|
Cheetham Close
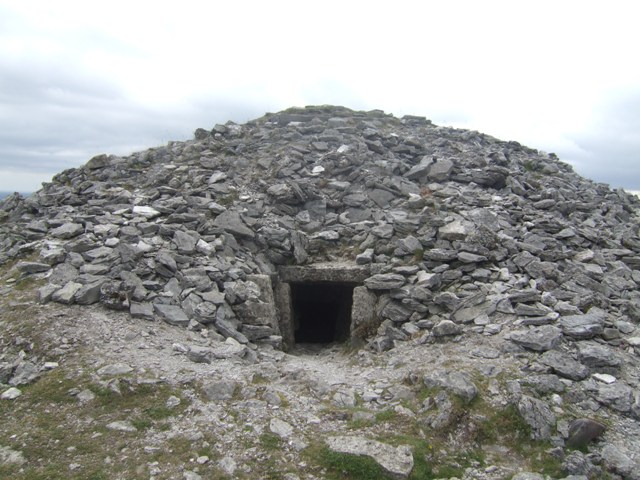
Cheetham Close is a megalithic site and scheduled ancient monument located in Lancashire, very close to the boundary with Greater Manchester, England. The megalith was in good condition until a farmer from Turton sledgehammered the circle in the 1870s. According to an article published in 1829, Cheetham Close was once a druidical ritual place and a Roman road passed 'within two hundred yards' of the megalith. The stone circle at Cheetham Close measured about in diameter. Six stones are definitely part of the circle and other smaller stones are scattered about the place. The monument has been damaged, and the stones fractured. Archaeological surveys The area was surveyed in 1850 by Dryden, who identified a circle of six stones. In 1871 Greenhalgh identified a seventh stone and drew attention to the destruction of the site. In 1894 French discovered a second site which was a "ring bank" type cairn. A saddle quern was found in 1954 and the site was scheduled in 1958. Three barbed ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lancashire
Lancashire ( , ; abbreviated ''Lancs'') is a ceremonial county in North West England. It is bordered by Cumbria to the north, North Yorkshire and West Yorkshire to the east, Greater Manchester and Merseyside to the south, and the Irish Sea to the west. The largest settlement is Preston, Lancashire, Preston, and the county town is the city of Lancaster, Lancashire, Lancaster. The county has an area of and a population of 1,490,300. Preston is located near the centre of the county, which is urbanised and includes the towns of Blackburn and Burnley; the seaside resort of Blackpool lies to the west, and Lancaster, Lancashire, Lancaster is in the north. For Local government in England, local government purposes the county comprises a non-metropolitan county, with twelve districts, and two Unitary authorities of England, unitary authority areas: Blackburn with Darwen and Borough of Blackpool, Blackpool. Lancashire County Council and the two unitary councils collaborate through the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cairn
A cairn is a human-made pile (or stack) of stones raised for a purpose, usually as a marker or as a burial mound. The word ''cairn'' comes from the (plural ). Cairns have been and are used for a broad variety of purposes. In prehistory, they were raised as markers, as memorials and as burial monuments (some of which Chambered cairn, contained chambers). In the modern era, cairns are often raised as landmarks, especially to mark the summits of mountains, and as Trail blazing, trail markers. They vary in size from small piles of stones to entire artificial hills, and in complexity from loose conical rock piles to elaborate megalithic structures. Cairns may be painted or otherwise decorated, whether for increased visibility or for religious reasons. History Europe The building of cairns for various purposes goes back into prehistory in Eurasia, ranging in size from small rock sculptures to substantial human-made hills of stone (some built on top of larger, natural hills). ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
History Of Lancashire
Lancashire is a county of England, in the northwest of the country. The county did not exist in 1086, for the Domesday Book, and was apparently first created in 1182, making it one of the youngest of the traditional counties. The historic county consisted of two separate parts. The main part runs along the northwestern coast of England. When it included Manchester and Liverpool, it had a greatest length of 76 miles, and breadth of 45 miles, and an area of 1,208,154 acres. The northern detached part of the old county palatine, consisting of Furness and Cartmell, was 25 miles in length, 23 miles in breadth and was separated from the main portion of Lancashire by Morecambe Bay and the Kendal district of Westmorland. The highest point in the historic county is at the Old Man of Coniston. As a county palatine, the Duke of Lancaster had sovereignty rights in the areas of justice and administration within the county. However the third man to hold the title, Henry Bolingbroke, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Buildings And Structures In Blackburn With Darwen
A building or edifice is an enclosed structure with a roof, walls and windows, usually standing permanently in one place, such as a house or factory. Buildings come in a variety of sizes, shapes, and functions, and have been adapted throughout history for numerous factors, from building materials available, to weather conditions, land prices, ground conditions, specific uses, prestige, and aesthetic reasons. To better understand the concept, see ''Nonbuilding structure'' for contrast. Buildings serve several societal needs – occupancy, primarily as shelter from weather, security, living space, privacy, to store belongings, and to comfortably live and work. A building as a shelter represents a physical separation of the human habitat (a place of comfort and safety) from the ''outside'' (a place that may be harsh and harmful at times). buildings have been objects or canvasses of much artistic expression. In recent years, interest in sustainable planning and building practi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Humphrey Chetham
Humphrey Chetham (10 July 1580 – 20 September 1653) was an English textile merchant, financier and philanthropist, responsible for the creation of Chetham's Hospital and Chetham's Library, the oldest public library in the English-speaking world.Crosby 2008. Life Chetham was born in Crumpsall, Lancashire, England, the son of Henry Chetham, a successful Manchester merchant who lived in Crumpsall Hall and his wife, Jane (c.1542–1616), the daughter of Robert Wroe of Heaton. He was educated at Manchester Grammar School, and in 1597 was apprenticed to Samuel Tipping, a Manchester linen draper. In 1605, he moved to London with his brother George and set up a partnership with him trading in various textiles. The business was successful, since the fabric was bought in London and sold for a higher price in Manchester. He acquired Clayton Hall in Manchester as his home, and in 1628 was also able to buy Turton Tower from William Orrell. In 1631, he was asked to be knighted afte ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scheduled Monuments In Lancashire
__NOTOC__ This is a list of scheduled monuments in the English county of Lancashire. In the United Kingdom, a scheduled monument is a "nationally important" archaeological site or historic building that has been given protection against unauthorised change by being placed on a list (or "schedule") by the Secretary of State for Digital, Culture, Media and Sport; Historic England takes the leading role in identifying such sites. Scheduled monuments are defined in the Ancient Monuments and Archaeological Areas Act 1979 and the National Heritage Act 1983. There are about 20,000 scheduled monument entries on the list, which is maintained by Historic England; more than one site can be included in a single entry. While a scheduled monument can also be recognised as a listed building, Historic England considers listed building status as a better way of protecting buildings than scheduled monument status. If a monument is considered by Historic England to "no longer merit scheduling" i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arrowhead
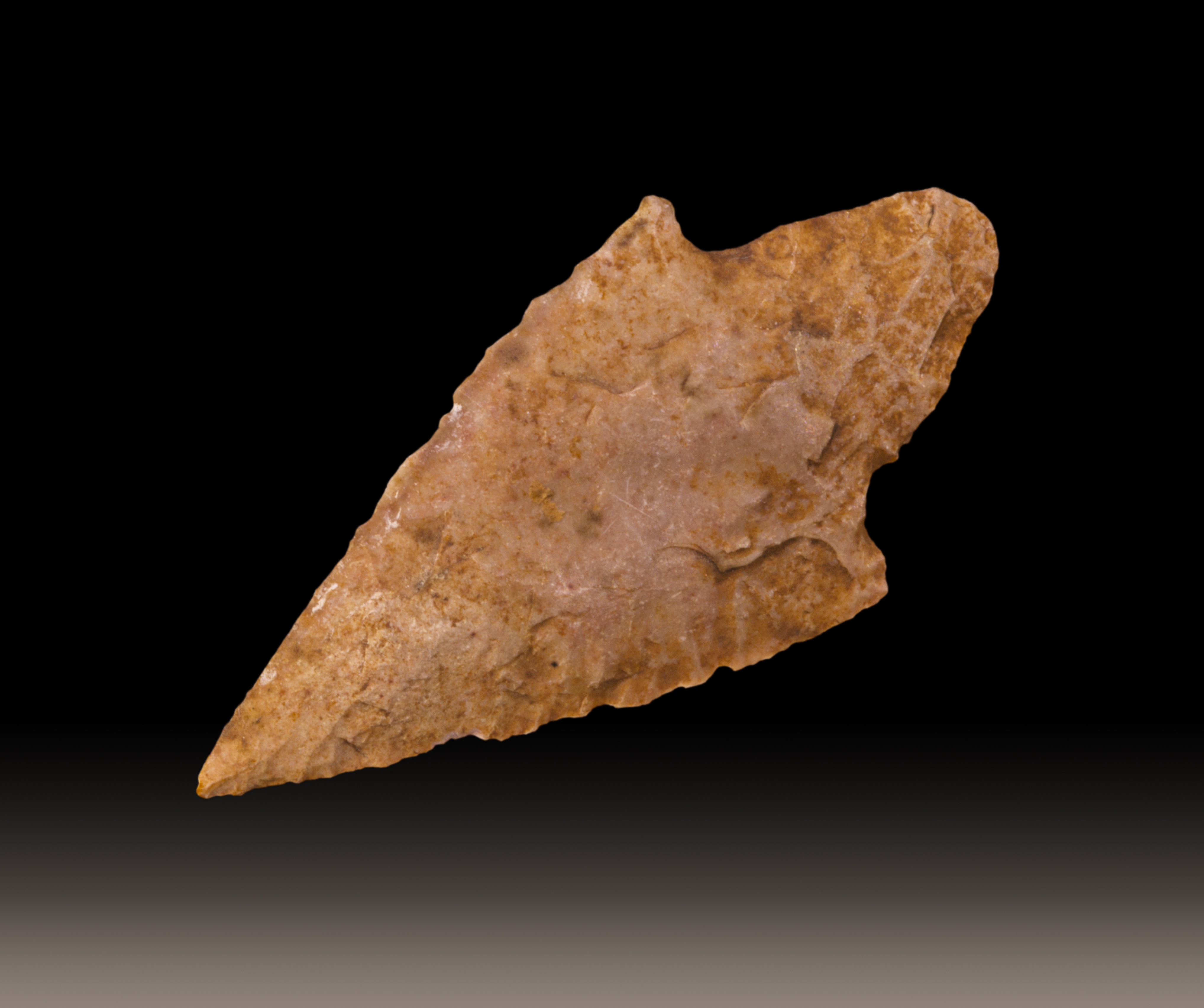
An arrowhead or point is the usually sharpened and hardened tip of an arrow, which contributes a majority of the projectile mass and is responsible for impacting and penetrating a target, or sometimes for special purposes such as signaling. The earliest arrowheads were made of stone and of organic materials; as human civilizations progressed, other alloy materials were used. Arrowheads are important archaeological artifacts; they are a subclass of projectile points. Modern enthusiasts still "produce over one million brand-new spear and arrow points per year". A craftsman who manufactures arrowheads is called an arrowsmith. History In the Stone Age, people used sharpened bone, flintknapped stones, flakes, and chips and bits of rock as weapons and tools. Such items remained in use throughout human civilization, with new materials used as time passed. As archaeological artifacts such objects are classed as projectile points, without specifying whether they were ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Barb
Barb or the BARBs or ''variation'' may refer to: People * Barb (name), a list of people and fictional characters with the given name or surname * Barb, a term used by fans of Nicki Minaj to refer to themselves * The Barbs, a band Places * Barb, Ontario, Canada * DeKalb, Illinois, USA; nicknamed ''Barb City'' Animals * Barb (feather), the branches issuing from the rachis of feathers * Barb (fish), common name for a range of freshwater fish * Barb horse, a breed from North Africa * Barb (pigeon), a breed of domestic pigeon * Australian Kelpie or barb, a breed of dog * The Barb (1863–1888), Australian Thoroughbred racehorse Implements * Barding or barb, a type of armor for horses * A backward-facing point on a fish hook or similar implement, rendering extraction from the victim's flesh more difficult * A type of pipe fitting called Piping_and_plumbing_fittings#Barb, barb, used to connect hosing (the ridges face backward, making insertion easy and removal difficult) * Barb, a sho ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quern-stone
A quern-stone is a stone tool for hand-grinding a wide variety of materials, especially for various types of grains. They are used in pairs. The lower stationary stone of early examples is called a ''saddle quern'', while the upper mobile stone is called a ''muller'', ''rubber'', or ''handstone''. The upper stone was moved in a back-and-forth motion across the saddle quern. Later querns are known as ''rotary querns''. The central hole of a rotary quern is called the ''eye'', and a dish in the upper surface is known as the ''hopper''. A ''handle slot'' contained a handle which enabled the rotary quern to be rotated. They were first used in the Neolithic era to grind cereals into flour. Design The upper stones were usually concave while the lower ones were convex. Quern-stones are frequently identifiable by their grooved working surfaces which enabled the movement of flour. Sometimes a millrind was present as a piece of wood (or other material), which allowed the cereal et ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stone Circle
A stone circle is a ring of megalithic standing stones. Most are found in Northwestern Europe – especially Stone circles in the British Isles and Brittany – and typically date from the Late Neolithic and Early Bronze Age, with most being built between 3300 and 2500 BC. The best known examples include those at the henge monument at Avebury, the Rollright Stones, Castlerigg, and elements within the ring of standing stones at Stonehenge. Scattered examples exist from other parts of Europe. Later, during the Iron Age, stone circles were built in southern Scandinavia. The archetypical stone circle is an uncluttered enclosure, large enough to congregate inside, and composed of megalithic stones. Often similar structures are named 'stone circle', but these names are either historic, or incorrect. Examples of commonly misinterpreted stone circles are ring cairns, burial mounds, and kerb cairns. Although it is often assumed there are thousands of stone circles across the Br ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
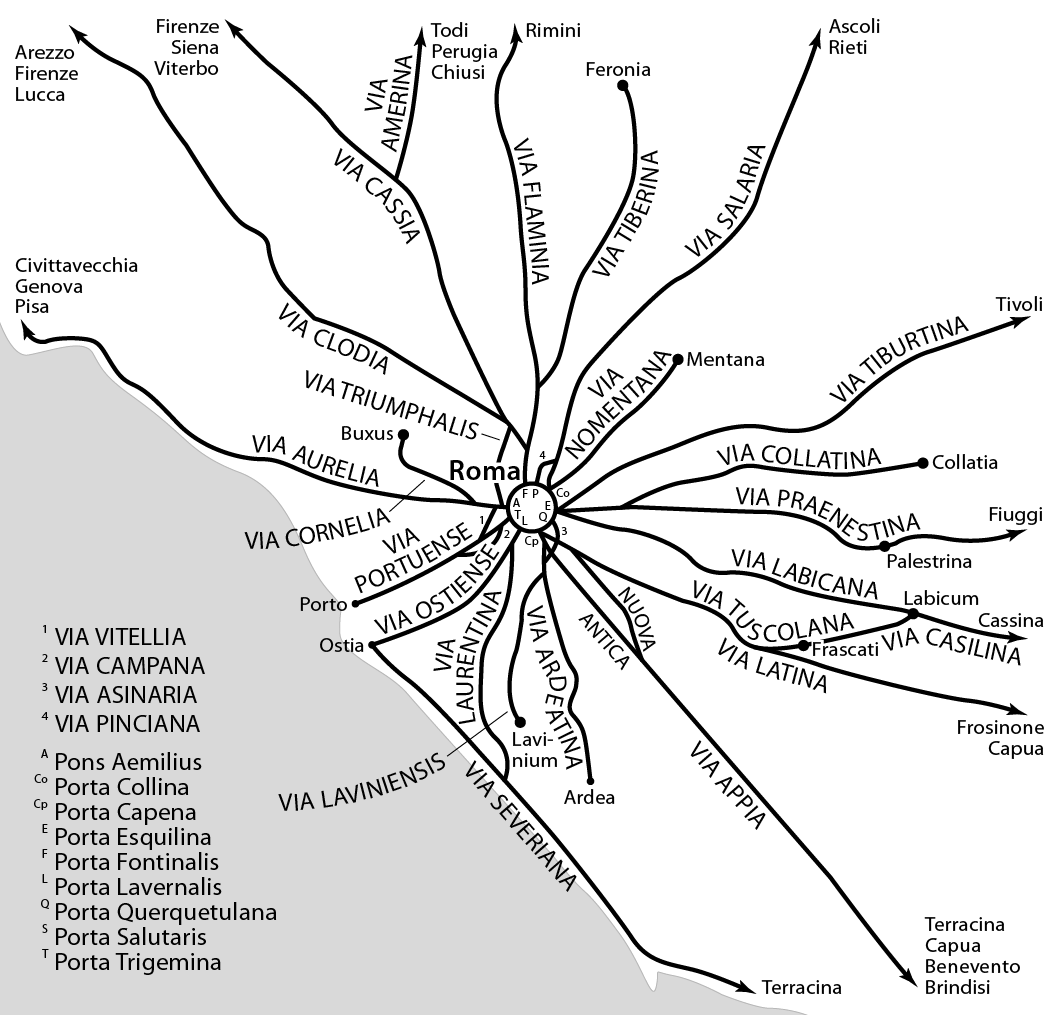
Roman Road
Roman roads ( ; singular: ; meaning "Roman way") were physical infrastructure vital to the maintenance and development of the Roman state, built from about 300 BC through the expansion and consolidation of the Roman Republic and the Roman Empire. They provided efficient means for the overland movement of armies, officials, civilians, inland carriage of official communications, and trade goods. Roman roads were of several kinds, ranging from small local roads to broad, long-distance highways built to connect cities, major towns and military bases. These major roads were often stone-paved and metaled, cambered for drainage, and were flanked by footpaths, bridleways and drainage ditches. They were laid along accurately surveyed courses, and some were cut through hills or conducted over rivers and ravines on bridgework. Sections could be supported over marshy ground on rafted or piled foundations.Corbishley, Mike: "The Roman World", page 50. Warwick Press, 1986. At the peak of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |