|
Convair X-6
The Convair X-6 was an experimental aircraft project to develop and evaluate a nuclear-powered jet aircraft. Experiments were carried out on a testbed aircraft named Convair NB-36H, based on the B-36 bomber. The program was canceled before the actual X-6 and its nuclear reactor engines were completed. The X-6 was part of a larger series of programs that ran from 1946 through 1961, and cost 7 billion USD. The basic idea was that nuclear-powered strategic bombers would be able to stay airborne for weeks at a time, as their range would not be limited by liquid jet fuel. Development and design In May 1946, the Nuclear Energy for the Propulsion of Aircraft (NEPA) project was started by the United States Army Air Forces. Studies under this program were done until May 1951 when NEPA was replaced by the Aircraft Nuclear Propulsion (ANP) program. The ANP program included plans for Convair to modify two B-36s under the MX-1589 project. One of the B-36s was used to study shielding r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
WikiProject Aircraft
A WikiProject, or Wikiproject, is an affinity group for contributors with shared goals within the Wikimedia movement. WikiProjects are prevalent within the largest wiki, Wikipedia, and exist to varying degrees within Wikimedia project, sibling projects such as Wiktionary, Wikiquote, Wikidata, and Wikisource. They also exist in different languages, and translation of articles is a form of their collaboration. During the COVID-19 pandemic, CBS News noted the role of Wikipedia's WikiProject Medicine in maintaining the accuracy of articles related to the disease. Another WikiProject that has drawn attention is WikiProject Women Scientists, which was profiled by ''Smithsonian Magazine, Smithsonian'' for its efforts to improve coverage of women scientists which the profile noted had "helped increase the number of female scientists on Wikipedia from around 1,600 to over 5,000". On Wikipedia Some Wikipedia WikiProjects are substantial enough to engage in cooperative activities with outsi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Project Rover
Project Rover was a United States project to develop a nuclear-thermal rocket that ran from 1955 to 1973 at the Los Alamos Scientific Laboratory (LASL). It began as a United States Air Force project to develop a nuclear-powered upper stage for an intercontinental ballistic missile (ICBM). The project was transferred to NASA in 1958 after the Sputnik crisis triggered the Space Race. It was managed by the Space Nuclear Propulsion Office (SNPO), a joint agency of the Atomic Energy Commission (AEC), and NASA. Project Rover became part of NASA's Nuclear Engine for Rocket Vehicle Application (NERVA) project and henceforth dealt with the research into nuclear rocket reactor design, while NERVA involved the overall development and deployment of nuclear rocket engines, and the planning for space missions. Nuclear reactors for Project Rover were built at LASL Technical Area 18 (TA-18), also known as the Pajarito Canyon Site. They were tested there at very low power and then shipped to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Project Pluto
Project Pluto was a United States government program to develop nuclear-powered ramjet engines for use in cruise missiles. Two experimental engines were tested at the Nevada Test Site (NTS) in 1961 and 1964 respectively. On 1 January 1957, the U.S. Air Force and the U.S. Atomic Energy Commission selected the Lawrence Radiation Laboratory to study the feasibility of applying heat from a nuclear reactor to power a ramjet engine for a Supersonic Low Altitude Missile. This would have many advantages over other contemporary nuclear weapons delivery systems: operating at Mach number, Mach 3, or around , and flying as low as , it would be invulnerable to interception by contemporary air defenses, carry more nuclear warheads with greater nuclear weapon yield, deliver them with greater accuracy than was possible with intercontinental ballistic missile (ICBMs) at the time and, unlike them, could be recalled. This research became known as Project Pluto, and was directed by Theodore Charl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
List Of Nuclear-powered Aircraft
Below is a list of Nuclear-powered aircraft, nuclear powered aircraft and concepts: References Bibliography * {{refend Lists of aircraft by power source, Nuclear-powered aircraft Nuclear-powered aircraft ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Tupolev Tu-95LAL
The Tupolev Tu-95LAL experimental aircraft () which flew from 1961 to 1965 was a modified Tupolev Tu-95 Soviet bomber aircraft, analogous to the United States' earlier Convair NB-36H. It was intended to see whether a nuclear reactor could be used to power an aircraft, primarily testing airborne operation of a reactor and shielding for components and crew. The reactor did not actually power the aircraft. Design and development During the Cold War the USSR had an experimental nuclear aircraft program. Without the need to refuel, a nuclear-powered aircraft would have greatly extended range compared to conventional designs. On 12 August 1955 the Council of Ministers of the USSR issued a directive ordering bomber-related design bureaus to join forces in researching nuclear aircraft. The design bureaus of Andrei Tupolev and Vladimir Myasishchev became the chief design teams, while N. D. Kuznetsov and A. M. Lyulka were assigned to develop the engines. They chose to focus on the d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
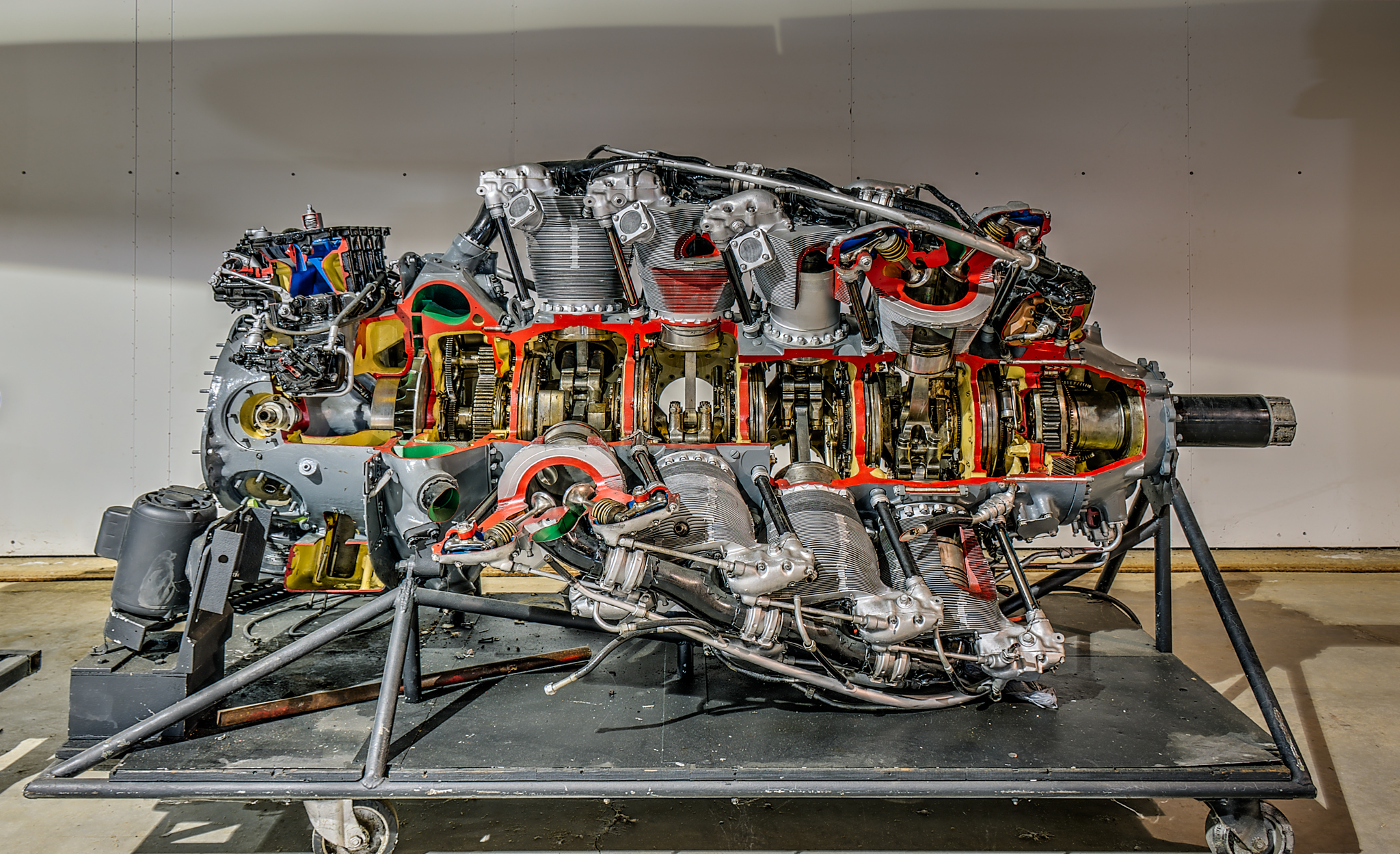
Pratt & Whitney R-4360
The Pratt & Whitney R-4360 Wasp Major is an American 28-cylinder four-row radial piston aircraft engine designed and built during World War II. At , it is the largest-displacement aviation piston engine to be mass-produced in the United States, and at the most powerful. First run in 1944, it was the last of the Pratt & Whitney Wasp family, and the culmination of its maker's piston engine technology. The war was over before it could power airplanes into combat. It powered many of the last generation of large piston-engined aircraft before turbojets, but was supplanted by equivalent (and superior) powered turboprops (such as the Allison T56). Its main rival was the twin-row, 18-cylinder, nearly displacement, up to Wright R-3350 Duplex-Cyclone, first run some seven years earlier (May 1937). Design and development The R-4360 was a 28-cylinder four-row air-cooled radial engine. Each row of seven air-cooled cylinders possessed a slight angular offset from the previous, forming a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Turbojet
The turbojet is an airbreathing jet engine which is typically used in aircraft. It consists of a gas turbine with a propelling nozzle. The gas turbine has an air inlet which includes inlet guide vanes, a compressor, a combustion chamber, and a turbine (that drives the compressor). The compressed air from the compressor is heated by burning fuel in the combustion chamber and then allowed to expand through the turbine. The turbine exhaust is then expanded in the propelling nozzle where it is accelerated to high speed to provide thrust. Two engineers, Frank Whittle in the United Kingdom and Hans von Ohain in Germany, developed the concept independently into practical engines during the late 1930s. Turbojets have poor efficiency at low vehicle speeds, which limits their usefulness in vehicles other than aircraft. Turbojet engines have been used in isolated cases to power vehicles other than aircraft, typically for attempts on land speed records. Where vehicles are "turbine-powere ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Monteview, Idaho
Monteview is an unincorporated community in Jefferson County, Idaho, United States. Monteview is north-northwest of Mud Lake, and has a post office A post office is a public facility and a retailer that provides mail services, such as accepting letter (message), letters and parcel (package), parcels, providing post office boxes, and selling postage stamps, packaging, and stationery. Post o ... with ZIP code 83435. History The first wave of settlers in the community of Monteview arrived in the area in 1914. They came as dry farmers but after years of hauling drinking and household water were delighted to find sufficient water near the surface of the rich level soil for that purpose. Martin Landgren arrived in 1915 and said that at the time the community had no school, post office, or roads. After setting up their own housing and doing the necessary farming, the settlers joined together to build a log structure which served as school and church as well as a community cent ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Idaho National Laboratory
Idaho National Laboratory (INL) is one of the national laboratories of the United States Department of Energy and is managed by the Battelle Energy Alliance. Historically, the lab has been involved with nuclear research, although the laboratory does other research as well. Much of current knowledge about how nuclear reactors behave and misbehave was discovered at what is now Idaho National Laboratory. John Grossenbacher, former INL director, said, "The history of nuclear energy for peaceful application has principally been written in Idaho". The present facility resulted from the 2005 merger of two neighboring laboratories, the National Engineering and Environmental Laboratory, and the Idaho site of the western branch of Argonne National Laboratory (Argonne-West). Various organizations have built more than 50 reactors at what is commonly called "the Site", including the ones that gave the world its first usable amount of electricity from nuclear power and the power plant fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Arco, Idaho
Arco is a city in Butte County, Idaho, United States. The population was 879 as of the 2020 United States census, down from 995 at the 2010 census. Arco is the county seat and largest city in Butte County. History Arco was named as early as 1860 based on the name of a local rancher, Louis Arco. Louis Arco is also mentioned in the National Park Service’s Teacher's Guide to Craters of the Moon with the line “round1862 Louis Arco establishe a ranch and trading post at Arco." Arco was the first community in the world ever to be lit by electricity generated solely by nuclear power. This occurred for about an hour on July 17, 1955, powered by Argonne National Laboratory’s BORAX-III reactor at the nearby National Reactor Testing Station (NRTS), now the Idaho National Laboratory. NRTS made further history on January 3, 1961, when the SL-1 reactor was destroyed through an operator maintenance error, with the ensuing steam explosion causing the deaths of all three personnel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Experimental Breeder Reactor I
Experimental Breeder Reactor I (EBR-I) is a decommissioned research reactor and U.S. National Historic Landmark located in the desert about southeast of Arco, Idaho. It was the world's first breeder reactor. At 1:50 p.m. on December 20, 1951, it became one of the world's first electricity-generating nuclear power plants when it produced sufficient electricity to illuminate four 200-watt light bulbs. EBR-I soon generated sufficient electricity to power its building and the town of Arco, and continued to be used for experimental research until it was decommissioned in 1964. The museum is open for visitors from late May until early September. History EBR-I's construction started in late 1949. The reactor was designed and built by a team led by Walter Zinn at the Idaho site of the Argonne National Laboratory, known as Argonne-West (since 2005 part of Idaho National Laboratory). In its early stages, the reactor plant was referred to as Chicago Pile 4 (CP-4) and Zinn's ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |