|
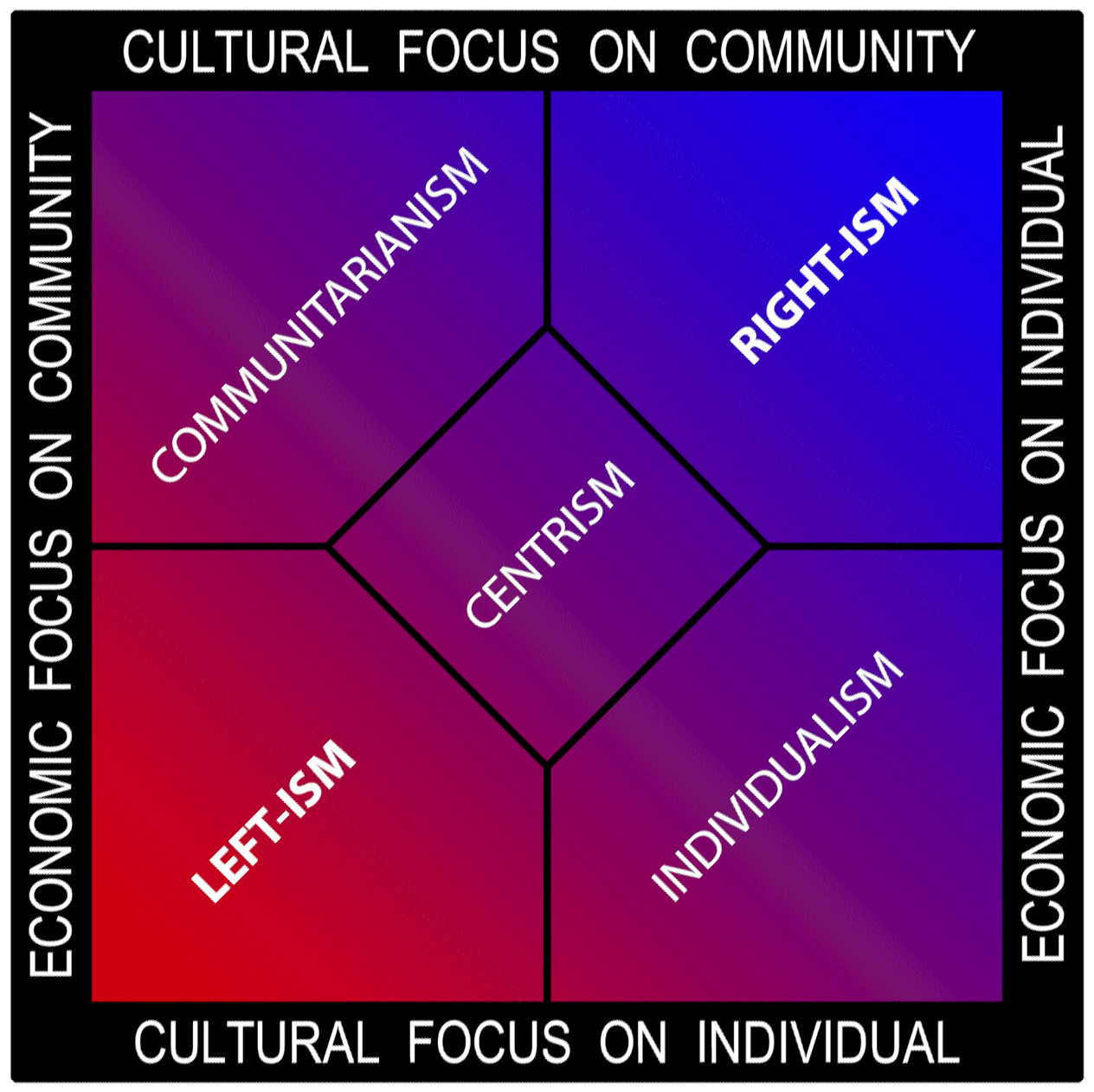
Communitarianism
Communitarianism is a philosophy that emphasizes the connection between the individual and the community. Its overriding philosophy is based on the belief that a person's social identity and personality are largely molded by community relationships, with a smaller degree of development being placed on individualism. Although the community might be a family, communitarianism usually is understood, in the wider, philosophical sense, as a collection of interactions, among a community of people in a given place (geographical location), or among a community who share an interest or who share a history. Communitarianism is often contrasted with individualism, and generally opposes '' laissez-faire'' policies that deprioritize the stability of the overall community. Terminology The philosophy of communitarianism originated in the 20th century, but the term "communitarian" was coined in 1841, by John Goodwyn Barmby, a leader of the British Chartist movement, who used it in referri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Amitai Etzioni
Amitai Etzioni (; Hebrew: אמיתי עציוני; né Werner Falk; 4 January 1929 – 31 May 2023) was an Israeli-American sociologist, best known for his work on socioeconomics and communitarianism. He founded the Communitarian Network, a non-profit, non-partisan organization dedicated to supporting the moral, social, and political foundations of society. He established the network to disseminate the movement's ideas. His writings argue for a carefully crafted balance between individual rights and social responsibilities, and between autonomy and order, in social structure. In 2001, he was named among the top 100 American intellectuals, as measured by academic citations, in Richard Posner's book, ''Public Intellectuals: A Study of Decline''. Etzioni was the Director of the Institute for Communitarian Policy Studies at The George Washington University, where he also served as a professor of International Affairs. Early life and education Amitai Etzioni was born Werner F ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Michael Walzer
Michael Laban Walzer (born March 3, 1935) is an American Political theory, political theorist and public intellectual. A professor emeritus at the Institute for Advanced Study (IAS) in Princeton, New Jersey, he is editor emeritus of the left-wing magazine ''Dissent (American magazine), Dissent,'' which he has been affiliated with since his years as an undergraduate at Brandeis University, an advisory editor of the Jews, Jewish journal ''Fathom Journal, Fathom,'' and sits on the editorial board of the ''Jewish Review of Books.'' He has written books and essays on a wide range of topics—many in political ethics—including Just war theory, just and unjust wars, nationalism, ethnicity, Zionism, antisemitism, economic justice, social criticism, Radicalization, radicalism, Toleration, tolerance, and political obligation. He is also a contributing editor to ''The New Republic''. To date, he has written 27 books and published over 300 articles, essays, and book reviews in ''Dissent ( ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Radical Centrist
Radical centrism, also called the radical center, the radical centre, and the radical middle, is a concept that arose in Western nations in the late 20th century. The '' radical'' in the term refers to a willingness on the part of most radical centrists to call for fundamental reform of institutions. The ''centrism'' refers to a belief that genuine solutions require realism and pragmatism, not just idealism and emotion. One radical centrist text defines radical centrism as "idealism without illusions", a phrase originally from John F. Kennedy. Radical centrists borrow ideas from the political left and the political right, often melding them. Most support market economy-based solutions to social problems, with strong governmental oversight in the public interest. There is support for increased global engagement and the growth of an empowered middle class in developing countries. In the United States, many radical centrists work within the major political parties; they also su ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Political Philosophy
Political philosophy studies the theoretical and conceptual foundations of politics. It examines the nature, scope, and Political legitimacy, legitimacy of political institutions, such as State (polity), states. This field investigates different forms of government, ranging from democracy to authoritarianism, and the values guiding political action, like justice, equality, and liberty. As a normative field, political philosophy focuses on desirable norms and values, in contrast to political science, which emphasizes empirical description. Political ideologies are systems of ideas and principles outlining how society should work. Anarchism rejects the coercive power of centralized governments. It proposes a stateless society to promote liberty and equality. Conservatism seeks to preserve traditional institutions and practices. It is skeptical of the human ability to radically Social change, reform society, arguing that drastic changes can destroy the wisdom of past generations. Li ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Individualism
Individualism is the moral stance, political philosophy, ideology, and social outlook that emphasizes the intrinsic worth of the individual. Individualists promote realizing one's goals and desires, valuing independence and self-reliance, and advocating that the interests of the individual should gain precedence over the state or a social group, while opposing external interference upon one's own interests by society or institutions such as the government. Individualism makes the individual its focus, and so starts "with the fundamental premise that the human individual is of primary importance in the struggle for liberation". L. Susan Brown. '' The Politics of Individualism: Liberalism, Liberal Feminism, and Anarchism''. Black Rose Books Ltd. 1993 Individualism represents one kind of sociocultural perspective and is often defined in contrast to other perspectives, such as communitarianism, collectivism and corporatism. Individualism is also associated with artistic and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Robert Owen
Robert Owen (; 14 May 1771 – 17 November 1858) was a Welsh textile manufacturer, philanthropist, political philosopher and social reformer, and a founder of utopian socialism and the cooperative movement, co-operative movement. He strove to improve factory working conditions, promoted experimental socialistic communities, sought a more collective approach to child-rearing, and 'believed in lifelong education, establishing an Institute for the Formation of Character and School for Children that focused less on job skills than on becoming a better person'. He gained wealth in the early 1800s from a textile mill at New Lanark, Scotland. Having trained as a draper in Stamford, Lincolnshire he worked in London before relocating at age 18 to Manchester and textile manufacturing. In 1824, he moved to America and put most of his fortune in an experimental socialistic community at New Harmony, Indiana, as a preliminary for his utopian society. It lasted about two years. Other Owenite c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Charles Fourier
François Marie Charles Fourier (; ; 7 April 1772 – 10 October 1837) was a French philosopher, an influential early socialist thinker, and one of the founders of utopian socialism. Some of his views, held to be radical in his lifetime, have become mainstream in modern society. For instance, Fourier is credited with having originated the word ''feminism'' in 1837. Fourier's social views and proposals inspired a whole movement of intentional communities. Among them in the United States were the community of Utopia, Ohio; La Reunion near present-day Dallas, Texas; Lake Zurich, Illinois; the North American Phalanx in Red Bank, New Jersey; Brook Farm in West Roxbury, Massachusetts; the Community Place and Sodus Bay Phalanx in New York State; Silkville, Kansas, and several others. In Guise, France, he influenced the . Fourier later inspired a diverse array of revolutionary thinkers and writers. Life Fourier was born in Besançon, France, on 7 April 1772. Serenyi 1967, p. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Mikhail Bakunin
Mikhail Alexandrovich Bakunin. Sometimes anglicized to Michael Bakunin. ( ; – 1 July 1876) was a Russian revolutionary anarchist. He is among the most influential figures of anarchism and a major figure in the revolutionary socialist, social anarchist, and collectivist anarchist traditions. Bakunin's prestige as a revolutionary also made him one of the most famous ideologues in Europe, gaining substantial influence among radicals throughout Russia and Europe. Bakunin grew up in Pryamukhino, a family estate in Tver Governorate. From 1840, he studied in Moscow, then in Berlin hoping to enter academia. Later in Paris, he met Karl Marx and Pierre-Joseph Proudhon, who deeply influenced him. Bakunin's increasing radicalism ended hopes of a professorial career. He was expelled from France for opposing the Russian Empire's occupation of Poland. After participating in the 1848 Prague and 1849 Dresden uprisings, Bakunin was imprisoned, tried, sentenced to death, and extradit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Pierre Joseph Proudhon
Pierre-Joseph Proudhon (, ; ; 1809 – 19 January 1865) was a French anarchist, socialist, philosopher, and economist who founded mutualist philosophy and is considered by many to be the "father of anarchism". He was the first person to call himself an ''anarchist'', using that term, and is widely regarded as one of anarchism's most influential theorists. Proudhon became a member of the French Parliament after the Revolution of 1848, whereafter he referred to himself as a ''federalist''. Proudhon described the liberty he pursued as the synthesis of community and individualism. Some consider his mutualism to be part of individualist anarchism while others regard it to be part of social anarchism.The Anarchist FAQ Collective; McKay, Ian, ed. (2008/2012). ''An Anarchist Faq''. I/II. Oakland/Edinburgh: AK Press. . . Proudhon, who was born in Besançon, was a printer who taught himself Latin in order to better print books in the language. His best-known assertion is that "prope ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Karl Marx
Karl Marx (; 5 May 1818 – 14 March 1883) was a German philosopher, political theorist, economist, journalist, and revolutionary socialist. He is best-known for the 1848 pamphlet '' The Communist Manifesto'' (written with Friedrich Engels), and his three-volume (1867–1894), a critique of classical political economy which employs his theory of historical materialism in an analysis of capitalism, in the culmination of his life's work. Marx's ideas and their subsequent development, collectively known as Marxism, have had enormous influence. Born in Trier in the Kingdom of Prussia, Marx studied at the universities of Bonn and Berlin, and received a doctorate in philosophy from the University of Jena in 1841. A Young Hegelian, he was influenced by the philosophy of Georg Wilhelm Friedrich Hegel, and both critiqued and developed Hegel's ideas in works such as '' The German Ideology'' (written 1846) and the '' Grundrisse'' (written 1857–1858). While in Paris, Marx wrote ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
François-Noël Babeuf
François-Noël Babeuf (; 23 November 1760 – 27 May 1797), also known as Gracchus Babeuf, was a French proto-communist, revolutionary, and journalist of the French Revolutionary period. His newspaper ''Le tribun du peuple'' (''The Tribune of the People'') was best known for its advocacy for the poor and calling for a popular revolt against the Directory, the government of France. He was a leading advocate for democracy and the abolition of private property. He made his own variant of Jacobinism ( Robespierrism) which is called ''Neo-Jacobinism''. Besides the influence of Robespierrism on his thought, due to his proto-communism, his political views were more aligned with the ideology of the Enragés. He angered the authorities who were clamping down hard on their radical enemies. In spite of the efforts of his Jacobin friends to save him, Babeuf was executed for his role in the Conspiracy of the Equals. The nickname "Gracchus" likened him to the Gracchi brothers, who serve ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Plato
Plato ( ; Greek language, Greek: , ; born BC, died 348/347 BC) was an ancient Greek philosopher of the Classical Greece, Classical period who is considered a foundational thinker in Western philosophy and an innovator of the written dialogue and dialectic forms. He influenced all the major areas of theoretical philosophy and practical philosophy, and was the founder of the Platonic Academy, a philosophical school in History of Athens, Athens where Plato taught the doctrines that would later become known as Platonism. Plato's most famous contribution is the theory of forms, theory of forms (or ideas), which aims to solve what is now known as the problem of universals. He was influenced by the pre-Socratic thinkers Pythagoras, Heraclitus, and Parmenides, although much of what is known about them is derived from Plato himself. Along with his teacher Socrates, and his student Aristotle, Plato is a central figure in the history of Western philosophy. Plato's complete ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |