|
Buryad Unen
''Buryad Unen'' ( bxr, Буряад үнэн, , "The Buryat Truth") is the main newspaper in the Buryat language, founded in December 1921 and originally published in the top-down Mongolian script before switching to Latin script in 1931-1938 and eventually Cyrillic script from 1939. It was founded as (Буряад-Монголиин үнэн, , ''Buryat-Mongol Truth'') in 1921 in Chita, Buryat-Mongol ASSR, within Russian SFSR. Now it published in Ulan-Ude, as Chita was carved out of the Buryat-Mongol ASSR. In 1958, Buryat-Mongol ASSR removed the "-Mongol" from its official name, and the name of this newspaper followed the change. In the 1970s, it was published six times a week, with a circulation of approximately 8500. History of the newspaper .The paper was originally published in Chita. In 1923, the publication of the paper moved to Ulan-Ude. It was printed in the vertical Mongolian script, which, due to its universality, leveled the dialect differences of the Buryats an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ulan-Ude
Ulan-Ude (; bua, Улаан-Үдэ, , ; russian: Улан-Удэ, p=ʊˈlan ʊˈdɛ; mn, Улаан-Үд, , ) is the capital city of the Republic of Buryatia, Russia, located about southeast of Lake Baikal on the Uda River at its confluence with the Selenga. According to the 2021 Census, 437,565 people lived in Ulan-Ude; up from 404,426 recorded in the 2010 Census, making the city the third-largest in the Russian Far East by population. Names Ulan-Ude was first called Udinskoye (, ) for its location on the Uda River. It was founded as a small fort in 1666. From around 1735, the settlement was called Udinsk (, ) and was granted town status under that name in 1775. It was renamed Verkhneudinsk (, ; "Upper Udinsk") in 1783, to differentiate it from Nizhneudinsk ("Lower Udinsk") lying on a different Uda River near Irkutsk which was granted town status that year. The descriptors "upper" and "lower" refer to the positions of the two cities relative to each other, rather than ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
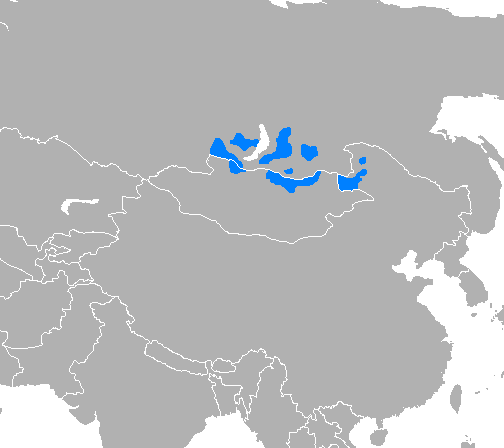
Buryat Language
Buryat, or Buriat (; Buryat Cyrillic: , , ), known in foreign sources as the Bargu-Buryat dialect of Mongolian, and in pre-1956 Soviet sources as Buryat-Mongolian,In China, the Buryat language is classified as the Bargu-Buryat dialect of the Mongolian language. is a variety of the Mongolic languages spoken by the Buryats and Bargas that is classified either as a language or major dialect group of Mongolian. Geographic distribution The majority of Buryat speakers live in Russia along the northern border of Mongolia where it is an official language in the Buryat Republic and was an official language in the former Ust-Orda Buryatia and Aga Buryatia autonomous okrugs. In the Russian census of 2002, 353,113 people out of an ethnic population of 445,175 reported speaking Buryat (72.3%). Some other 15,694 can also speak Buryat, mostly ethnic Russians. Buryats in Russia have a separate literary standard, written in a Cyrillic alphabet. It is based on the Russian alphabet with thr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mongolian Script
The classical or traditional Mongolian script, also known as the , was the first writing system created specifically for the Mongolian language, and was the most widespread until the introduction of Cyrillic script, Cyrillic in 1946. It is traditionally written in vertical lines . Derived from the Old Uyghur alphabet, Mongolian is a true alphabet, with separate letters for consonants and vowels. The Mongolian script has been adapted to write languages such as Oirat language, Oirat and Manchu language, Manchu. Alphabets based on this classical vertical script are used in Mongolia and Inner Mongolia to this day to write Mongolian, Xibe language, Xibe and, experimentally, Evenki language, Evenki. Computer operating systems have been slow to adopt support for the Mongolian script, and almost all have incomplete support or other text rendering difficulties. History The Mongolian vertical script developed as an adaptation of the Old Uyghur alphabet for the Mongolian language. From ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cyrillic Script
The Cyrillic script ( ), Slavonic script or the Slavic script, is a writing system used for various languages across Eurasia. It is the designated national script in various Slavic, Turkic, Mongolic, Uralic, Caucasian and Iranic-speaking countries in Southeastern Europe, Eastern Europe, the Caucasus, Central Asia, North Asia, and East Asia. , around 250 million people in Eurasia use Cyrillic as the official script for their national languages, with Russia accounting for about half of them. With the accession of Bulgaria to the European Union on 1 January 2007, Cyrillic became the third official script of the European Union, following the Latin and Greek alphabets. The Early Cyrillic alphabet was developed during the 9th century AD at the Preslav Literary School in the First Bulgarian Empire during the reign of tsar Simeon I the Great, probably by disciples of the two Byzantine brothers Saint Cyril and Saint Methodius, who had previously created the Glagoli ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chita, Zabaykalsky Krai
Chita ( rus, Чита, p=tɕɪˈta, , ) is a city and the administrative center of Zabaykalsky Krai, Russia, located on the Trans-Siberian Railway route, roughly east of Irkutsk. Geography Chita lies at the confluence of the Chita and Ingoda Rivers, between the Yablonoi Mountains to the west and the Chersky Range to the east. Lake Kenon is located to the west, within the city limits, and the Ivan-Arakhley Lake System is a group of lakes lying about west of Chita. Google Earth History Pyotr Beketov's Cossacks founded Chita in 1653. The name of the settlement apparently came from the local River Chita. Following the Decembrist revolt of 1825, from 1827 several of the Decembrists suffered exile to Chita. According to George Kennan, who visited the area in the 1880s, "Among the exiles in Chita were some of the brightest, most cultivated, most sympathetic men and women that we had met in Eastern Siberia." When Richard Maack visited the city in 1855, he saw a w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Buryat-Mongol ASSR
The Buryat Autonomous Soviet Socialist Republic (russian: Бурятская Автономная Советская Социалистическая Республика; bua, Буряадай Автономито Совет Социалис Республика), abbreviated as Buryat ASSR ( rus, Бурятская АССР; bua, Буряадай АССР, link=no), was an autonomous republic of the Russian SFSR within the Soviet Union. In 1923, the republic was created with the name Buryat-Mongol Autonomous Soviet Socialist Republic; its predecessor was the Buryat-Mongol Autonomous Oblast. In 1958, the name "Mongol" was removed from the name of the republic. The Buryat ASSR declared its sovereignty in 1990 and adopted the name Republic of Buryatia in 1992. However, it remained an autonomous republic within the Russian Federation. In the 1930s, Buryat-Mongolia was one of the sites of Soviet studies aimed to disprove Nazi race theories. Amongst other things, Soviet p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Russian SFSR
The Russian Soviet Federative Socialist Republic, Russian SFSR or RSFSR ( rus, Российская Советская Федеративная Социалистическая Республика, Rossíyskaya Sovétskaya Federatívnaya Socialistíčeskaya Respúblika, rɐˈsʲijskəjə sɐˈvʲetskəjə fʲɪdʲɪrɐˈtʲivnəjə sətsɨəlʲɪˈsʲtʲitɕɪskəjə rʲɪˈspublʲɪkə, Ru-Российская Советская Федеративная Социалистическая Республика.ogg), previously known as the Russian Soviet Republic and the Russian Socialist Federative Soviet Republic as well as being unofficially known as Soviet Russia,Declaration of Rights of the laboring and exploited people, article I. the Russian Federation or simply Russia, was an independent federal socialist state from 1917 to 1922, and afterwards the largest and most populous of the Soviet socialist republics of the Soviet Union (USSR) from 1922 to 1991, until becoming a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Latinisation In The Soviet Union
In the USSR, latinisation or latinization (russian: латиниза́ция, ') was the name of the campaign during the 1920s–1930s which aimed to replace traditional writing systems for all languages of the Soviet Union with systems that would use the Latin script or to create Latin-script-based systems for languages that, at the time, did not have a writing system. History Background Since at least 1700, some Russian intellectuals have sought to Latinise the Russian language in their desire for close relations with the West. The early 20th-century Bolsheviks had four goals: to break with Tsarism, to spread socialism to the whole world, to isolate the Muslim inhabitants of the Soviet Union from the Arabic–Islamic world and religion, and to eradicate illiteracy through simplification. They concluded the Latin alphabet was the right tool to do so, and, after seizing power during the Russian Revolution of 1917, they made plans to realise these ideals. Although progres ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cyrillic
The Cyrillic script ( ), Slavonic script or the Slavic script, is a writing system used for various languages across Eurasia. It is the designated national script in various Slavic, Turkic, Mongolic, Uralic, Caucasian and Iranic-speaking countries in Southeastern Europe, Eastern Europe, the Caucasus, Central Asia, North Asia, and East Asia. , around 250 million people in Eurasia use Cyrillic as the official script for their national languages, with Russia accounting for about half of them. With the accession of Bulgaria to the European Union on 1 January 2007, Cyrillic became the third official script of the European Union, following the Latin and Greek alphabets. The Early Cyrillic alphabet was developed during the 9th century AD at the Preslav Literary School in the First Bulgarian Empire during the reign of tsar Simeon I the Great, probably by disciples of the two Byzantine brothers Saint Cyril and Saint Methodius, who had previously created the Glagoli ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Literary Language
A literary language is the form (register) of a language used in written literature, which can be either a nonstandard dialect or a standardized variety of the language. Literary language sometimes is noticeably different from the spoken language (''lects''), but the difference between literary language and non-literary language is greater in some languages; thus a great divergence between a written form and a spoken vernacular, the language exhibits diglossia, a community's use of two forms of speech. The understanding of the term differs from one linguistic tradition to another and is dependent on the terminological conventions adopted. Notably, in Eastern European and Slavic linguistics, the term "literary language" has also been used as a synonym of " standard language". Literary English For much of its history, there has been a distinction in the English language between an elevated literary language and a colloquial idiom.Matti Rissanen, ''History of Englishes: New ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Buryat Autonomous Soviet Socialist Republic
The Buryat Autonomous Soviet Socialist Republic (russian: Бурятская Автономная Советская Социалистическая Республика; bua, Буряадай Автономито Совет Социалис Республика), abbreviated as Buryat ASSR ( rus, Бурятская АССР; bua, Буряадай АССР, link=no), was an autonomous republic An autonomous republic is a type of administrative division similar to a province or Federated state, state. A significant number of autonomous republics can be found within the successor states of the Soviet Union, but the majority are located wi ... of the Russian Socialist Federative Soviet Republic, Russian SFSR within the Soviet Union. In 1923, the republic was created with the name Buryat-Mongol Autonomous Soviet Socialist Republic; its predecessor was the Buryat-Mongol Autonomous Oblast. In 1958, the name "Mongol" was removed from the name of the republic. The Buryat ASSR de ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
YouTube
YouTube is a global online video sharing and social media platform headquartered in San Bruno, California. It was launched on February 14, 2005, by Steve Chen, Chad Hurley, and Jawed Karim. It is owned by Google, and is the second most visited website, after Google Search. YouTube has more than 2.5 billion monthly users who collectively watch more than one billion hours of videos each day. , videos were being uploaded at a rate of more than 500 hours of content per minute. In October 2006, YouTube was bought by Google for $1.65 billion. Google's ownership of YouTube expanded the site's business model, expanding from generating revenue from advertisements alone, to offering paid content such as movies and exclusive content produced by YouTube. It also offers YouTube Premium, a paid subscription option for watching content without ads. YouTube also approved creators to participate in Google's AdSense program, which seeks to generate more revenue for both parties. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |