|
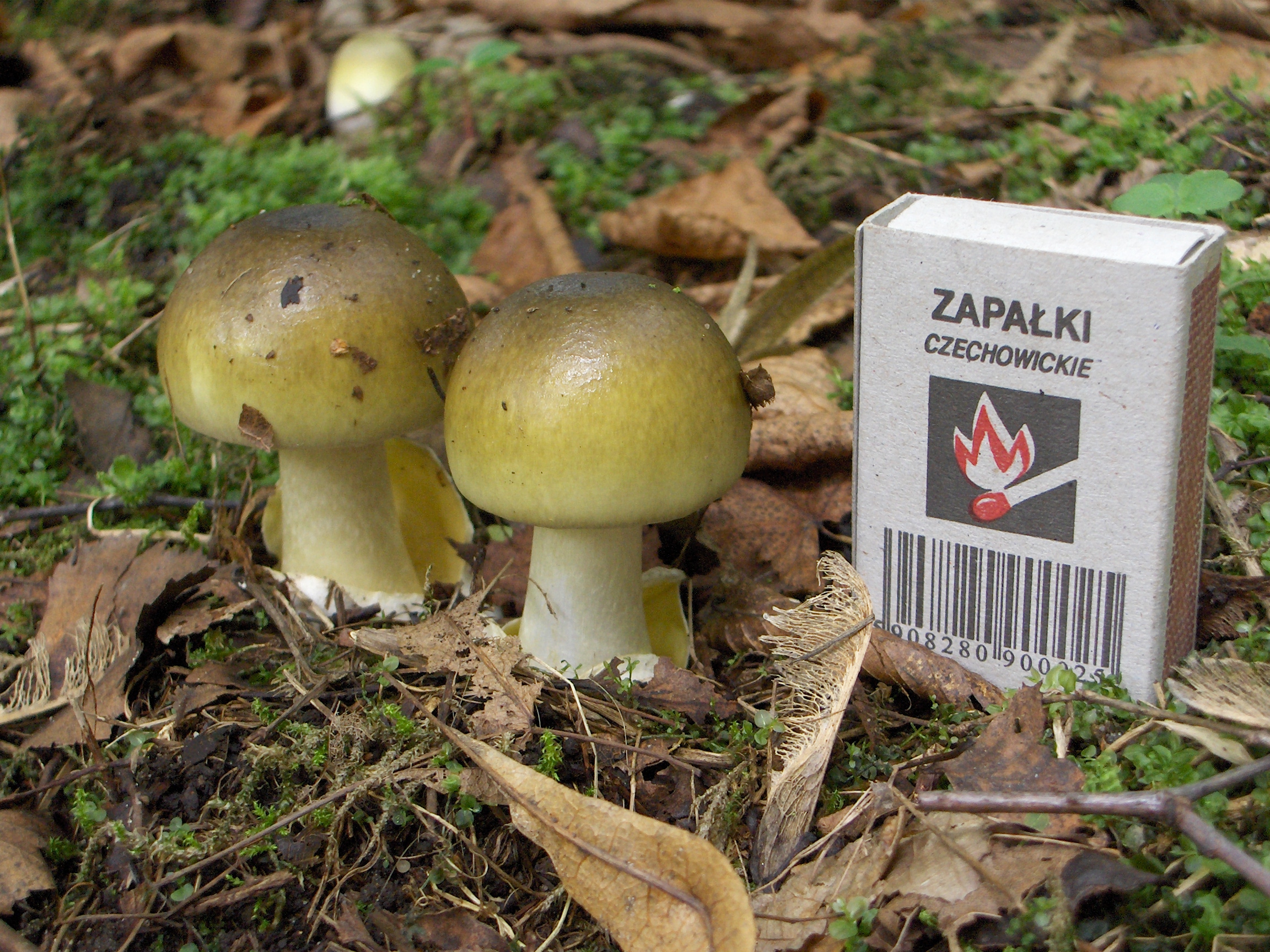
Blusher
The blusher is the common name for several closely related species of the genus ''Amanita''. ''A. rubescens'' (the blushing amanita) is found in Eurasia and ''A. novinupta'' (the new bride blushing amanita or blushing bride) is found in western North America. Both their scientific and common names stem from the tendency of their flesh to bruise pink. Blushers are difficult to distinguish from similar species, but one identifying feature is the pink bruising. The mushroom is Edible mushroom, edible and tasty, sought for in several European countries. Taxonomy ''Amanita rubescens'' is native to Europe and Asia, with related species being confused for it in other regions. ''Amanita novinupta'' can be found in western North America. Other closely related species and variants include ''Amanita brunneolocularis'', ''A. orsonii'', ''A. rubescens'' var. ''alba'', and ''A. rubescens'' var. ''congolensis''. Description ''A. rubescens'' has a reddish-brown ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Amanita Species
The following is a list of species of the agaric genus ''Amanita'', one that contains over 500 named species and varieties. Building on the taxonomical outline of ''Amanita'' by Corner and Bas (1962) and Bas (1969), the subgenus and section scheme of Cui et al. (2018) is followed by this list. Bolding of the species name and an asterisk (*) following indicates the species is the type species of that section, with a double asterisk (**) indicating the type species of the entire genus. The use of common names follows Tulloss (2007), Holden (2003), Arora (1986), and Lincoff (1981). The names of the remainder of the species in the genus not assigned to subgenera by those authors are sourced from Index Fungorum and have been appended to the end of the list. Subgenus ''Amanita'' Section ''Amanita'' * ''Amanita albocreata'' – (North America) * ''Amanita aliena'' – (south Brazil) * ''Amanita altipes'' – (southwestern China) * ''Amanita aprica'' – (North Ame ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amanita
The genus ''Amanita'' contains about 600 species of agarics, including some of the most toxic known mushrooms found worldwide, as well as some well-regarded Edible mushroom, edible species (and many species of unknown edibility). The genus is responsible for approximately 95% of fatalities resulting from mushroom poisoning, with the death cap accounting for about 50% on its own. The most potent toxin present in these mushrooms is . The genus also contains many edible mushrooms, but mycologists discourage mushroom hunters, other than experts, from selecting any of these for human consumption. Nonetheless, in some cultures, the larger local edible species of ''Amanita'' are mainstays of the markets in the local growing season. Samples of this are ''Amanita zambiana'' and other fleshy species in central Africa, ''Amanita basii, A. basii'' and similar species in Mexico, ''Amanita caesarea, A. caesarea'' and the "Blusher" ''Amanita rubescens, A. rubescens'' in Europe, a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amanita Rubescens 333
The genus ''Amanita'' contains about 600 species of agarics, including some of the most toxic known mushrooms found worldwide, as well as some well-regarded edible species (and many species of unknown edibility). The genus is responsible for approximately 95% of fatalities resulting from mushroom poisoning, with the death cap accounting for about 50% on its own. The most potent toxin present in these mushrooms is . The genus also contains many edible mushrooms, but mycologists discourage mushroom hunters, other than experts, from selecting any of these for human consumption. Nonetheless, in some cultures, the larger local edible species of ''Amanita'' are mainstays of the markets in the local growing season. Samples of this are '' Amanita zambiana'' and other fleshy species in central Africa, '' A. basii'' and similar species in Mexico, '' A. caesarea'' and the "Blusher" '' A. rubescens'' in Europe, and '' A. chepangiana'' in Southeast Asia. Other species are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Christian Hendrik Persoon
Christiaan Hendrik Persoon (31 December 1761 – 16 November 1836) was a Cape Colony mycologist who is recognized as one of the founders of mycology, mycological Taxonomy (biology), taxonomy. Early life Persoon was born in Cape Colony at the Cape of Good Hope, the third child of an immigrant Pomeranian father, Christiaan Daniel Persoon, and Netherlands, Dutch mother, Wilhelmina Elizabeth Groenwald. His mother died soon after he was born. In 1775, at the age of thirteen, he was sent to Europe for his education. His father died a year later in 1776. Education Initially a student of theology at University of Halle-Wittenberg, Halle, Persoon switched his studies to medicine, which he pursued in Leiden and then Göttingen. He received a doctorate from the German National Academy of Sciences Leopoldina, Deutsche Akademie der Naturforscher in Erlangen 1799. Later years He moved to Paris by 1803, where he spent the rest of his life, renting the upper floor of a house in a poor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amanita Pantherina
''Amanita pantherina'', also known as the panther cap, false blusher, and the panther amanita due to its similarity to the true blusher (''Amanita rubescens''), is a species of fungus found in Eurasia with poisonous and psychoactive properties. Description The cap is wide, hemispheric at first, then convex to plano-convex, deep brown to hazel-brown to pale ochraceous brown, densely distributed warts that are pure white to sordid cream, minutely verruculose, floccose, easily removable. Viscid when wet, with a short striate margin. The flesh is white, unchanging when injured. The gills are adnexed to free, close to crowded, white becoming greyish, truncate. The spores are white in deposit, smooth, broadly ellipsoid to ellipsoid to elongate, inamyloid, infrequently globose. 8–14 x 6–10 μm. The stipe is 5–15 cm long × .6–3 cm wide, subcylindric, somewhat narrowing upward, white, becoming slightly tannish in age, stuffed then hollow, finely floccos ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ten Speed Press
Ten Speed Press is a publishing house founded in Berkeley, California, in 1971 by Phil Wood. It was bought by Random House in February 2009 and became part of their Crown Publishing Group division. History Wood worked with Barnes & Noble in 1962, Penguin Books in 1965, and had a senior sales position at Penguin Books in Baltimore and New York before founding Ten Speed Press. Wood died of cancer in December 2010. Ten Speed's first book was ''Anybody's Bike Book'', which is still in print. It inspired the publisher's name and has sold more than a million copies. Ten Speed's all-time best-seller is '' What Color is Your Parachute? A Practical Manual for Job-Hunters and Career-Changers'' by Richard N. Bolles (1972). It has been reissued in new editions and, as of 2009, has sold more than ten million copies, translated into 20 languages. Ten Speed has published numerous other non-fiction titles, including '' Moosewood Cookbook'', '' White Trash Cooking,'' '' Why Cats Paint,'' ''Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
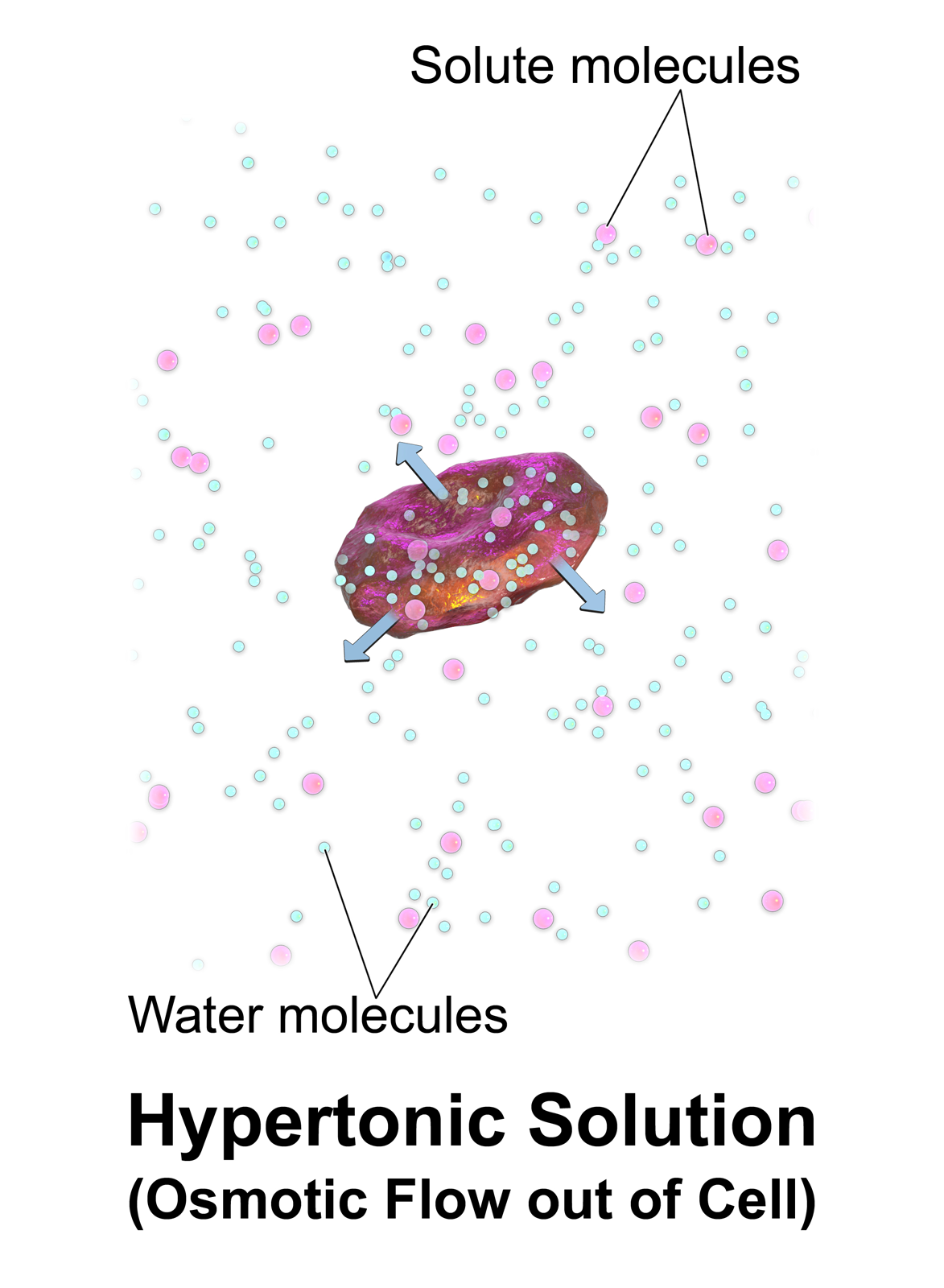
Haemolytic
Hemolysis or haemolysis (), also known by several other names, is the rupturing (lysis) of red blood cells (erythrocytes) and the release of their contents (cytoplasm) into surrounding fluid (e.g. blood plasma). Hemolysis may occur in vivo or in vitro. One cause of hemolysis is the action of hemolysins, toxins that are produced by certain pathogenic bacteria or fungi. Another cause is intense physical exercise. Hemolysins damage the red blood cell's cytoplasmic membrane, causing lysis and eventually cell death. Etymology From hemo- + -lysis, from Ancient Greek (, 'blood') + , 'loosening'). Inside the body Hemolysis inside the body can be caused by a large number of medical conditions, including some parasites (''e.g.'', ''Plasmodium''), some autoimmune disorders (''e.g.'', autoimmune haemolytic anaemia, drug-induced hemolytic anemia, atypical hemolytic uremic syndrome (aHUS)), some genetic disorders (''e.g.'', Sickle-cell disease or G6PD deficiency), or blood with too l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Blood Cell
A blood cell (also called a hematopoietic cell, hemocyte, or hematocyte) is a cell produced through hematopoiesis and found mainly in the blood. Major types of blood cells include red blood cells (erythrocytes), white blood cells (leukocytes), and platelets (thrombocytes). Together, these three kinds of blood cells add up to a total 45% of the blood tissue by volume, with the remaining 55% of the volume composed of plasma, the liquid component of blood. Red blood cells Red blood cells or ''erythrocytes'' primarily carry oxygen and collect carbon dioxide through the use of hemoglobin. Hemoglobin is an iron-containing protein that gives red blood cells their color and facilitates transportation of oxygen from the lungs to tissues and carbon dioxide from tissues to the lungs to be exhaled. Red blood cells are the most abundant cell in the blood, accounting for about 40–45% of its volume. Red blood cells are circular, biconcave, disk-shaped and deformable to allow them to sque ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anaemia
Anemia (also spelt anaemia in British English) is a blood disorder in which the blood has a reduced ability to carry oxygen. This can be due to a lower than normal number of red blood cells, a reduction in the amount of hemoglobin available for oxygen transport, or abnormalities in hemoglobin that impair its function. The name is derived . When anemia comes on slowly, the symptoms are often vague, such as tiredness, weakness, shortness of breath, headaches, and a reduced ability to exercise. When anemia is acute, symptoms may include confusion, feeling like one is going to pass out, loss of consciousness, and increased thirst. Anemia must be significant before a person becomes noticeably pale. Additional symptoms may occur depending on the underlying cause. Anemia can be temporary or long term and can range from mild to severe. Anemia can be caused by blood loss, decreased red blood cell production, and increased red blood cell breakdown. Causes of blood loss inclu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
David Pegler
David Norman Pegler (born 2 November 1938) is a British mycologist who spent his entire professional career at Kew Gardens, where he became Head of Mycology and assistant keeper of the herbarium. A leading authority on tropical agarics, he described 11 new genera and over 180 species of fungi during expeditions to regions including East Africa, the Caribbean, and South America. He authored more than 200 scholarly articles and 35 books on fungal systematicswhilst also producing popular field guides, and received the Distinguished Mycologist Award from the Mycological Society of America upon his retirement in 1998. His contributions to mycology have been honoured with several species named after him and with two fungal genera, '' Pegleromyces'' and '' Peglerochaete''. Early life and education Pegler developed an interest in natural history during his childhood, joining natural history societies and bird-watching groups. This led to his fascination with fungi, which eventually shap ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
University Of Chicago Press
The University of Chicago Press is the university press of the University of Chicago, a Private university, private research university in Chicago, Illinois. It is the largest and one of the oldest university presses in the United States. It publishes a wide range of academic titles, including ''The Chicago Manual of Style'', numerous academic journals, and advanced monographs in the academic fields. The press is located just south of the Midway Plaisance on the University of Chicago campus. One of its quasi-independent projects is the BiblioVault, a digital repository for scholarly books. History The University of Chicago Press was founded in 1890, making it one of the oldest continuously operating university presses in the United States. Its first published book was Robert F. Harper's ''Assyrian and Babylonian Letters Belonging to the Kouyunjik Collections of the British Museum''. The book sold five copies during its first two years, but by 1900, the University of Chicago Pr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hemolytic
Hemolysis or haemolysis (), also known by several other names, is the rupturing (lysis) of red blood cells (erythrocytes) and the release of their contents (cytoplasm) into surrounding fluid (e.g. blood plasma). Hemolysis may occur in vivo or in vitro. One cause of hemolysis is the action of hemolysins, toxins that are produced by certain pathogenic bacteria or fungi. Another cause is intense physical exercise. Hemolysins damage the red blood cell's cytoplasmic membrane, causing lysis and eventually cell death. Etymology From hemo- + -lysis, from Ancient Greek (, 'blood') + , 'loosening'). Inside the body Hemolysis inside the body can be caused by a large number of medical conditions, including some parasites (''e.g.'', ''Plasmodium''), some autoimmune disorders (''e.g.'', autoimmune haemolytic anaemia, drug-induced hemolytic anemia, atypical hemolytic uremic syndrome (aHUS)), some genetic disorders (''e.g.'', Sickle-cell disease or G6PD deficiency), or blood with t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |