|
Church Of St. Nicholas, Brezova
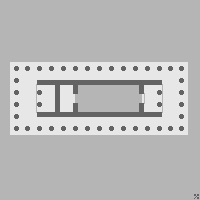
The Church of Saint Nicholas () is a Church (building), church of the Serbian Orthodox Church, located in the village of Brezova (Ivanjica), Brezova, 26 km southwest of Ivanjica. Situated on Mučanj mountain, it was built during the first half of the 17th century at the place of an older church. Folk tradition links the construction of the church with Despot (court title), Despot Stefan Lazarević whose fresco portrait is located in the church, although he lived in the 15th century.Radojčić (1996) An Archeological survey of the church, but also its Conservation (cultural heritage), conservation and restoration was being conducted at several instances (1971–1972, 1973–1975. and 1987), resulting in church's present status of state protected monument of great cultural significance. Architecture Saint Nicholas' Church in Brezova is a single-nave building with polygonal dome and backside rose windows. The church's cella is divided into three aisles. The dome is raised ove ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brezova, Ivanjica
Brezova is a village in the municipality of Ivanjica, Serbia. According to the 2011 census, the village has a population of 483 inhabitants. Notable people * Ljuba Čupa (1877–1913), guerrilla fighter * Petar Stambolić (1912–2007), politician * Ivan Stambolić Ivan Stambolić (; 5 November 1936 – 25 August 2000) was a Serbian politician who served as the president of the League of Communists of Serbia (SKS) from 1984 to 1986. A prominent member of SKS, he also served as prime minister of Serbia from ... (1936–2000), politician References {{commonscat, Brezova (Ivanjica) Populated places in Moravica District ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cella
In Classical architecture, a or naos () is the inner chamber of an ancient Greek or Roman temple. Its enclosure within walls has given rise to extended meanings: of a hermit's or monk's cell, and (since the 17th century) of a biological cell in plants or animals. Greek and Roman temples In ancient Greek and Roman temples, the ''cella'' was a room at the center of the building, usually containing a cult image or statue representing the particular deity venerated in the temple. In addition, the ''cella'' might contain a table to receive supplementary votive offerings, such as votive statues of associated deities, precious and semi-precious stones, helmets, spear and arrow heads, swords, and war trophies. No gatherings or sacrifices took place in the ''cella'', as the altar for sacrifices was always located outside the building along the axis and temporary altars for other deities were built next to it. The accumulated offerings made Greek and Roman temples virtual treasuri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Saint Nicholas
Saint Nicholas of Myra (traditionally 15 March 270 – 6 December 343), also known as Nicholas of Bari, was an early Christian bishop of Greeks, Greek descent from the maritime city of Patara (Lycia), Patara in Anatolia (in modern-day Antalya Province, Turkey) during the time of the Roman Empire. Because of the many miracles attributed to his intercession, he is also known as Nicholas the Wonderworker. Saint Nicholas is the patron saint of sailors, merchants, archers, repentant thieves, children, brewers, pawnbrokers, toymakers, unmarried people, and students in various cities and countries around Europe. His reputation evolved among the pious, as was common for early Christian saints, and his legendary habit of secret gift-giving gave rise to the folklore of Santa Claus ("Saint Nick") through Sinterklaas. Little is known about the historical Saint Nicholas. The earliest accounts of his life were written centuries after his death and probably contain legendary elaborations. H ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Priest
A priest is a religious leader authorized to perform the sacred rituals of a religion, especially as a mediatory agent between humans and one or more deity, deities. They also have the authority or power to administer religious rites; in particular, rites of sacrifice to, and propitiation of, a deity or deities. Their office or position is the "priesthood", a term which also may apply to such persons collectively. A priest may have the duty to hear confessions periodically, give marriage counseling, provide prenuptial counseling, give spiritual direction, teach catechism, or visit those confined indoors, such as the sick in hospitals and nursing homes. Description According to the trifunctional hypothesis of prehistoric Proto-Indo-European society, priests have existed since the earliest of times and in the simplest societies, most likely as a result of agricultural surplus#Neolithic, agricultural surplus and consequent social stratification. The necessity to read sacred text ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Iconography
Iconography, as a branch of art history, studies the identification, description and interpretation of the content of images: the subjects depicted, the particular compositions and details used to do so, and other elements that are distinct from artistic style. The word ''iconography'' comes from the Ancient Greek, Greek ("image") and ("to write" or ''to draw''). A secondary meaning (based on a non-standard translation of the Greek and Russian equivalent terms) is the production or study of the religious images, called "Icon, icons", in the Byzantine art, Byzantine and Eastern Orthodox Churches, Orthodox Christian tradition. This usage is mostly found in works translated from languages such as Greek or Russian, with the correct term being "icon painting". In art history, "an iconography" may also mean a particular depiction of a subject in terms of the content of the image, such as the number of figures used, their placing and gestures. The term is also used in many academic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Raška Architectural School
Raška architectural school (), also known as the Raška style (Рашки стил, ''Raški stil''), or simply as the Raška school, is an ecclesiastical architectural style that flourished in the Serbian Middle Ages (ca. 1170–1300), during the reign of the Nemanjić dynasty. The style is present in several notable churches and monasteries: Studenica, Peć, Sopoćani, Morača, Arilje and many others. This style combines traditional Slavic architecture with early Christian church-design, and often utilizes a combination of stone and wood material. Raška has the only extant significant, historical monument from the time of the acceptance of Christianity -- Church of the Holy Apostles Peter and Paul, Ras -- in Novi Pazar. Meanwhile, the other state, Zeta, had characteristics of the early Romanesque period, Latin in style. Towards the end of the 12th century, however, Stefan Nemanja united Raška and Duklja. When his young son Sava founded the independent church in 1219, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ottoman Serbia
Ottoman Serbia refers to the Ottoman Empire, Ottoman period in the history of Serbia. Various regions of medieval Serbia came under Ottoman rule already at the end of the 14th century, while the Serbian Despotate fell in 1459. Northern regions of what is now the Republic of Serbia were incorporated into the Ottoman Empire during later conquests, from 1521 to 1552. Since the Habsburg Empire, Habsburg expansion towards those northern regions, in 1699 and 1718, Ottoman rule was gradually reduced to Serbian territories south of the Sava and Danube rivers (1739). From 1804 to 1830, the Principality of Serbia was gradually restored, as a vassal state of the Ottoman Empire. It gained independence in 1878, and expanded into southern regions, thus reducing Ottoman control to the historical region of the Old Serbia, that was liberated in 1912, thus ending Ottoman rule in Serbian lands. The Ottoman conquest of the Balkans was initiated in the middle of the 15th century, leding to consequent ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Iconostasis
In Eastern Christianity, an iconostasis () is a wall of icons and religious paintings, separating the nave from the sanctuary in a Church (building), church. ''Iconostasis'' also refers to a portable icon stand that can be placed anywhere within a church. The iconostasis evolved from the Byzantine architecture, Byzantine templon, a process complete by the 15th century. A direct comparison for the function of the main iconostasis can be made to the layout of the great Temple in Jerusalem. That Temple was designed with three parts. The holiest and inner-most portion was that where the Ark of the Covenant was kept. This portion, the Holy of Holies, was separated from the second larger part of the building's interior by a curtain, the parochet , "veil of the temple". Only the High Priest (Judaism), High Priest was allowed to enter the Holy of Holies. The third part was the entrance court. This architectural tradition for the two main parts can be seen carried forward in Christian ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Narthex
The narthex is an architectural element typical of Early Christian art and architecture, early Christian and Byzantine architecture, Byzantine basilicas and Church architecture, churches consisting of the entrance or Vestibule (architecture), vestibule, located at the west end of the nave, opposite the church's main altar. Traditionally the narthex was a part of the church building, but was not considered part of the church proper. In early Christian churches the narthex was often divided into two distinct parts: an esonarthex (inner narthex) between the west wall and the body of the church proper, separated from the nave and aisles by a wall, arcade (architecture), arcade, colonnade, screen, or rail, and an external closed space, the exonarthex (outer narthex), a court in front of the church façade delimited on all sides by a colonnade as in the first Old St. Peter's Basilica, St. Peter's Basilica in Rome or in the Basilica of Sant'Ambrogio in Milan. The exonarthex may have bee ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Apse
In architecture, an apse (: apses; from Latin , 'arch, vault'; from Ancient Greek , , 'arch'; sometimes written apsis; : apsides) is a semicircular recess covered with a hemispherical Vault (architecture), vault or semi-dome, also known as an ''exedra''. In Byzantine architecture, Byzantine, Romanesque architecture, Romanesque, and Gothic architecture, Gothic Architecture of cathedrals and great churches, Christian church architecture, church (including cathedral and abbey) architecture, the term is applied to a semi-circular or polygonal termination of the main building at the liturgical east and west, liturgical east end (where the altar is), regardless of the shape of the roof, which may be flat, sloping, domed, or hemispherical. Smaller apses are found elsewhere, especially in shrines. Definition An apse is a semicircular recess, often covered with a hemispherical vault. Commonly, the apse of a church, cathedral or basilica is the semicircular or polygonal termination to the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |