|
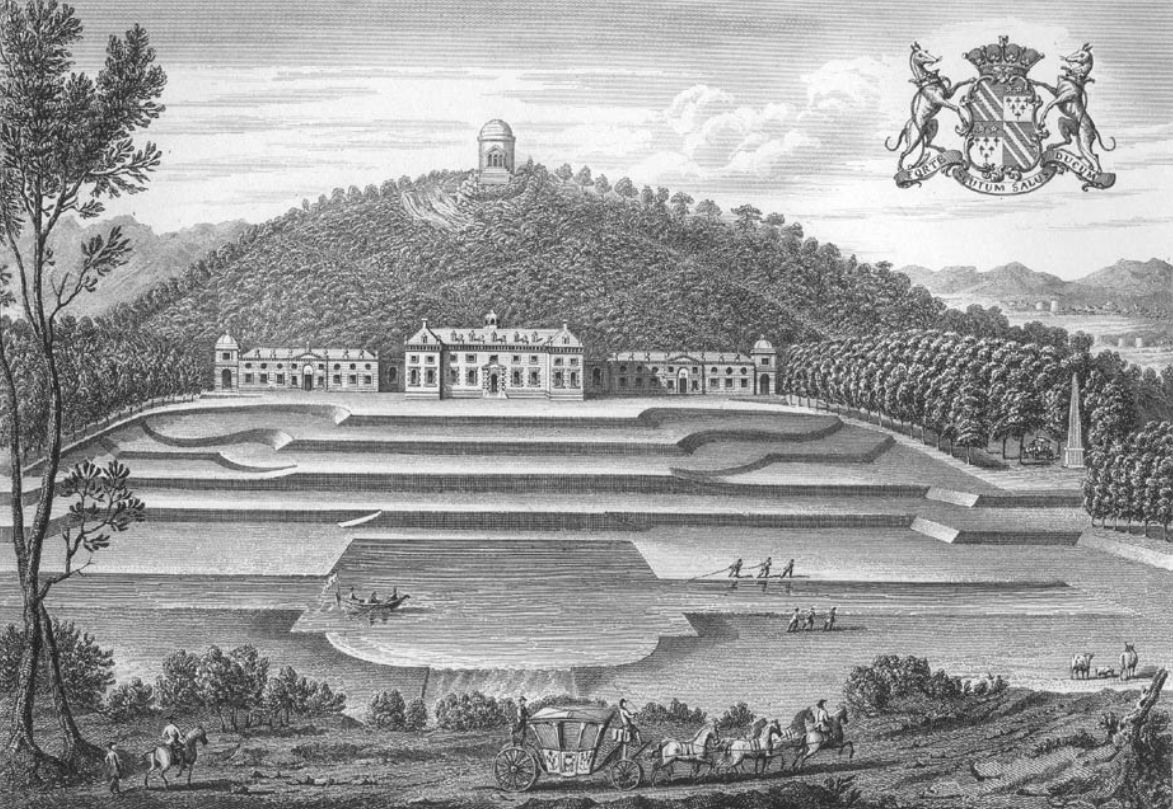
Castle Hill, Filleigh
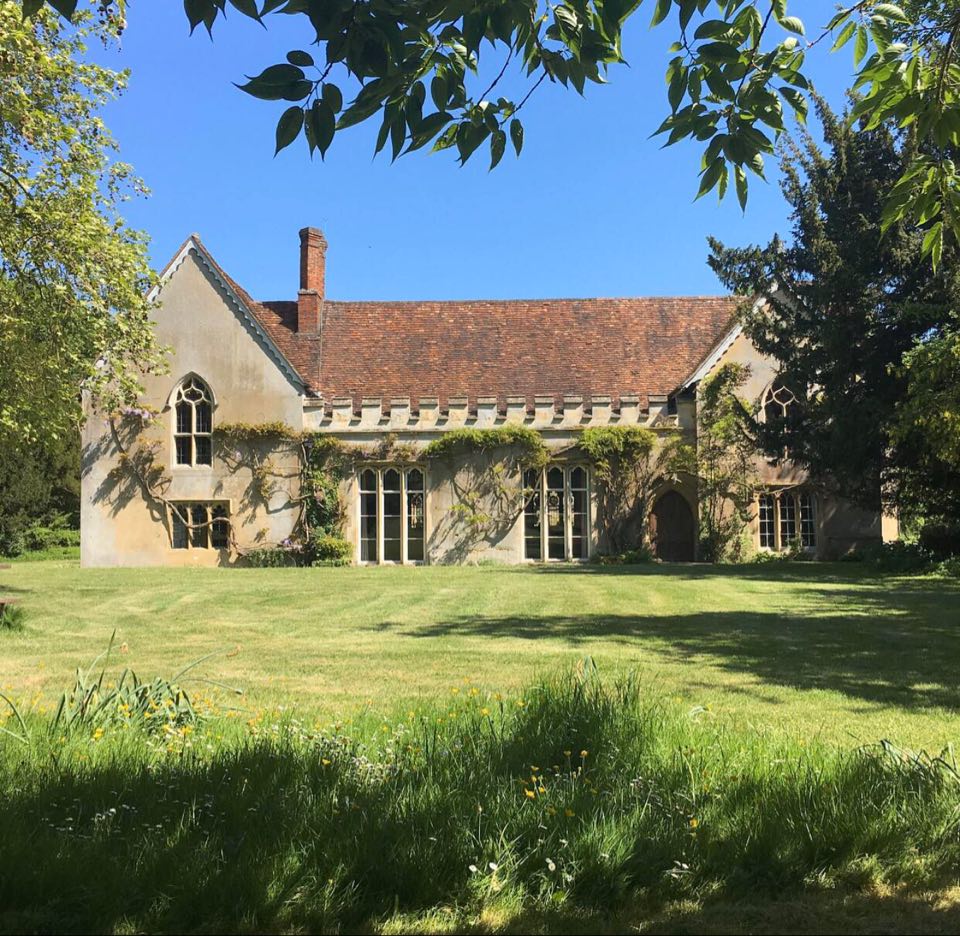
Castle Hill in the parish of Filleigh in North Devon, is an early Neo-Palladian country house situated north-west of South Molton and south-east of Barnstaple. It was built in 1730 by Baron Clinton, Hugh Fortescue, 14th Baron Clinton (1696–1751), who was later created in 1751 1st Earl Fortescue, Baron Fortescue and 1st Baron Clinton, Earl of Clinton, the son of Hugh Fortescue (1665–1719), Hugh Fortescue (died 1719), lord of the manor of Filleigh, Weare Giffard, etc., whose family is earliest recorded as residing in the 12th century at the manor of Whympston, Modbury, Whympston in the parish of Modbury in South Devon. The Earl Fortescue, Fortescue family became major land owners, influential in British and Westcountry, West Country history. Castle Hill is a rare example in Devon of an 18th-century country house, country mansion "on the grand scale". The house was substantially reconstructed following a disastrous fire in 1934. It was designated a Grade II* listed buildi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Whympston, Modbury
Whympston in the parish of Modbury in Devon, England, was a historic manor that belonged to the Fortescue family. Descent Fortescue As the 17th-century Fortescue mural monument in the parish church of Weare Giffard (see below) states, "Whympstone" (modern spelling "Whympston") in the parish of Modbury is the oldest known home of the Fortescue family. The manor of Whympston is thought to have been granted to them by King John in 1209, but according to Hoskins they were already in the district in about 1140, when Ralph Fortescue donated some land to Modbury Priory at about the time of its foundation. William Fortescue (died post-1406) William Fortescue (died post-1406), of Whympston married Elizabeth Beauchamp, widow of Richard Branscombe, a daughter of Sir John Beauchamp of Ryme in Dorset by his wife Margaret Whalesborough, and a co-heiress of her brother Thomas Beauchamp of Ryme. The Beauchamp family of Ryme was a junior branch of the Beauchamp feudal barons of Hatch B ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Portland Stone
Portland stone is a limestone geological formation (formally named the Portland Stone Formation) dating to the Tithonian age of the Late Jurassic that is quarried on the Isle of Portland in Dorset, England. The quarries are cut in beds of white-grey limestone separated by chert beds. It has been used extensively as a building stone throughout the British Isles, notably in major public buildings in London such as St Paul's Cathedral and Buckingham Palace. Portland stone is also exported to many countries, being used for example at the United Nations headquarters in New York City. Geology Portland stone formed in a marine environment, on the floor of a shallow, warm, sub-tropical sea probably near land (as evidenced by fossilised driftwood, which is not uncommon). When seawater is warmed by the sun, its capacity to hold dissolved gas is reduced; consequently, dissolved carbon dioxide (CO2) is released into the atmosphere as a gas. Calcium and bicarbonate ions within the wat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Richard Boyle, 3rd Earl Of Burlington
Richard Boyle, 3rd Earl of Burlington and 4th Earl of Cork (25 April 1694 – 4 December 1753) was a British architect and noble often called the "Apollo of the Arts" and the "Architect Earl". The son of the 2nd Earl of Burlington and 3rd Earl of Cork, Burlington never took more than a passing interest in politics despite his position as a Privy Counsellor and a member of both the British House of Lords and the Irish House of Lords. His great interests in life were architecture and landscaping, and he is remembered for being a builder and a patron of architects, craftsmen and landscapers, Indeed, he is credited with bringing Palladian architecture to Britain and Ireland. His major projects include Burlington House, Westminster School, Chiswick House and Northwick Park. Life Lord Burlington was born in Yorkshire into a wealthy Anglo-Irish aristocratic family, the only son of Charles Boyle, 2nd Earl of Burlington and his wife, Juliana Boyle ( Noel; 1672–1750). He succe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Manor House
A manor house was historically the main residence of the lord of the manor. The house formed the administrative centre of a manor in the European feudal system; within its great hall were usually held the lord's manorial courts, communal meals with manorial tenants and great banquets. The term is today loosely (though erroneously) applied to various English country houses, mostly at the smaller end of the spectrum, sometimes dating from the Late Middle Ages, which currently or formerly house the landed gentry. Manor houses were sometimes fortified, albeit not as fortified as castles, but this was often more for show than for defence. They existed in most European countries where feudalism was present. Function The lord of the manor may have held several properties within a county or, for example in the case of a feudal baron, spread across a kingdom, which he occupied only on occasional visits. Even so, the business of the manor was directed and controlled by regular mano ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tudor Architecture
The Tudor architectural style is the final development of medieval architecture in England and Wales, during the Tudor period (1485–1603) and even beyond, and also the tentative introduction of Renaissance architecture to Britain. It followed the Late Gothic Perpendicular style and, gradually, it evolved into an aesthetic more consistent with trends already in motion on the continent, evidenced by other nations already having the Northern Renaissance underway Italy, and especially French Renaissance architecture, France already well into its revolution in art, architecture, and thought. A subtype of Tudor architecture is Elizabethan architecture, from about 1560 to 1600, which has continuity with the subsequent Jacobean architecture in the early Stuart period. In the much more slow-moving styles of vernacular architecture, "Tudor" has become a designation for half-timbering, half-timbered buildings, although there are cruck and frame houses with half-timbering that consi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Weare Giffard
Weare Giffard is a small village, civil parish and former Manorialism, manor in the Torridge District, Torridge district, in north Devon, England. The church and manor house are situated 2 1/2 miles NW of Great Torrington in Devon. Most of the houses within the parish are situated some 1/2-mile east of the church. The church is situated on a hillside to the north and slightly above the wide and flat valley floor of the River Torridge. The Church of the Holy Trinity and the adjacent Weare Giffard Hall are designated members of the Grade I listed buildings in Devon. In 2011 the parish had a population of 345. History The historian of Devon Tristram Risdon (d. 1640) supposed the name Weare to be derived from a fish weir which was historically situated in the river to catch fish. The construction of a fish-weir generally required a licence from the feudal overlord, as naturally these affected the catches of other inhabitants further along the river. Many disputes are recorded in t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Manorialism
Manorialism, also known as seigneurialism, the manor system or manorial system, was the method of land ownership (or "Land tenure, tenure") in parts of Europe, notably France and later England, during the Middle Ages. Its defining features included a large, sometimes fortified manor house in which the lord of the manor and his dependants lived and administered a rural estate, and a population of labourers or Serfdom, serfs who worked the surrounding land to support themselves and the lord. These labourers fulfilled their obligations with labour time or in-kind produce at first, and later by cash payment as commercial activity increased. Manorialism was part of the Feudalism, feudal system. Manorialism originated in the Roman villa system of the Late Roman Empire, and was widely practised in Middle Ages, medieval western Europe and parts of central Europe. An essential element of feudal society, manorialism was slowly replaced by the advent of a money-based market economy and new ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hugh Fortescue, 5th Earl Fortescue
Hugh William Fortescue, 5th Earl Fortescue (14 June 1888 – 14 June 1958), styled Viscount Ebrington from 1905 until 1932, of Castle Hill in the parish of Filleigh, of Weare Giffard Hall, both in Devon and of Ebrington Manor in Gloucestershire, was a British peer, military officer, and Conservative politician. Origins Hugh Fortescue was the eldest son of Hugh Fortescue, 4th Earl Fortescue (1854–1932) by his wife Emily Ormsby-Gore, a daughter of William Ormsby-Gore, 2nd Baron Harlech. Career Early life He was educated at Eton College from 1901 to 1905, followed by the Royal Military College, Sandhurst. Military service In 1907 Fortescue joined the Royal Scots Greys. During the First World War (1914–18) he served in France as a regimental officer for the Scots Greys, followed by the Royal Corps of Signals. He was twice wounded in battle and received the Military Cross in 1917. Following the war he went to India where he served as an instructor at the Cavalry School at ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arthur Gore, 9th Earl Of Arran
Arthur Desmond Colquhoun Gore, 9th Earl of Arran (born 14 July 1938), styled Viscount Sudley between 1958 and 1983, is a British peer and Lord Temporal in the House of Lords, sitting with the Conservative Party. Early life Lord Arran was born in Westminster, the eldest son of The 8th Earl of Arran and the former Fiona Colquhoun, first daughter of Sir Iain Colquhoun of Luss, 7th Baronet. He was educated at Eton College and Balliol College, Oxford. Career He served in the Grenadier Guards, gaining the rank of second lieutenant. He was the assistant manager of the ''Daily Mail'', then assistant general manager of the ''Daily Express'' and the ''Sunday Express'' in the 1970s. He was a director of Waterstone's (1984–87). He succeeded as 9th Earl of Arran of the Aran Islands on 23 February 1983, upon the death of his father. In the Lords, Lord Arran has played an active role for the Conservative Party, serving in several junior ministerial roles. Marriage and children On 28 Se ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
National Register Of Historic Parks And Gardens
{{R from move ...
#REDIRECT Register of Historic Parks and Gardens of Special Historic Interest in England #REDIRECT Register of Historic Parks and Gardens of Special Historic Interest in England {{R from move ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |