Castle Hill, Filleigh on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
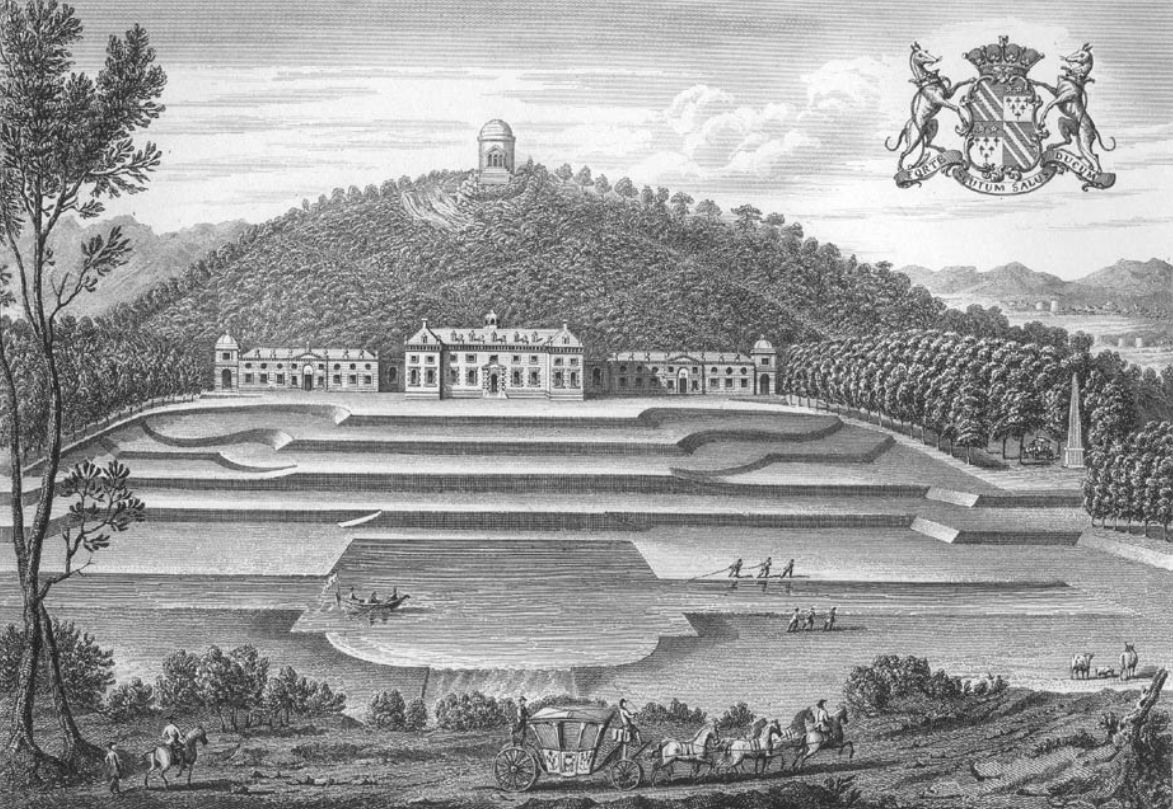



 Castle Hill in the
Castle Hill in the

 A circular library was added in the early 19th century. In 1841 the architect
A circular library was added in the early 19th century. In 1841 the architect
 The house is surrounded by landscaped grounds containing many picturesque structures and decorative '' points-de-vue''. The former include three small classical-style
The house is surrounded by landscaped grounds containing many picturesque structures and decorative '' points-de-vue''. The former include three small classical-style
 A sham castle dating from about 1746 occupies the hill behind the house to the north, possibly inspired by Vanbrugh, and is said to be the feature which gave the house its name. When
A sham castle dating from about 1746 occupies the hill behind the house to the north, possibly inspired by Vanbrugh, and is said to be the feature which gave the house its name. When
 The original
The original
 The last Earl Fortescue to own Castle Hill was Hugh Fortescue, 5th Earl Fortescue (1888–1958) who died in June 1958, aged 70. As he had no surviving male issue he was succeeded in the earldom by his younger brother, Denzil Fortescue, 6th Earl Fortescue. However the 5th Earl bequeathed Castle Hill, his principal seat, to his elder surviving daughter, Lady Margaret Fortescue (born 1923). Lady Margaret had married in 1948
The last Earl Fortescue to own Castle Hill was Hugh Fortescue, 5th Earl Fortescue (1888–1958) who died in June 1958, aged 70. As he had no surviving male issue he was succeeded in the earldom by his younger brother, Denzil Fortescue, 6th Earl Fortescue. However the 5th Earl bequeathed Castle Hill, his principal seat, to his elder surviving daughter, Lady Margaret Fortescue (born 1923). Lady Margaret had married in 1948




parish
A parish is a territorial entity in many Christianity, Christian denominations, constituting a division within a diocese. A parish is under the pastoral care and clerical jurisdiction of a priest#Christianity, priest, often termed a parish pries ...
of Filleigh in North Devon
North Devon is a Non-metropolitan district, local government district in Devon, England. Its council is based just outside Barnstaple, the district's largest town. The district also includes the towns of Ilfracombe, Lynton and Lynmouth and Sout ...
, is an early Neo-Palladian
Palladian architecture is a European architectural style derived from the work of the Republic of Venice, Venetian architect Andrea Palladio (1508–1580). What is today recognised as Palladian architecture evolved from his concepts of symmetr ...
country house
image:Blenheim - Blenheim Palace - 20210417125239.jpg, 300px, Blenheim Palace - Oxfordshire
An English country house is a large house or mansion in the English countryside. Such houses were often owned by individuals who also owned a Townhou ...
situated north-west of South Molton and south-east of Barnstaple
Barnstaple ( or ) is a river-port town and civil parish in the North Devon district of Devon, England. The town lies at the River Taw's lowest crossing point before the Bristol Channel. From the 14th century, it was licensed to export wool from ...
. It was built in 1730 by Hugh Fortescue, 14th Baron Clinton (1696–1751), who was later created in 1751 1st Baron Fortescue and 1st Earl of Clinton, the son of Hugh Fortescue (died 1719), lord of the manor
Lord of the manor is a title that, in Anglo-Saxon England and Norman England, referred to the landholder of a historical rural estate. The titles date to the English Feudalism, feudal (specifically English feudal barony, baronial) system. The ...
of Filleigh, Weare Giffard, etc., whose family is earliest recorded as residing in the 12th century at the manor of Whympston in the parish of Modbury in South Devon. The Fortescue family became major land owners, influential in British and West Country
The West Country is a loosely defined area within southwest England, usually taken to include the counties of Cornwall, Devon, Dorset, Somerset and Bristol, with some considering it to extend to all or parts of Wiltshire, Gloucestershire and ...
history. Castle Hill is a rare example in Devon of an 18th-century country mansion "on the grand scale".
The house was substantially reconstructed following a disastrous fire in 1934. It was designated a Grade II* listed building
In the United Kingdom, a listed building is a structure of particular architectural or historic interest deserving of special protection. Such buildings are placed on one of the four statutory lists maintained by Historic England in England, Hi ...
in 1967. The park and gardens are Grade I listed in the National Register of Historic Parks and Gardens. Today the property is leased by Eleanor, Countess of Arran (born 1949), the granddaughter of Hugh Fortescue, 5th Earl Fortescue (1888–1958).
Predecessor
The manor of Filleigh has been held by the Fortescue family since the 15th century, although the family's main seat until the late 17th century wasWeare Giffard
Weare Giffard is a small village, civil parish and former Manorialism, manor in the Torridge District, Torridge district, in north Devon, England. The church and manor house are situated 2 1/2 miles NW of Great Torrington in Devon. Most of th ...
, some to the west. An older late Tudor manor house
A manor house was historically the main residence of the lord of the manor. The house formed the administrative centre of a manor in the European feudal system; within its great hall were usually held the lord's manorial courts, communal mea ...
on the site was re-modelled in 1684 by Arthur Fortescue and his son Hugh Fortescue (died 1719). A plaque to the left of the north entrance front of the main range is inscribed in Latin: ("Re-built by Arthur Fortescue, esquire, AD 1684").
Lady Fortescue kept a record of the rainfall at Filleigh Castle Hill. A project being carried out at the University of Reading is recording handwritten weather records from the past. Her name is shown as being the observer making the records at Filleigh Castle Hill.
Palladian rebuilding
Hugh Fortescue (1696–1751), who in 1721 inherited the title 14th Baron Clinton, via his mother, consulted Lord Burlington (1694–1753), the pioneer and arbiter of Palladianism in England, on the design of his proposed new mansion. In 1728/9 he appointed Burlington's favoured builder Roger Morris to reface the house in Portland stone. The former hall was remodelled as a double-height saloon.19th-century additions

 A circular library was added in the early 19th century. In 1841 the architect
A circular library was added in the early 19th century. In 1841 the architect Edward Blore
Edward Blore (13 September 1787 – 4 September 1879) was a 19th-century English landscape and architectural artist, architect and antiquary.
Early career
Blore was born in Derby, the son of the antiquarian writer Thomas Blore.
Blore's backg ...
(1787–1879) added a porte-cochere on the north side of the main range, now demolished and replaced in 1974 by an entrance porch to the design of Raymond Erith. Blore also refashioned the entrance hall and stairs and added a top storey with mansard roof
A mansard or mansard roof (also called French roof or curb roof) is a multi-sided gambrel-style hip roof characterised by two slopes on each of its sides, with the lower slope at a steeper angle than the upper, and often punctured by dormer wi ...
. In 1861 Blore added at the east side of the house service wings and stables, thus considerably elongating the southern appearance of the building beyond the east wing. The service wing is set back from the east wing by the width of the entry road which passes directly in front of it, and is topped in its centre by a clock tower. Adjoining it on its east end and extending backwards to give the ensemble an L-shape, is Blore's stable block. This has small circular windows with portrait busts, and is pierced on its long eastern face by the imposing full height main entrance arch, through which vehicles pass and continue past the front of the service wing and through decorative inner gates into the courtyard situated between the north facade of the main range and the steep and rocky hillside.
1934 fire damage
A major fire broke out in the early morning of 9 March 1934 and burned for two days. It destroyed much of the interior and killed two members of staff, the housekeeper and a maid. The 5th Earl had recently installed a central heating system, the boiler of which, situated underneath the library floor, had malfunctioned. After the fire, the house was restored to the 18th-century style by Lord Gerald Wellesley (1885–1972), soldier, diplomat and architect, with Trenwith Wills. Although 49 paintings, including many Fortescue family portraits, were saved from the fire with only minor smoke damage, all were shortly afterwards destroyed by fire when the delivery lorry returning them from the restorer caught fire whilst parked overnight in a garage pending their return to Castle Hill.Grounds
 The house is surrounded by landscaped grounds containing many picturesque structures and decorative '' points-de-vue''. The former include three small classical-style
The house is surrounded by landscaped grounds containing many picturesque structures and decorative '' points-de-vue''. The former include three small classical-style Greek temple
Greek temples (, semantically distinct from Latin , " temple") were structures built to house deity statues within Greek sanctuaries in ancient Greek religion. The temple interiors did not serve as meeting places, since the sacrifices and ritu ...
s, the Sunrise Temple (1831), the Sunset Temple (1831) and Satyr
In Greek mythology, a satyr (, ), also known as a silenus or ''silenos'' ( ), and sileni (plural), is a male List of nature deities, nature spirit with ears and a tail resembling those of a horse, as well as a permanent, exaggerated erection. ...
's Temple (1861); the Traveller's Cross, erected in 1831, but formerly situated on a roadside near North Aller; Ugley Bridge (1861), an imitation of an old Devon packhorse bridge; The Sybils' Cave (1861), filled in while the house served as a home for evacuated children during World War II
World War II or the Second World War (1 September 1939 – 2 September 1945) was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War II, Allies and the Axis powers. World War II by country, Nearly all of the wo ...
, but since re-opened. The ancient parish church formerly situated next to the former pre-Palladian manor house was demolished in 1732 by Lord Clinton with the licence of Stephen Weston, Bishop of Exeter
The Bishop of Exeter is the Ordinary (officer), ordinary of the Church of England Diocese of Exeter in the Province of Canterbury. The current bishop is Mike Harrison (bishop), Mike Harrison, since 2024.
From the first bishop until the sixteent ...
, and was rebuilt to a new design in its present position some to the west of the house, visible from the terrace. This made available an unencumbered site for the planned landscaping. Other ''points-de-vue'' include the Sham Castle, the Triumphal Arch, the Ebrington Tower and the Sham Village (now demolished).
Sham castle
 A sham castle dating from about 1746 occupies the hill behind the house to the north, possibly inspired by Vanbrugh, and is said to be the feature which gave the house its name. When
A sham castle dating from about 1746 occupies the hill behind the house to the north, possibly inspired by Vanbrugh, and is said to be the feature which gave the house its name. When Lord Lieutenant of Devon
The Office of the Lord Lieutenant was created during the reign of Henry VIII (1509–1547), taking over the military duties of the Sheriffs and control of the military forces of the Crown. From 1569 there was provision for the appointment of Dep ...
, Hugh Fortescue, 4th Earl Fortescue (1854–1932) flew the Fortescue standard from the castle, he noted in his diary that his ancestor Matthew Fortescue, 2nd Baron Fortescue (d.1785) had "armed" it, as a modern reference to which in 1991 Lady Margaret Fortescue installed the decorative cannon now present on its south lawn. It served for a while as a banqueting hall, at which time it was lined with oak panelling from nearby North Aller House, which in 1812 was moved on to Weare Giffard
Weare Giffard is a small village, civil parish and former Manorialism, manor in the Torridge District, Torridge district, in north Devon, England. The church and manor house are situated 2 1/2 miles NW of Great Torrington in Devon. Most of th ...
Hall. The building was later converted into a dwelling house, originally intended for a couple to tend the tame pheasants, and later lived in by the huntsman of the Fortescue Harriers, Abraham Moggeridge. From the castle can be seen to the west Lundy Island and at a closer distance, Bampfylde Clump to the north in North Molton
North Molton is a village, parish and former Manorialism, manor in North Devon, England. The population of the parish in 2001 was 1,047, decreasing to 721 in the United Kingdom Census 2011, 2011 census. An electoral ward with the same name also ...
parish.
Triumphal arch
 The original
The original Triumphal Arch
A triumphal arch is a free-standing monumental structure in the shape of an archway with one or more arched passageways, often designed to span a road, and usually standing alone, unconnected to other buildings. In its simplest form, a triumphal ...
, situated on top of the hill opposite the south front of the house and on the same axis as the sham castle behind, was built by Lord Clinton in 1730. It had been allowed to become covered in ivy and in 1951 collapsed during a strong wind. Following the death of both her parents in 1958, Lady Margaret Fortescue in 1961 rebuilt the Arch in its original form in their memory. Financial contributions were made by the tenants of the estate and by friends of the family. The modern structure is of reinforced concrete faced with the original stone.
Sham village
A sham village, now demolished, with church tower was constructed by Lord Clinton on the horizon at High Bray.Ebrington Tower
The Ebrington Tower was built in 1992 by Lady Margaret Fortescue on the site of the former Sham Village. The tower was built in memory of her only brother Viscount Ebrington, 21, who was killed in 1942 in action with the Royal Scots Greys at the Battle of El Alamein in Egypt, and whose mural memorial marble tablet can be seen in the Fortescue Chapel in Filleigh Church. Due to his loss, on the death of his father the 5th Earl in 1958, the family titles passed by law to the latter's younger brother, but in the absence of an entail, the Castle Hill andWeare Giffard
Weare Giffard is a small village, civil parish and former Manorialism, manor in the Torridge District, Torridge district, in north Devon, England. The church and manor house are situated 2 1/2 miles NW of Great Torrington in Devon. Most of th ...
estates he was free to bequeath to his two daughters. The tower, made from local stone, consists of three stories and is crenellated on top. It was designed by Hal Moggridge who had organised much of the reparatory landscaping work following the great storm of 1990, and was built by Graham Davey.
Descent to Countess of Arran
Bernard van Cutsem
Bernard Henry Richard Harcourt van Cutsem (23 January 1916 – 8 December 1975) was an English horsebreeder and racehorse trainer.
Ancestry and early life
The van Cutsem family are Catholics, and of Belgian origin.Arthur Gore, 9th Earl of Arran (born 1938). She was awarded the MBE in the Queen's Birthday Honours 2008. They have two daughters, Lady Laura Duckworth-Chad and Lady Lucy Fortescue-Gore.
www.devon.gov.uk/historicfilleighCastle Hill web-siteListed buildings text, Castle Hill
{{coord, 51.0401, -3.8969, type:landmark_region:GB, display=title Country houses in Devon Grade II* listed buildings in Devon Grade II* listed houses Grade I listed parks and gardens in Devon Palladian architecture in England Edward Blore buildings Houses completed in 1730 1730 establishments in England
Public access
The gardens are open to the public for much of the year. The house is not open to the public but occasional guided tours for small groups are arranged on application. The Grand Hall of the house and three other main rooms are however available for civil wedding ceremonies and marquee receptions are also provided. A conference room with a capacity for 100 people is available for hire.Filleigh History Group, back cover advertisementSources
*Cherry, Bridget & Pevsner, Nikolaus, The Buildings of England: Devon, London, 2004, Castle Hill, Filleigh, pp. 247–249 *Lauder, Rosemary, Devon Families, Tiverton, 2002, Fortescue, pp. 75–82 *Filleigh History Group & Arran, Countess of, The Secrets of Castle Hill Gardens, 2003. (Booklet for sale on site)References
11 Rainfall records University of ReadingFurther reading
*External links
www.devon.gov.uk/historicfilleigh
{{coord, 51.0401, -3.8969, type:landmark_region:GB, display=title Country houses in Devon Grade II* listed buildings in Devon Grade II* listed houses Grade I listed parks and gardens in Devon Palladian architecture in England Edward Blore buildings Houses completed in 1730 1730 establishments in England