|
Bury, West Sussex
Bury is a village and civil parish in the Chichester district of West Sussex, England. It is located on the A29 road, around south-west of Pulborough. The villages of Bury and nearby West Burton are sited at the foot of the scarp slope of the South Downs, where springs from the chalk strata provided a constant supply of clean water. The Anglican parish church of St. John the Evangelist lies east of the village centre on the west bank of the River Arun. The church is dominated by a 12th Century tower with a cedar-shingled spire. There was formerly a passenger ferry by rowing boat to Amberley on the east bank. There are many old houses in the village and a large modern village hall. There is one pub, the Squire and Horse, beside the A29 road. Bury House close to the pub was the home of author John Galsworthy for the final seven years of his life. West Burton, across some fields to the west, is smaller than Bury and has many interesting old houses. The village has a crick ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
United Kingdom Census 2011
A Census in the United Kingdom, census of the population of the United Kingdom is taken every ten years. The 2011 census was held in all countries of the UK on 27 March 2011. It was the first UK census which could be completed online via the Internet. The Office for National Statistics (ONS) is responsible for the census in England and Wales, the General Register Office for Scotland (GROS) is responsible for the census in Scotland, and the Northern Ireland Statistics and Research Agency (NISRA) is responsible for the census in Northern Ireland. The Office for National Statistics is the executive office of the UK Statistics Authority, a non-ministerial department formed in 2008 and which reports directly to Parliament. ONS is the UK Government's single largest statistical producer of independent statistics on the UK's economy and society, used to assist the planning and allocation of resources, policy-making and decision-making. ONS designs, manages and runs the census in England an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
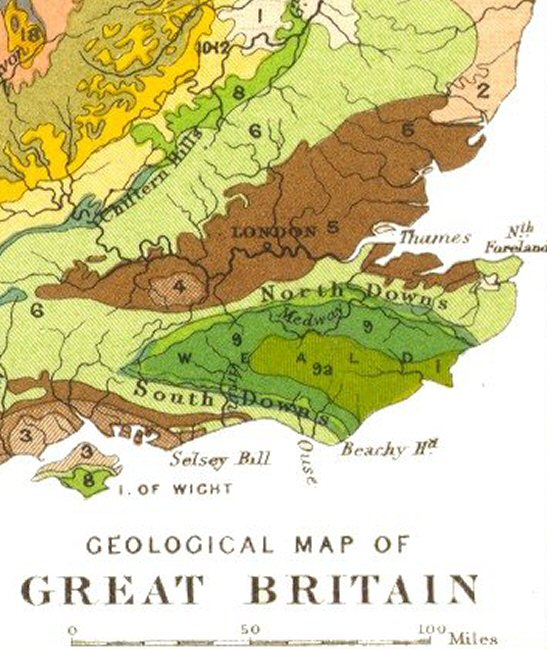
South Downs
The South Downs are a range of chalk hills in the south-eastern coastal counties of England that extends for about across the south-eastern coastal counties of England from the Itchen valley of Hampshire in the west to Beachy Head, in the Eastbourne Downland Estate, East Sussex, in the east. The Downs are bounded on the northern side by a steep escarpment, from whose crest there are extensive views northwards across the Weald. The South Downs National Park forms a much larger area than the chalk range of the South Downs, and includes large parts of the Weald. The national park is the UK's most visited, attracting an estimated 39 million visitor-days annually. The South Downs are characterised by rolling chalk downland with close-cropped turf and dry valleys, and are recognised as one of the most important chalk landscapes in England. The range is one of the four main areas of chalk downland in southern England. The South Downs are relatively less populated compared to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wards And Electoral Divisions Of The United Kingdom
The wards and electoral divisions in the United Kingdom are electoral districts at sub-national level, represented by one or more councillors. The ''ward (subnational entity), ward'' is the primary unit of English electoral geography for civil parishes and borough and district councils, the ''electoral ward'' is the unit used by Welsh principal councils, while the ''electoral division'' is the unit used by English county councils and some unitary authority, unitary authorities. Each ward/division has an average electorate of about 5,500 people, but ward population counts can vary substantially. As of 2021 there are 8,694 electoral wards/divisions in the UK. An average area of wards or electoral divisions in the United Kingdom is . England The London boroughs, metropolitan boroughs and non-metropolitan districts (including most unitary authority, unitary authorities) are divided into wards for local elections. However, county council elections (as well as those for several unitary ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bury In West Sussex
Bury may refer to: *The burial of human remains *-bury, a suffix in English placenames Places England * Bury, Cambridgeshire, a village * Bury, Greater Manchester, a town, historically in Lancashire ** Bury (UK Parliament constituency) (1832–1950) ***Bury and Radcliffe (UK Parliament constituency) (1950–1983) ***Bury North (UK Parliament constituency), from 1983 ***Bury South (UK Parliament constituency), from 1983 ** County Borough of Bury, 1846–1974 ** Metropolitan Borough of Bury, from 1974 ** Bury Rural District, 1894–1933 * Bury, Somerset, a hamlet * Bury, West Sussex, a village and civil parish ** Bury (UK electoral ward) * Bury St Edmunds, a town in Suffolk, commonly referred to as Bury * New Bury, a suburb of Farnworth in the Bolton district of Greater Manchester Elsewhere * Bury, Hainaut, Belgium, a village in the commune of Péruwelz, Wallonia * Bury, Quebec, Canada, a municipality * Bury, Oise, France, a commune Sports * Bury (professional wrestling), a slang ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John Galsworthy
John Galsworthy (; 14 August 1867 – 31 January 1933) was an English novelist and playwright. He is best known for his trilogy of novels collectively called '' The Forsyte Saga'', and two later trilogies, ''A Modern Comedy'' and ''End of the Chapter''. He was awarded the 1932 Nobel Prize in Literature. Born to a prosperous upper-middle-class family, Galsworthy was destined for a career as a lawyer, but found it uncongenial and turned instead to writing. He was thirty before his first book was published in 1897, and did not achieve real success until 1906, when '' The Man of Property'', the first of his novels about the Forsyte family was published. In the same year his first play, '' The Silver Box'' was staged in London. As a dramatist, he became known for plays with a social message, reflecting, among other themes, the struggle of workers against exploitation, the use of solitary confinement in prisons, the repression of women, jingoism and the politics and morality of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amberley, West Sussex
Amberley is a village and civil parish in the Horsham (district), Horsham District of West Sussex, England. It is situated at the foot of the South Downs, north of Arundel. Its neighbours are Storrington and West Chiltington. The village is noted for its thatched cottages. A house named "The Thatched House" is one of the village's few non-thatched houses. One of the attractions is Amberley Working Museum. Amberley has a Amberley railway station, railway station on the Arun Valley Line, with regular services to Bognor Regis, Portsmouth and London. To the north of the village is the tidal plain of the River Arun, known as Amberley Wild Brooks. The wetland is a Site of Special Scientific Interest which floods in winter and is known for its wildfowl. Amberley Castle is now a hotel. The castle was a fortified manor house next to which is the Norman architecture, Norman St Michael's Church. Cultural links William Champion Streatfeild, who became Bishop of Lewes was vicar of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cedar Wood
Cedar is part of the English common name of many trees and other plants, particularly those of the genus ''Cedrus''. Some botanical authorities consider the Old-World ''Cedrus'' the only "true cedars". Many other species worldwide with similarly aromatic wood, including several species of genera '' Calocedrus'', '' Thuja'', and '' Chamaecyparis'' in the Pacific Northwest of North America, are referred to as "false cedars". Plants called "cedar" include: Family Pinaceae *''Cedrus'', common English name cedar, a genus of coniferous trees in the plant family Pinaceae **''Cedrus libani'', the Lebanon cedar, native to Lebanon, western Syria and south-central Turkey **'' Cedrus atlantica'', the Atlas cedar, native to the Atlas Mountains of Morocco and Algeria **'' Cedrus deodara'', the Deodar cedar, native to the western Himalayas **'' Cedrus brevifolia'', the Cyprus cedar, found in the island of Cyprus' Cedar Valley in the Troodos Mountains *'' Pinus sibirica'', the Siberian pine, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
River Arun
The River Arun () is a river in the English county of West Sussex. At long, it is the longest river entirely in Sussex and one of the longest starting in Sussex after the River Medway, River Wey and River Mole. From the series of small streams that form its source in the area of St Leonard's Forest in the Weald, the Arun flows westwards through Horsham to Nowhurst where it is joined by the North River. Turning to the south, it is joined by its main tributary, the western River Rother, and continues through a gap in the South Downs to Arundel to join the English Channel at Littlehampton. It is one of the faster flowing rivers in England, and is tidal as far inland as Pallingham Quay, upstream from the sea at Littlehampton. The Arun gives its name to the Arun local government district of West Sussex. The first major improvements to the river were made between the 1540s and the 1570s, when Arundel became a port, and navigation up to Pallingham was improved, but barges ha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anglican
Anglicanism, also known as Episcopalianism in some countries, is a Western Christianity, Western Christian tradition which developed from the practices, liturgy, and identity of the Church of England following the English Reformation, in the context of the Protestant Reformation in Europe. It is one of the largest branches of Christianity, with around 110 million adherents worldwide . Most are members of national or regional Ecclesiastical province#Anglican Communion, ecclesiastical provinces of the international Anglican Communion, one of the largest Christian bodies in the world, and the world's third-largest Christian communion. When united and uniting churches, united churches in the Anglican Communion and the breakaway Continuing Anglican movement were not counted, there were an estimated 97.4 million Anglicans worldwide in 2020. Adherents of Anglicanism are called ''Anglicans''; they are also called ''Episcopalians'' in some countries. The provinces within the Anglican ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chalk
Chalk is a soft, white, porous, sedimentary carbonate rock. It is a form of limestone composed of the mineral calcite and originally formed deep under the sea by the compression of microscopic plankton that had settled to the sea floor. Chalk is common throughout Western Europe, where deposits underlie parts of France, and steep cliffs are often seen where they meet the sea in places such as the Dover cliffs on the Kent coast of the English Channel. Chalk is mined for use in industry, such as for quicklime, bricks and builder's putty, and in agriculture, for raising pH in soils with high acidity. It is also used for " blackboard chalk" for writing and drawing on various types of surfaces, although these can also be manufactured from other carbonate-based minerals, or gypsum. Description Chalk is a fine-textured, earthy type of limestone distinguished by its light colour, softness, and high porosity. It is composed mostly of tiny fragments of the calcite shells or sk ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Escarpment
An escarpment is a steep slope or long cliff that forms as a result of faulting or erosion and separates two relatively level areas having different elevations. Due to the similarity, the term '' scarp'' may mistakenly be incorrectly used interchangeably with ''escarpment.'' ''Escarpment'' referring to the margin between two landforms, and ''scarp'' referring to a cliff or a steep slope. In this usage an escarpment is a ridge which has a gentle slope on one side and a steep scarp on the other side. More loosely, the term ''scarp'' also describes a zone between a coastal lowland and a continental plateau which shows a marked, abrupt change in elevation caused by coastal erosion at the base of the plateau. Formation and description Scarps are generally formed by one of two processes: either by differential erosion of sedimentary rocks, or by movement of the Earth's crust at a geologic fault. The first process is the more common type: the escarpment is a transition from one seri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Points Of The Compass
The points of the compass are a set of horizontal, Radius, radially arrayed compass directions (or Azimuth#In navigation, azimuths) used in navigation and cartography. A ''compass rose'' is primarily composed of four cardinal directions—north, east, south, and west—each separated by 90 degree (angle), degrees, and secondarily divided by four ordinal (intercardinal) directions—northeast, southeast, southwest, and northwest—each located halfway between two cardinal directions. Some disciplines such as meteorology and navigation further divide the compass with additional azimuths. Within European tradition, a fully defined compass has 32 "points" (and any finer subdivisions are described in fractions of points). Compass points or compass directions are valuable in that they allow a user to refer to a specific azimuth in a Colloquialism, colloquial fashion, without having to compute or remember degrees. Designations The names of the compass point directions follow these r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |