results in low vibrations. However, the downside is the greater width of the engine compared to those that use a smaller V-angle. V8 engines with a 60-degree V-angle were used in the 1996–1999 Ford Taurus SHO#Third generation (1996–1999 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Curtiss OX-5
The Curtiss OX-5 was an early V-8 American liquid-cooled aircraft engine built by Curtiss. It was the first American-designed aircraft engine to enter mass production, although it was considered obsolete when it did so in 1917.Smith, 1981, page 46 It nevertheless found widespread use on a number of aircraft, perhaps the most famous being the JN-4 "Jenny". Some 12,600 units were built through early 1919. The wide availability of the engine in the surplus market made it common until the 1930s, although it was considered unreliable for most of its service life. Design and development The OX-5 was the last in a series of Glenn Curtiss designed V engines, which started as a series of air-cooled V-twins for motorcycles in 1902. A modified version of one of these early designs was sold as an aircraft engine in 1906, and from then on the company's primary market was aircraft. The basic design had slowly expanded by adding additional cylinders until they reached the V-8 in 1906. They ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
East Wenatchee, Washington
East Wenatchee is a city in Douglas County, Washington, United States. The population at the 2010 census was 13,190, a 129.1% increase on the 2000 census, having annexed much of the East Wenatchee Bench CDP. As of the 2020 census, the population increased to 14,158. East Wenatchee lies on the east shore of the Columbia River, opposite Wenatchee on the west shore. On November 10, 2002, East Wenatchee was designated a principal city of the Wenatchee – East Wenatchee Metropolitan Statistical Area by the Office of Management and Budget. History Founding and early years At the turn of the 20th century irrigation projects, including the Columbia Basin Project east of the region, fostered the development of intensive agriculture in the shrub-steppe native to the region. Fruit orchards become one of the area's leading industries. In 1908, the first highway bridge to span the Columbia River opened. The privately owned bridge carried people, horses, wagons, and automobiles; ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polk City, Florida
Polk City is a city in Polk County, Florida, Polk County, Florida, United States. It is part of the Lakeland, Florida, Lakeland–Winter Haven, Florida, Winter Haven Lakeland-Winter Haven, Florida Metropolitan Statistical Area, metropolitan statistical area. Its population was 2,713 at the 2020 census. History Polk City was incorporated as the Town of Polk City in 1925, and changed by ordinance to the City of Polk City in 2005. The city was named after the county, itself named after James Knox Polk, the 11th President of the United States. Geography The exact coordinates for the City of Polk City are . According to the United States Census Bureau, the city has a total area of , all land. Polk City is located within the Central Florida Highlands area of the Atlantic coastal plain, with a terrain consisting of flatland interspersed with gently rolling hills. Climate The climate for the City of Polk City is characterized by hot, humid summers and generally mild to cool wint ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |