|
Chaturmukha Basadi, Gerusoppa
Chaturmukha Basadi is a symmetrical Jain temple located in Gerusoppa in Honnavar Taluk of Uttara Kannada district in the Indian state of Karnataka. The temple is situated near the banks of the Sharavati. History The territory of Gerusoppa was a Jain capital during 1409–1610 CE ruled by the Saluva dynasty of the Vijayanagara Empire. It is said that 1,084 temples existed in the region, but were destroyed and presently only six remain. In 1865, the veranda roof, the spire and the floor slabs were carted away by tehsildars from Honnavar for construction of another temple. There is an inscription dated from the 16th century that mentions Rani Chennabhairadevi's (popularly called the "Pepper Queen") ascension to power. The chaturmukha temple was constructed in 1562 CE during the reign of Chennabhairadevi. Gerusoppa also received royal patronage from the Hoysala Empire. Architecture Chaturmukha Basadi is a famous Jain center located in the Gerusoppa. The temple is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jainism
Jainism ( ), also known as Jain Dharma, is an Indian religion. Jainism traces its spiritual ideas and history through the succession of twenty-four tirthankaras (supreme preachers of ''Dharma''), with the first in the current time cycle being Rishabhadeva, whom the tradition holds to have lived millions of years ago, the twenty-third ''tirthankara'' Parshvanatha, whom historians date to the 9th century BCE, and the twenty-fourth ''tirthankara'' Mahavira, around 600 BCE. Jainism is considered to be an eternal ''dharma'' with the ''tirthankaras'' guiding every time cycle of the cosmology. The three main pillars of Jainism are ''ahiṃsā'' (non-violence), ''anekāntavāda'' (non-absolutism), and ''aparigraha'' (asceticism). Jain monks, after positioning themselves in the sublime state of soul consciousness, take five main vows: ''ahiṃsā'' (non-violence), ''satya'' (truth), ''asteya'' (not stealing), ''brahmacharya'' (chastity), and ''aparigraha'' (non-possessiveness). These pr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
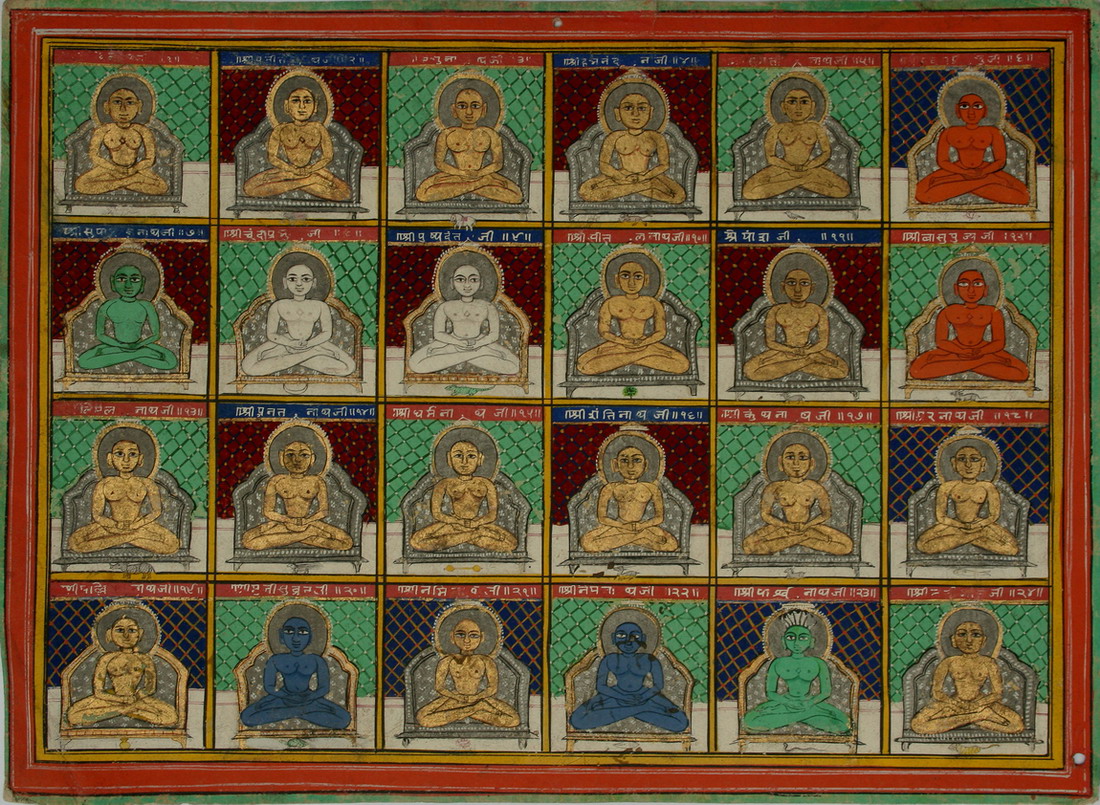
Tirthankara
In Jainism, a ''Tirthankara'' (Sanskrit: '; English language, English: literally a 'Ford (crossing), ford-maker') is a saviour and spiritual teacher of the ''Dharma (Jainism), dharma'' (righteous path). The word ''tirthankara'' signifies the founder of a ''Tirtha (Jainism), tirtha'', which is a fordable passage across the sea of interminable births and deaths, the ''Saṃsāra (Jainism), saṃsāra''. According to Jains, a ''Tirthankara'' is an individual who has conquered the ''saṃsāra'', the cycle of death and rebirth, on their own, and made a path for others to follow. After understanding the true nature of the self or soul, the ''Tīrthaṅkara'' attains ''Kevala Jnana'' (omniscience). Tirthankara provides a bridge for others to follow the new teacher from ''saṃsāra'' to ''moksha'' (liberation). In Jain cosmology, the wheel of time is divided in two halves, Utsarpiṇī' or ascending time cycle and ''avasarpiṇī'', the descending time cycle (said to be current no ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mahavira
Mahavira (Sanskrit: महावीर) also known as Vardhaman, was the 24th ''tirthankara'' (supreme preacher) of Jainism. He was the spiritual successor of the 23rd ''tirthankara'' Parshvanatha. Mahavira was born in the early part of the 6th century BCE into a royal Kshatriya Jain family in ancient India. His mother's name was Trishala and his father's name was Siddhartha. They were lay devotees of Parshvanatha. Mahavira abandoned all worldly possessions at the age of about 30 and left home in pursuit of spiritual awakening, becoming an ascetic. Mahavira practiced intense meditation and severe austerities for twelve and a half years, after which he attained '' Kevala Jnana'' (omniscience). He preached for 30 years and attained Moksha (liberation) in the 6th century BCE, although the year varies by sect. Historically, Mahavira, who revived and preached Jainism in ancient India, was an older contemporary of Gautama Buddha. Jains celebrate ''Mahavir Janma Kalyanak'' every yea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ganesha
Ganesha ( sa, गणेश, ), also known as Ganapati, Vinayaka, and Pillaiyar, is one of the best-known and most worshipped deities in the Hindu pantheon and is the Supreme God in Ganapatya sect. His image is found throughout India. Hindu denominations worship him regardless of affiliations. Devotion to Ganesha is widely diffused and extends to Jains and Buddhists and includes Nepal, Sri Lanka, Thailand, Indonesia ( Java and Bali), Singapore, Malaysia, Philippines, and Bangladesh and in countries with large ethnic Indian populations including Fiji, Guyana, Mauritius, and Trinidad and Tobago. Although Ganesha has many attributes, he is readily identified by his elephant head. He is widely revered, more specifically, as the remover of obstacles and thought to bring good luck; the patron of arts and sciences; and the deva of intellect and wisdom. As the god of beginnings, he is honoured at the start of rites and ceremonies. Ganesha is also invoked as a patron of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Virabhadra
Virabhadra (), also rendered Veerabhadra, Veerabathira, and Veerabathiran, is a fierce form of the Hindu god Shiva. He is created by the wrath of Shiva, when the deity hurls a lock of his matted hair upon the ground, upon hearing of the self-immolation of his consort, Sati, at the Daksha yajna.the Horse-sacrifice of the Prajapati Daksha The Mahabharata translated by Kisari Mohan Ganguli (1883–1896), Book 12: Santi Parva: Mokshadharma Parva: Section CCLXXXIV. p. 315 Mahadeva created from his mouth a terrible Being whose very sight could make one's hair stand on its end. The blazing flames that emanated from his body r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jwalamalini
Jwalamalini or ( sa, ज्वालामालिनी, kan, ಜ್ವಾಲಾಮಾಲಿನೀ) is the Yakshini (guardian spirit) of the Eighth Tirthankara, Shri Bhagwan Chandraprabhu in Jainism and was one of the most widely invoked Yakshinis in Karnataka during the early medieval period. Etymology and origin ' refers to ''the glow of fire'', ' implies ''one of bears the garlands (of)''. A well known historical text Jwalamalini Kalpa was composed by Jain Acharya Indranandi in 939 AD in Manyakheta during the rule of Rashtrakuta Krishnaraj. It was inspired by and older and complex text written by Helacharya before him, who had vanquished a Brahma-Rakshasa by invoking Jwalamalini. Jwalamalini also appears in various Puranas, the Vayu Purana associates her with Shiva, the Brahmanda Purana and the Matsya Purana associate her with Shakti. Jwalamailni in Jain Mythology Jain literature also recognize her as or the fire goddess. Her iconic forms depict her with flames issu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gajalakshmi
Gajalakshmi (), also spelt as Gajalaxmi, is one of the most significant '' Ashtalakshmi'' aspects of the Hindu goddess of prosperity, Lakshmi. Mythology In Hindu mythology, Gajalakshmi is regarded to have restored the wealth and power lost by Indra when she rose from the Samudra Manthana, the churning of the ocean. She is the form of the goddess who stands for animal wealth, as well as other symbols of wealth that represent strength. Iconography In a sixth century BCE sculpture, the goddess is depicted holding a lotus in her left hand and a lotus cornucopia in her right hand. There are two lions at her feet, two elephants bathing her with life giving waters, and two female attendants to her left and right side holding flywhisks. Depictions An image is found from the 2nd century BCE, possibly in Buddhist contexts, and appears on the railings from the Buddhist site of Bharhut, from 125-100 BCE. It appears on a 1st-century BCE coin of Azilises, and a 3rd-century CE coin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dvarapala
A Dvarapala or Dvarapalaka (Sanskrit, "door guard"; IAST: ' ) is a door or gate guardian often portrayed as a warrior or fearsome giant, usually armed with a weapon - the most common being the ''gada'' (mace). The dvarapala statue is a widespread architectural element throughout Hindu, Buddhist and Jaina cultures, as well as in areas influenced by them like Java. Names In most Southeast Asian languages (including Thai, Burmese, Vietnamese, Khmer and Javanese), these protective figures are referred to as ''dvarapala''. Sanskrit ''dvāra'' means "gate" or "door", and ''pāla'' means "guard" or "protector". The related name in Indonesian and Malaysia is ''dwarapala''. Equivalent door guardians in northern Asian languages are ''Kongōrikishi'' or '' Niō'' in Japanese, ''Heng Ha Er Jiang'' in Chinese, and ''Narayeongeumgang'' in Korean. Origin and forms Dvarapalas as an architectural feature have their origin in tutelary deities, like Yaksha and warrior figures ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hoysala Empire
The Hoysala Empire was a Kannadiga power originating from the Indian subcontinent that ruled most of what is now Karnataka between the 10th and the 14th centuries. The capital of the Hoysalas was initially located at Belur, but was later moved to Halebidu. The Hoysala rulers were originally from Malenadu, an elevated region in the Western Ghats. In the 12th century, taking advantage of the internecine warfare between the Western Chalukya Empire and Kalachuris of Kalyani, the Hoysalas annexed areas of present-day Karnataka and the fertile areas north of the Kaveri delta in present-day Tamil Nadu. By the 13th century, they governed most of Karnataka, minor parts of Tamil Nadu and parts of western Andhra Pradesh and Telangana in the Deccan Plateau. The Hoysala era was an important period in the development of South Indian art, architecture, and religion. The empire is remembered today primarily for Hoysala architecture; 100 surviving temples are scattered across Karnataka. Well ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
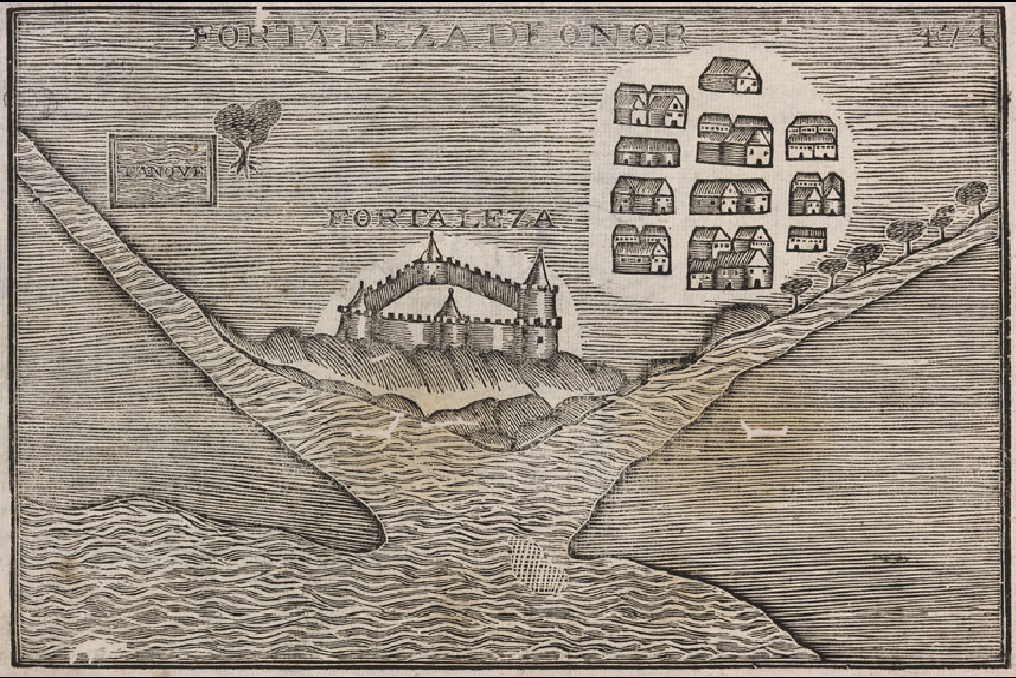
Honnavar
Honnavar is a town in Uttara Kannada district of Karnataka, India. History Honnavar is a port town in Coastal Karnataka known for its beautiful landscapes and rich history. The port hosted foreign traders from the Arab world, as well as later from European countries such as Portugal, England and the Netherlands. The 14th century Moroccan traveler Ibn Batutta stopped in the port during his voyage. Portuguese Rule During the Portuguese domination a Fortress was built in the 16th century to protect trade in the Indian Ocean. Later in the 18th the English built warehouses at the port. Transportation ;Rail The Konkan Railway line passes through Honnavar, and its longest bridge is 2.065 km in length and is in Honnavar, over the Sharavati River. ;Sea In October 2013 the Karnataka government announced plans to develop a new port at Honnavar, to be funded by a public–private partnership (PPP) model. ;Inland Water There are proposals for improvements to the Inland Water Tr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.png)