|
Chain Gun
A chain gun is a type of autocannon or machine gun that uses an external source of power to cycle the weapon's action via a continuous loop of chain, similar to that used on a motorcycle or bicycle, instead of diverting excess energy from the cartridges' propellant as in a typical automatic firearm. History In 1972, Hughes Helicopters began a company-funded research effort to design a single machine gun to fire the U.S. Army's M50 round. In April 1973, the program fired test rounds in more powerful WECOM linked ammunition, from a prototype A model. In January 1975, a model "C" was added, a linkless version for the proposed Advanced Attack Helicopter YAH-64. The helicopter was later adopted as the Hughes Model 77/AH-64A Apache, with the model C receiving the designation M230 chain gun as its standard armament. In 1976, Hughes Helicopters patented the chain gun, and it has since been further developed into several other systems of different calibers.Richardson & Peaco ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
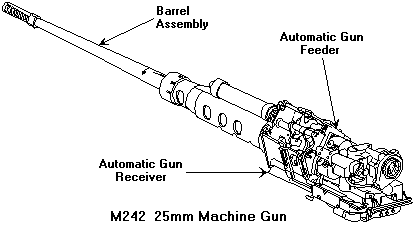
M242-2
M, or m, is the thirteenth letter of the Latin alphabet, used in the modern English alphabet, the alphabets of several western European languages and others worldwide. Its name in English is ''em'' (pronounced ), plural ''ems''. History The letter M is derived from the Phoenician Mem via the Greek Mu (Μ, μ). Semitic Mem is most likely derived from a " Proto-Sinaitic" (Bronze Age) adoption of the "water" ideogram in Egyptian writing. The Egyptian sign had the acrophonic value , from the Egyptian word for "water", ''nt''; the adoption as the Semitic letter for was presumably also on acrophonic grounds, from the Semitic word for "water", '' *mā(y)-''. Use in writing systems English In English, represents the voiced bilabial nasal . The Oxford English Dictionary (first edition) says that is sometimes a vowel, such as in words like ''spasm'' and in the suffix ''-ism''. In modern terminology, this is described as a syllabic consonant (IPA: ). M is the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chaingun
A chain gun is a type of autocannon or machine gun that uses an external source of power to cycle the weapon's action via a continuous loop of chain, similar to that used on a motorcycle or bicycle, instead of diverting excess energy from the cartridges' propellant as in a typical automatic firearm. History In 1972, Hughes Helicopters began a company-funded research effort to design a single machine gun to fire the U.S. Army's M50 round. In April 1973, the program fired test rounds in more powerful WECOM linked ammunition, from a prototype A model. In January 1975, a model "C" was added, a linkless version for the proposed Advanced Attack Helicopter YAH-64. The helicopter was later adopted as the Hughes Model 77/AH-64A Apache, with the model C receiving the designation M230 chain gun as its standard armament. In 1976, Hughes Helicopters patented the chain gun, and it has since been further developed into several other systems of different calibers.Richardson & Peacock, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bolt (firearms)
Bolt from a Karabiner 98k bolt-action rifle. Note the curved handle on the side for manual operation thumb"> Slide locked back on a Desert Eagle pistol, showing the gas-operated rotating bolt mechanism A bolt is the part of a repeating, breechloading firearm that blocks the rear opening (breech) of the barrel chamber while the propellant burns, and moves back and forward to facilitate loading/unloading of cartridges from the magazine. The firing pin and extractor are often integral parts of the bolt. The terms " breechblock" and "bolt" are often used interchangeably or without a clear distinction, though usually, a bolt is a type of breechblock that has a nominally circular cross-section. In most automatic firearms that use delayed blowback, recoil, or gas operation, the bolt itself is housed within the larger bolt carrier group (BCG), which contains additional parts that receives rearward push from a gas tube ( direct impingement) or a gas piston (short-stroke o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
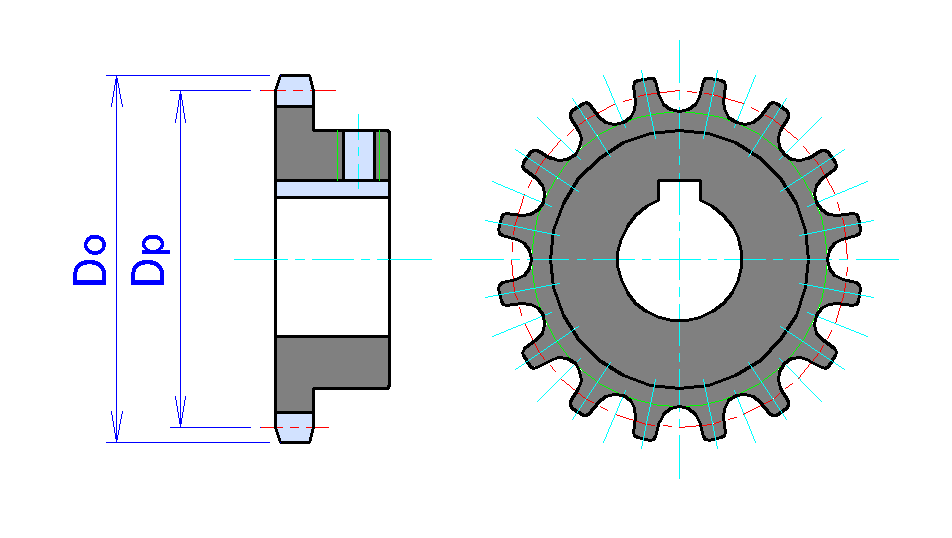
Sprocket
A sprocket, sprocket-wheel or chainwheel is a profiled wheel A wheel is a rotating component (typically circular in shape) that is intended to turn on an axle Bearing (mechanical), bearing. The wheel is one of the key components of the wheel and axle which is one of the Simple machine, six simple machin ... with teeth that mesh with a chain, rack and pinion, rack or other perforated or indented material. The name 'sprocket' applies generally to any wheel upon which radial projections engage a chain passing over it. It is distinguished from a gear in that sprockets are never meshed together directly, and differs from a pulley in that sprockets have teeth and pulleys are smooth except for timing pulleys used with toothed belts. Sprockets are used in bicycles, motorcycles, continuous track, tracked vehicles, and other machinery either to transmit rotary motion between two shafts where gears are unsuitable or to impart linear motion to a track, tape etc. Perhaps the most commo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electric Motor
An electric motor is a machine that converts electrical energy into mechanical energy. Most electric motors operate through the interaction between the motor's magnetic field and electric current in a electromagnetic coil, wire winding to generate Laplace force in the form of torque applied on the motor's shaft. An electric generator is mechanically identical to an electric motor, but operates in reverse, converting mechanical energy into electrical energy. Electric motors can be powered by direct current (DC) sources, such as from batteries or rectifiers, or by alternating current (AC) sources, such as a power grid, Inverter (electrical), inverters or electrical generators. Electric motors may also be classified by considerations such as power source type, construction, application and type of motion output. They can be brushed motor, brushed or brushless motor, brushless, single-phase electric power, single-phase, two-phase electric power, two-phase, or three-phase electric p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Roller Chain
Roller chain or bush roller chain is the type of chain drive most commonly used for transmission of mechanical power on many kinds of domestic, industrial and agricultural machinery, including conveyors, wire- and tube-drawing machines, printing presses, cars, motorcycles, and bicycles. It consists of a series of short cylindrical rollers held together by side links. It is driven by a toothed wheel called a sprocket. It is a simple, reliable, and efficientAs much as 98% efficient under ideal conditions, according to means of power transmission. Sketches by Leonardo da Vinci in the 16th century show a chain with a roller bearing. In 1800, James Fussell patented a roller chain on development of his balance lock and in 1880 Hans Renold patented a bush roller chain. Construction There are two types of links alternating in the bush roller chain. The first type is inner links, having two inner plates held together by two sleeves or bushings upon which rotate two rol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ShVAK Cannon
The ShVAK (, "Shpitalny-Vladimirov Aviation Large-calibre") was a 20 mm autocannon used by the Soviet Union during World War II. It was designed by Boris Shpitalniy and Semyon Vladimirov and entered production in 1936. ShVAK were installed in many models of Soviet aircraft. The TNSh was a version of the gun produced for light tanks (). ShVAK shares the name with its 12.7 mm heavy machine gun predecessor. Development and production 12.7x108mm ShVAK The development of the 12.7 mm ShVAK was in response to a Soviet government decree passed on 9 February 1931, directing domestic manufacturers to produce an aircraft machine gun for the 12.7×108mm cartridge that had been introduced a couple of years prior for the DK machine gun. Tula designer S.V. Vladimirov answered the call by producing basically an enlarged version of the ShKAS, with a 1246 mm long barrel and a total length of 1726 mm. The first prototype was ready for trials on May 28, 1932. The testing pr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Assault Rifle
An assault rifle is a select fire rifle that uses an intermediate cartridge, intermediate-rifle cartridge and a Magazine (firearms), detachable magazine.C. Taylor, ''The Fighting Rifle: A Complete Study of the Rifle in Combat'', F.A. Moyer ''Special Forces Foreign Weapons Handbook'', R.J. Scroggie, F.A. Moyer ''Special Forces Combat Firing Techniques'', Musgave, Daniel D., and Thomas B. Nelson, ''The World's Assault Rifles'', vol. II, The Goetz Company, Washington, D.C. (1967): 1 Assault rifles were first put into mass production and accepted into widespread service during World War II. The first assault rifle to see major usage was the German StG 44, a development of the earlier Maschinenkarabiner 42(H), Mkb 42.''Firearms: The Life Story of a Technology'', by Roger Pauly. Greenwood Publishing Group. 2004. pp. 145–146 [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gas-operated Reloading
Gas-operation is a system of operation used to provide energy to operate locked breech, autoloading firearms. In gas-operation, a portion of high-pressure gas from the cartridge being fired is used to power a mechanism to dispose of the spent case and insert a new cartridge into the chamber. Energy from the gas is harnessed through either a port in the barrel or a trap at the muzzle. This high-pressure gas impinges on a surface such as a piston head to provide motion for unlocking of the action, extraction of the spent case, ejection, cocking of the hammer or striker, chambering of a fresh cartridge, and locking of the action. History The first mention of using a gas piston in a single-shot breech-loading rifle comes from 1856, by the German Edward Lindner who patented his invention in the United States and Britain. In 1866, Englishman William Curtis filed the first patent on a gas-operated repeating rifle but subsequently failed to develop that idea further. Between 1883 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bofors 40 Mm L/60 Gun
The Bofors 40 mm Automatic Gun L/60 (often referred to simply as the "Bofors 40 mm gun", the "Bofors gun" and the like, see name) is an anti-aircraft autocannon, designed in the 1930s by the Swedish arms manufacturer AB Bofors. The gun was designed as an intermediate anti-aircraft gun, filling the gap between fast firing close-range small calibre anti-aircraft guns and slower firing long-range high calibre anti-aircraft guns. For its time, the Bofors 40 mm L/60 was perfectly suited for this role and outperformed competing designs in the years leading up to World War II in both effectiveness and reliability. It entered the export market around 1932 and was in service with 18 countries by 1939. Throughout World War II it became one of the most popular and widespread medium-weight anti-aircraft guns. It was used by the majority of the western Allies and some Axis powers such as Nazi Germany and Hungary. In the post-war era, the Bofors 40 mm L/60 design was not ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Recoil Operation
Recoil operation is an operating mechanism used to implement locked-breech autoloading firearms. Recoil operated firearms use the energy of recoil to cycle the action, as opposed to gas operation or blowback operation using the pressure of the propellant gas. History The earliest mention of recoil used to assist the loading of firearms is sometimes claimed to be in 1663 when an Englishman called Palmer proposed to employ either it or gases tapped along a barrel to do so. However no one has been able to verify this claim in recent times, although there is another automatic gun that dates from the same year, but its type and method of operation are unknown. Recoil-operation, if it was invented in 1663, would then lie dormant until the 19th century, when a number of inventors started to patent designs featuring recoil operation; this was due to the fact that the integrated disposable cartridge (both bullet and propellant in one easily interchangeable unit) made these designs vi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cam (mechanism)
A cam is a rotating or sliding piece in a linkage (mechanical), mechanical linkage used especially in transforming rotary motion into linear motion. It is often a part of a rotating wheel (e.g. an eccentric wheel) or shaft (e.g. a cylinder with an irregular shape) that strikes a lever at one or more points on its circular path. The cam can be a simple tooth, as is used to deliver pulses of power to a steam hammer, for example, or an Eccentric (mechanism), eccentric disc or other shape that produces a smooth reciprocating (back and forth) motion in the ''Cam follower, follower'', which is a lever making contact with the cam. A cam timer is similar, and these were widely used for electric machine control (an electromechanical timer in a washing machine being a common example) before the advent of inexpensive electronics, microcontrollers, integrated circuits, programmable logic controllers and digital control. Camshaft The cam can be seen as a device that converts rotational mot ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |