|
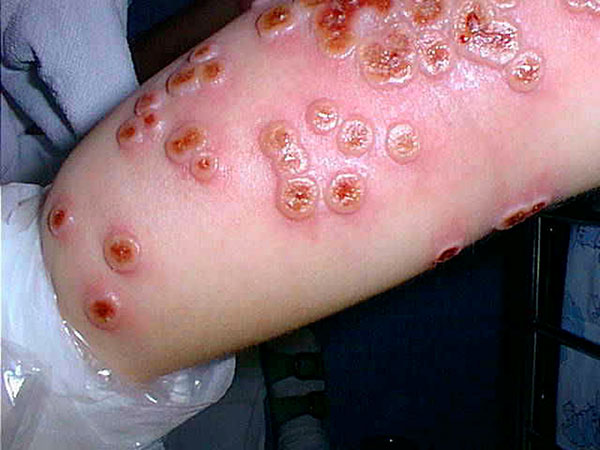
Cowpox Virus
Cowpox is an infectious disease caused by Cowpox virus (CPXV). It presents with large vesicle (dermatology), blisters in the skin, a fever and lymphadenopathy, swollen glands, historically typically following contact with an infected cow, though in the last several decades more often (though overall rarely) from infected cats. The hands and face are most frequently affected and the spots are generally very painful. The virus, part of the genus ''Orthopoxvirus'', is closely related to Vaccinia virus. The virus is Zoonosis, zoonotic, meaning that it is transferable between species, such as from cat to human. The transferral of the disease was first observed in dairy workers who touched the udders of infected cows and consequently developed the signature pustules on their hands.Vanessa Ngan, "Viral and Skin Infections" ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electron Micrograph
A micrograph is an image, captured photographically or digitally, taken through a microscope or similar device to show a magnify, magnified image of an object. This is opposed to a macrograph or photomacrograph, an image which is also taken on a microscope but is only slightly magnified, usually less than 10 times. Micrography is the practice or art of using microscopes to make photographs. A photographic micrograph is a photomicrograph, and one taken with an electron microscope is an electron micrograph. A micrograph contains extensive details of microstructure. A wealth of information can be obtained from a simple micrograph like behavior of the material under different conditions, the phases found in the system, failure analysis, grain size estimation, elemental analysis and so on. Micrographs are widely used in all fields of microscopy. Types Photomicrograph A light micrograph or photomicrograph is a micrograph prepared using an optical microscope, a process referred to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Monkeypox Virus
The monkeypox virus (MPV, MPXV, or hMPXV) is a species of double-stranded DNA viruses that cause mpox disease in humans and other mammals. It is a zoonotic virus belonging to the ''Orthopoxvirus'' genus, making it closely related to the variola, cowpox, and vaccinia viruses. MPV is oval, with a lipoprotein outer membrane. Its genome is approximately 190 kb. Smallpox and monkeypox viruses are both orthopoxviruses, and the smallpox vaccine is effective against mpox if given within 3–5 years before the disease is contracted. Symptoms of mpox in humans include a rash that forms blisters and then crusts over, fever, and swollen lymph nodes. The virus is transmissible between animals and humans by direct contact to the lesions or via bodily fluids. The virus was given the name monkeypox virus after being isolated from monkeys, but most of the carriers of this virus are smaller mammals. The virus is endemic in Central Africa, where infections in humans are relatively frequent. Tho ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cowpox Engraving (detail)
Cowpox is an infectious disease caused by Cowpox virus (CPXV). It presents with large blisters in the skin, a fever and swollen glands, historically typically following contact with an infected cow, though in the last several decades more often (though overall rarely) from infected cats. The hands and face are most frequently affected and the spots are generally very painful. The virus, part of the genus ''Orthopoxvirus'', is closely related to Vaccinia virus. The virus is zoonotic, meaning that it is transferable between species, such as from cat to human. The transferral of the disease was first observed in dairy workers who touched the udders of infected cows and consequently developed the signature pustules on their hands.Vanessa Ngan, "Viral and Skin Infections" 2009 Cowpox is more commonly found in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Incubation Period
Incubation period (also known as the latent period or latency period) is the time elapsed between exposure to a pathogenic organism, a chemical, or ionizing radiation, radiation, and when symptoms and signs are first apparent. In a typical infectious disease, the incubation period signifies the period taken by the multiplying organism to reach a threshold necessary to produce symptoms in the host. While ''latent'' or ''latency period'' may be synonymous, a distinction is sometimes made whereby the latent period (epidemiology), latent period is defined as the time from infection to infectiousness. Which period is shorter depends on the disease. A person may carry a disease, such as ''Streptococcus'' in the throat, without exhibiting any symptoms. Depending on the disease, the person may or may not be contagious disease, contagious during the incubation period. During latency, an infection is subclinical. With respect to viral infections, in incubation the virus is replicating. Thi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pustular
An abscess is a collection of pus that has built up within the tissue of the body, usually caused by bacterial infection. Signs and symptoms of abscesses include redness, pain, warmth, and swelling. The swelling may feel fluid-filled when pressed. The area of redness often extends beyond the swelling. Carbuncles and boils are types of abscess that often involve hair follicles, with carbuncles being larger. A cyst is related to an abscess, but it contains a material other than pus, and a cyst has a clearly defined wall. Abscesses can also form internally on internal organs and after surgery. They are usually caused by a bacterial infection. Often many different types of bacteria are involved in a single infection. In many areas of the world, the most common bacteria present is '' methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus''. Rarely, parasites can cause abscesses; this is more common in the developing world. Diagnosis of a skin abscess is usually made based on what it lo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Respiratory Tract Infection
Respiratory tract infections (RTIs) are infectious diseases involving the lower or upper respiratory tract. An infection of this type usually is further classified as an upper respiratory tract infection (URI or URTI) or a lower respiratory tract infection (LRI or LRTI). Lower respiratory infections, such as pneumonia, tend to be far more severe than upper respiratory infections, such as the common cold. Types Upper respiratory tract infection The upper respiratory tract is considered the airway above the glottis or vocal cords; sometimes, it is taken as the tract above the cricoid cartilage. This part of the tract includes the nose, sinuses, pharynx, and larynx. Typical infections of the upper respiratory tract include tonsillitis, pharyngitis, laryngitis, sinusitis, otitis media, certain influenza types, and the common cold. Symptoms of URIs can include cough, sore throat, runny nose, nasal congestion, headache, low-grade fever, facial pressure, and sneezing. Lower respira ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lesion
A lesion is any damage or abnormal change in the tissue of an organism, usually caused by injury or diseases. The term ''Lesion'' is derived from the Latin meaning "injury". Lesions may occur in both plants and animals. Types There is no designated classification or naming convention for lesions. Because lesions can occur anywhere in the body and their definition is so broad, the varieties of lesions are virtually endless. Generally, lesions may be classified by their patterns, sizes, locations, or causes. They can also be named after the person who discovered them. For example, Ghon lesions, which are found in the lungs of those with tuberculosis, are named after the lesion's discoverer, Anton Ghon. The characteristic skin lesions of a varicella zoster virus infection are called '' chickenpox''. Lesions of the teeth are usually called dental caries, or "cavities". Location Lesions are often classified by their tissue types or locations. For example, "skin lesions" or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vole
Voles are small rodents that are relatives of lemmings and hamsters, but with a stouter body; a longer, hairy tail; a slightly rounder head; smaller eyes and ears; and differently formed molars (high-crowned with angular cusps instead of low-crowned with rounded cusps). They are sometimes known as meadow mice or field mice. Vole species form the subfamily Arvicolinae with the lemmings and the muskrats. There are approximately 155 different vole species. Description Voles are small rodents that grow to , depending on the species. Females can have five to ten litters per year, though with an average lifespan of three months and requiring one month to adulthood, two litters is the norm. Gestation lasts for three weeks and the young voles reach sexual maturity in a month. As a result of this biological exponential growth, vole populations can grow very large within a short time. One mating pair can produce 100 offspring every year. Voles outwardly resemble several other ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rodent
Rodents (from Latin , 'to gnaw') are mammals of the Order (biology), order Rodentia ( ), which are characterized by a single pair of continuously growing incisors in each of the upper and Mandible, lower jaws. About 40% of all mammal species are rodents. They are native to all major land masses except for Antarctica, and several oceanic islands, though they have subsequently been introduced to most of these land masses by human activity. Rodents are extremely diverse in their ecology and lifestyles and can be found in almost every terrestrial habitat, including human-made environments. Species can be arboreal, fossorial (burrowing), saltatorial/ricochetal (leaping on their hind legs), or semiaquatic. However, all rodents share several morphological features, including having only a single upper and lower pair of ever-growing incisors. Well-known rodents include Mouse, mice, rats, squirrels, prairie dogs, porcupines, beavers, Cavia, guinea pigs, and hamsters. Once included wi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Woodland
A woodland () is, in the broad sense, land covered with woody plants (trees and shrubs), or in a narrow sense, synonymous with wood (or in the U.S., the '' plurale tantum'' woods), a low-density forest forming open habitats with plenty of sunlight and limited shade (see differences between British, American and Australian English explained below). Some savannas may also be woodlands, such as ''savanna woodland'', where trees and shrubs form a light canopy. Woodlands may support an understory of shrubs and herbaceous plants including grasses. Woodland may form a transition to shrubland under drier conditions or during early stages of primary or secondary succession. Higher-density areas of trees with a largely closed canopy that provides extensive and nearly continuous shade are often referred to as forests. Extensive efforts by conservationist groups have been made to preserve woodlands from urbanization and agriculture. For example, the woodlands of Northwest Indiana ha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cattle
Cattle (''Bos taurus'') are large, domesticated, bovid ungulates widely kept as livestock. They are prominent modern members of the subfamily Bovinae and the most widespread species of the genus '' Bos''. Mature female cattle are called cows and mature male cattle are bulls. Young female cattle are called heifers, young male cattle are oxen or bullocks, and castrated male cattle are known as steers. Cattle are commonly raised for meat, for dairy products, and for leather. As draft animals, they pull carts and farm implements. Cattle are considered sacred animals within Hinduism, and it is illegal to kill them in some Indian states. Small breeds such as the miniature Zebu are kept as pets. Taurine cattle are widely distributed across Europe and temperate areas of Asia, the Americas, and Australia. Zebus are found mainly in India and tropical areas of Asia, America, and Australia. Sanga cattle are found primarily in sub-Saharan Africa. These types, sometime ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Feline Zoonosis
A feline zoonosis is a viral, bacterial, fungal, protozoan, nematode or arthropod infection that can be transmitted to humans from the domesticated cat, ''Felis catus''. Some of these diseases are reemerging and newly emerging infections or infestations caused by zoonotic pathogens transmitted by cats. In some instances, the cat can display symptoms of infection (these may differ from the symptoms in humans) and sometimes the cat remains asymptomatic. There can be serious illnesses and clinical manifestations in people who become infected. This is dependent on the immune status and age of the person. Those who live in close association with cats are more prone to these infections, but those that do not keep cats as pets can also acquire these infections as the transmission can be from cat feces and the parasites that leave their bodies. People can acquire cat-associated infections through bites, scratches or other direct contact of the skin or mucous membranes with the cat. This in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |