|
Copaxone
Glatiramer acetate, sold under the brand name Copaxone among others, is an immunomodulator medication used to treat multiple sclerosis. Glatiramer acetate is approved in the United States to reduce the frequency of relapses, but not for reducing the progression of disability. Observational studies, but not randomized controlled trials, suggest that it may reduce progression of disability. While a conclusive diagnosis of multiple sclerosis requires a history of two or more episodes of symptoms and signs, glatiramer acetate is approved to treat a first episode anticipating a diagnosis. It is also used to treat relapsing-remitting multiple sclerosis. It is administered by subcutaneous injection. It is a mixture of random-sized peptides that are composed of the four amino acids found in myelin basic protein, namely glutamic acid, lysine, alanine, and tyrosine. Myelin basic protein is the antigen in the myelin sheaths of the neurons that stimulates an autoimmune reaction in people ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Weizmann Institute Of Science
The Weizmann Institute of Science ( ''Machon Weizmann LeMada'') is a Public university, public research university in Rehovot, Israel, established in 1934, fourteen years before the State of Israel was founded. Unlike other List of Israeli universities and colleges, Israeli universities it exclusively offers postgraduate-only degrees in the natural science, natural and exact sciences. The institute is a multidisciplinary research center, employing around 3,800 scientists, Postdoctoral researcher, postdoctoral fellows, Ph.D. and M.Sc. students, and scientific, technical, and administrative staff working at the institute. As of 2019, the Weizmann Institute of Science has been associated with six Nobel laureates and three Turing Award winners. The Weizmann Institute of Science and Elbit Systems have collaborated on various projects, notably including the development and supply of the space telescope for Israel's Ultraviolet Transient Astronomy Satellite (ULTRASAT) program and re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Multiple Sclerosis
Multiple sclerosis (MS) is an autoimmune disease resulting in damage to myelinthe insulating covers of nerve cellsin the brain and spinal cord. As a demyelinating disease, MS disrupts the nervous system's ability to Action potential, transmit signals, resulting in a range of signs and symptoms, including physical, cognitive disability, mental, and sometimes psychiatric problems. Symptoms include double vision, vision loss, eye pain, muscle weakness, and loss of Sensation (psychology), sensation or coordination. MS takes several forms, with new symptoms either occurring in isolated attacks (relapsing forms) or building up over time (progressive forms). In relapsing forms of MS, symptoms may disappear completely between attacks, although some permanent neurological problems often remain, especially as the disease advances. In progressive forms of MS, bodily function slowly deteriorates once symptoms manifest and will steadily worsen if left untreated. While its cause is unclear, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
WHO Model List Of Essential Medicines
The WHO Model List of Essential Medicines (aka Essential Medicines List or EML), published by the World Health Organization (WHO), contains the medications considered to be most effective and safe to meet the most important needs in a health system. The list is frequently used by countries to help develop their own local lists of essential medicines. , more than 155 countries have created national lists of essential medicines based on the World Health Organization's model list. This includes both Developed country, developed and Developing country, developing countries. The list is divided into core items and complementary items. The core items are deemed to be the most cost-effective options for key health problems and are usable with little additional health care resources. The complementary items either require additional infrastructure such as specially trained health care providers or diagnostic equipment or have a lower cost–benefit ratio. About 25% of items are in the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Placebo-controlled Studies
Placebo-controlled studies are a way of testing a medical therapy in which, in addition to a group of subjects that receives the treatment to be evaluated, a separate control group receives a sham "placebo" treatment which is specifically designed to have no real effect. Placebos are most commonly used in blinded trials, where subjects do not know whether they are receiving real or placebo treatment. Often, there is also a further "natural history" group that does not receive any treatment at all. The purpose of the placebo group is to account for the placebo effect, that is, effects from treatment that do not depend on the treatment itself. Such factors include knowing one is receiving a treatment, attention from health care professionals, and the expectations of a treatment's effectiveness by those running the research study. Without a placebo group to compare against, it is not possible to know whether the treatment itself had any effect. Patients frequently show improvement ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Blood–brain Barrier
The blood–brain barrier (BBB) is a highly selective semipermeable membrane, semipermeable border of endothelium, endothelial cells that regulates the transfer of solutes and chemicals between the circulatory system and the central nervous system, thus protecting the brain from harmful or unwanted substances in the blood. The blood–brain barrier is formed by endothelial cells of the Capillary, capillary wall, astrocyte end-feet ensheathing the capillary, and pericytes embedded in the capillary basement membrane. This system allows the passage of some small molecules by passive transport, passive diffusion, as well as the selective and active transport of various nutrients, ions, organic anions, and macromolecules such as glucose and amino acids that are crucial to neural function. The blood–brain barrier restricts the passage of pathogens, the diffusion of solutes in the blood, and Molecular mass, large or Hydrophile, hydrophilic molecules into the cerebrospinal fluid, while a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Regulatory T Cells
The regulatory T cells (Tregs or Treg cells), formerly known as suppressor T cells, are a subpopulation of T cells that modulate the immune system, maintain immune tolerance, tolerance to self-antigens, and prevent autoimmune disease. Treg cells are immunosuppression, immunosuppressive and generally suppress or downregulation and upregulation, downregulate induction and proliferation of effector T cells. Treg cells express the biomarkers CD4, FOXP3, and CD25 and are thought to be derived from the same cell lineage, lineage as naïve T helper cell, CD4+ cells. Because effector T cells also express CD4 and CD25, Treg cells are very difficult to effectively discern from effector CD4+, making them difficult to study. Research has found that the cytokine Transforming growth factor beta, transforming growth factor beta (TGF-β) is essential for Treg cells to differentiate from naïve CD4+ cells and is important in maintaining Treg cell homeostas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Experimental Autoimmune Encephalomyelitis
Experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis, sometimes experimental allergic encephalomyelitis (EAE), is an animal model of brain inflammation. It is an inflammatory demyelinating disease of the central nervous system (CNS). It is mostly used with rodents and is widely studied as an animal model of the human CNS demyelinating diseases, including multiple sclerosis (MS) and acute disseminated encephalomyelitis (ADEM). EAE is also the prototype for T-cell-mediated autoimmune disease in general. EAE development was motivated by observations during the convalescence from viral diseases by Thomas M. Rivers, D. H. Sprunt and G. P. Berry in 1933. Their findings upon a transfer of inflamed patient tissue to primates was published in the '' Journal of Experimental Medicine''. An acute monophasic illness, it has been suggested that EAE is far more similar to ADEM than to MS. Types of EAE EAE can be induced in a number of species, including mice, rats, guinea pigs, rabbits and primates. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
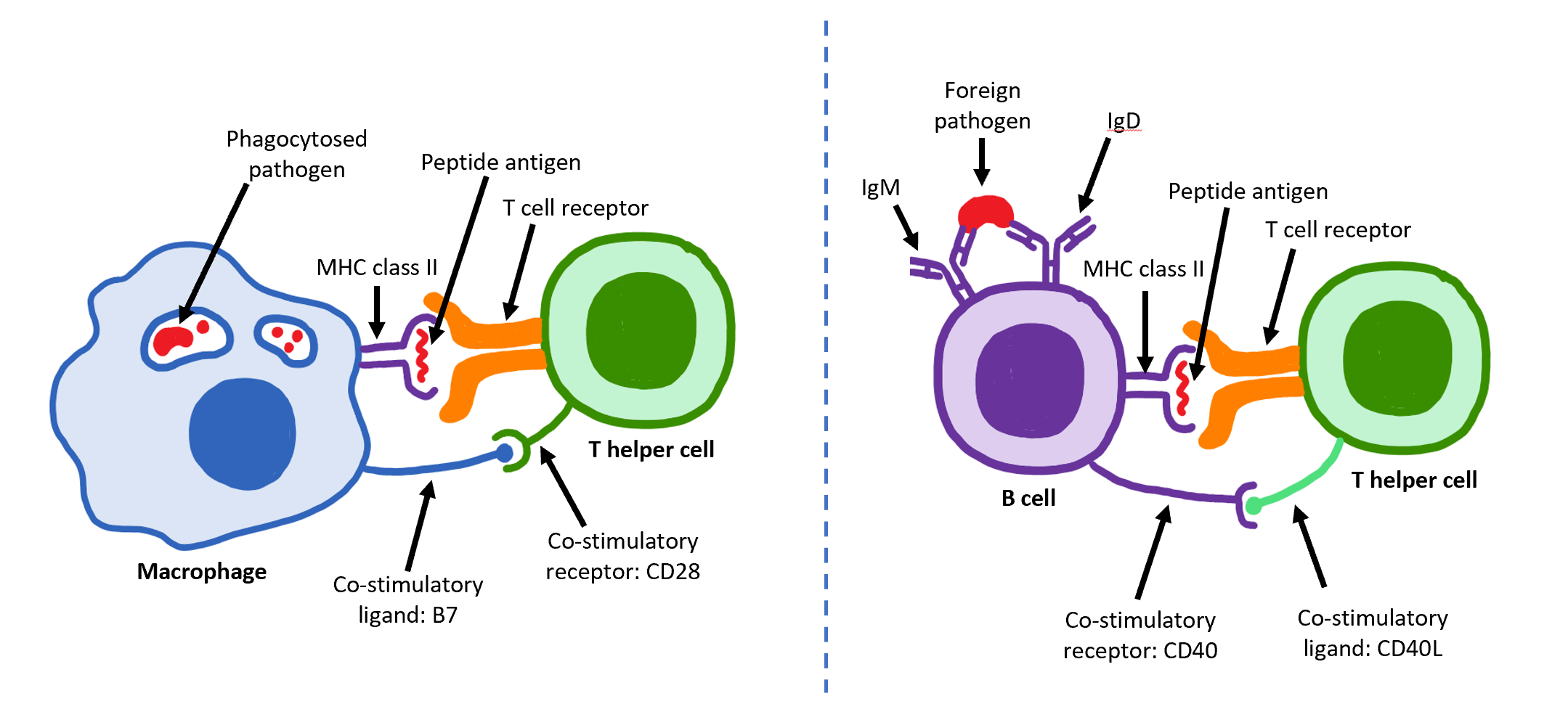
T Helper Cell
The T helper cells (Th cells), also known as CD4+ cells or CD4-positive cells, are a type of T cell that play an important role in the adaptive immune system. They aid the activity of other immune cells by releasing cytokines. They are considered essential in B cell Immunoglobulin class switching, antibody class switching, breaking Cross-presentation, cross-tolerance in dendritic cells, in the activation and growth of cytotoxic T cells, and in maximizing bactericidal activity of phagocytes such as macrophages and neutrophils. CD4+ cells are mature Th cells that express the surface protein CD4. Genetic variation in regulatory elements expressed by CD4+ cells determines susceptibility to a broad class of autoimmune diseases. Structure and function Th cells contain and release cytokines to aid other immune cells. Cytokines are small protein mediators that alter the behavior of target cells that express Receptor (biochemistry), receptors for those cytokines. These cells help polar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lipoatrophy
Lipoatrophy is the term describing the localized loss of fat tissue. This may occur as a result of subcutaneous injections of insulin in the treatment of diabetes, from the use of human growth hormone or from subcutaneous injections of copaxone used for the treatment of multiple sclerosis. In the latter case, an injection may produce a small dent at the injection site. Lipoatrophy occurs in HIV-associated lipodystrophy, one cause of which is an adverse drug reaction that is associated with some antiretroviral medications. A more general term for an abnormal or degenerative condition of the entire body's adipose tissue is ''lipodystrophy''. References Symptoms and signs {{Symptom-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Injection Site Reaction
Injection site reactions (ISRs) are reactions that occur at the site of injection of a drug. They may be mild or severe and may or may not require medical intervention. Some reactions may appear immediately after injection, and some may be delayed. Such reactions can occur with subcutaneous, intramuscular, or intravenous administration. Drugs commonly administered subcutaneously include local anesthetics, drugs used in palliative care (e.g., fentanyl and morphine), and biopharmaceuticals (e.g., vaccines, heparin, insulin, growth hormone, hematopoietic growth factors, interferons, and monoclonal antibodies). Signs and symptoms Some reactions, such as pain, may appear immediately. Others may be delayed, such as erythema which may appear 24–96 hours after injection. ISRs commonly seen with subcutaneous injections include: *Bleeding and bruising *Erythema (redness) *Pain *Pruritis (itching) *Swelling *Induration (hardening of the skin) *Discoloration Severe reactions may result i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anaphylaxis
Anaphylaxis (Greek: 'up' + 'guarding') is a serious, potentially fatal allergic reaction and medical emergency that is rapid in onset and requires immediate medical attention regardless of the use of emergency medication on site. It typically causes more than one of the following: an itchy rash, throat closing due to swelling that can obstruct or stop breathing; severe tongue swelling that can also interfere with or stop breathing; shortness of breath, vomiting, lightheadedness, loss of consciousness, low blood pressure, and medical shock. These symptoms typically start in minutes to hours and then increase very rapidly to life-threatening levels. Urgent medical treatment is required to prevent serious harm and death, even if the patient has used an epinephrine autoinjector or has taken other medications in response, and even if symptoms appear to be improving. Cause, mechanism, and diagnosis Common causes include allergies to insect bites and stings, allergies to fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |