|
Blitum
''Blitum'' is a genus of flowering plants in the amaranth family Amaranthaceae, subfamily Chenopodioideae. It is closely related to genus '' Spinacia''. Its 12 species were traditionally placed in the genera '' Chenopodium'', ''Monolepis'', or ''Scleroblitum''. The species of genus ''Blitum'' occur in Asia, Europe, North Africa, the Americas, and Australia. Description The species in genus ''Blitum'' are non-aromatic annual or perennial herbs. They are glabrous, or sometimes covered with stipitate vesicular hairs, young plants may be sticky. From the base emerge several erect, ascending or prostrate stems, that are unbranched or sparsely branched. The alternate leaves consist of a petiole and a simple blade. The basal leaves are often long-petiolate and forming a rosette. The leaf blade is thin oder slightly fleshy, and may be triangular, triangular-hastate, triangular-lanceolate, or spathulate, with entire to dentate margins. The inflorescences consist of spicately arrange ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Blitum Capitatum
Strawberry blite (''Blitum capitatum'', syn. ''Chenopodium capitatum'') is an edible annual plant, also known as blite goosefoot, strawberry goosefoot, strawberry spinach, Indian paint, and Indian ink. It is native to most of North America throughout the United States and Canada, including northern areas. It is considered to be endangered in Ohio. It is also found in parts of Europe and New Zealand. Fruit are small, pulpy, bright red and edible, resembling strawberries, though their taste is more bland. The juice from the fruit was also used as a red dye by native North Americans. The fruits contain small, black, lens-shaped seeds that are 0.7–1.2 mm long. The greens contain vitamins A and C; they are edible raw when young or as a potherb. If raw they should be eaten in moderation as they contain oxalates. The seeds may be toxic in large amounts. Strawberry blite is found in moist mountain valleys. References Susy Fuentes-Bazan, Pertti Uotila, Thomas Borsch: ''A nov ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
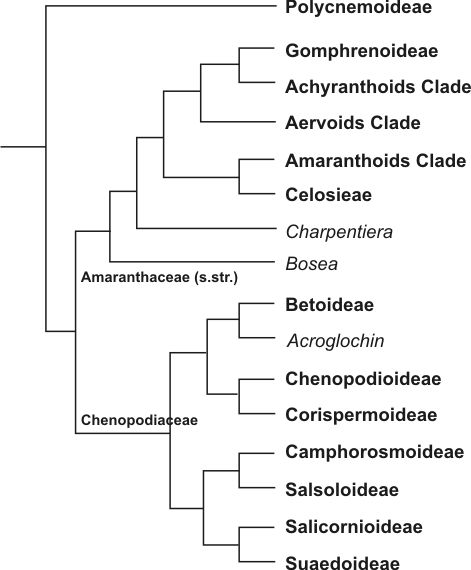
Chenopodioideae
The Chenopodioideae are a subfamily of the flowering plant family Amaranthaceae in the APG III system, which is largely based on molecular phylogeny, but were included – together with other subfamilies – in the family Chenopodiaceae, or goosefoot family, in the Cronquist system. Food species comprise spinach (''Spinacia oleracea''), Good King Henry (''Blitum bonus-henricus''), several ''Chenopodium'' species (quinoa, Chenopodium pallidicaule, kañiwa, Chenopodium album, fat hen), Atriplex, orache (''Atriplex'' spp.), and Dysphania ambrosioides, epazote (''Dysphania ambrosioides''). The name is Greek for goosefoot, the common name of a genus of plants having small greenish flowers. Description The Chenopodioideae are annual or perennial herbs, subshrubs, shrub or small trees. The leaves are usually alternate and flat. The flowers are often unisexual. Many species are monoecious or have mixed inflorescences of bisexual and unisexual flowers. Some species are dioecious, like ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chenopodium
''Chenopodium'' is a genus of numerous species of perennial or annual herbaceous flowering plants known as the goosefoot, which occur almost anywhere in the world. It is placed in the family Amaranthaceae in the APG II system; older classification systems, notably the widely used Cronquist system, separate it and its relatives as Chenopodiaceae, but this leaves the rest of the Amaranthaceae polyphyletic. However, among the Amaranthaceae, the genus ''Chenopodium'' is the namesake member of the subfamily Chenopodioideae. Description The species of ''Chenopodium'' (s.str., description according to Fuentes et al. 2012) are annual or perennial herbs, shrubs or small trees. They generally rely on alkaline soil. They are nonaromatic, but sometimes fetid (foul-smelling). The young stems and leaves are often densely covered by vesicular globose hairs, thus looking farinose. Characteristically, these trichomes persist, collapsing later and becoming cup-shaped. The branched stems gro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chenopodium Bonus-henricus ENBLA02
''Chenopodium'' is a genus of numerous species of perennial or annual plant, annual herbaceous flowering plants known as the goosefoot, which occur almost anywhere in the world. It is placed in the family Amaranthaceae in the APG II system; older classification systems, notably the widely used Cronquist system, separate it and its relatives as Chenopodiaceae, but this leaves the rest of the Amaranthaceae polyphyletic. However, among the Amaranthaceae, the genus ''Chenopodium'' is the namesake member of the subfamily Chenopodioideae. Description The species of ''Chenopodium'' (s.str., description according to Fuentes et al. 2012) are Annual plant, annual or perennial herbs, shrubs or small trees. They generally rely on alkaline soil. They are nonaromatic, but sometimes fetid (foul-smelling). The young stems and leaves are often densely covered by vesicular globose hairs, thus looking Epicuticular wax#Farina, farinose. Characteristically, these trichomes persist, collapsing later ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Monolepis Nuttalliana (6228342345)
''Blitum nuttallianum'', ( syn. ''Monolepis nuttalliana'') is a species of flowering plant in the amaranth family known by the common names povertyweed and Nuttall's povertyweed. It is native to North America, where it is widespread and common from Alaska to Mexico to New England. It can be found in many types of habitat, including disturbed areas, often favoring wet places. It is a fleshy annual herb producing two or more erect, reddish, hairless stems up to about 40 centimeters tall. The thick lance-shaped or arrowhead-shaped leaves are up to 4 centimeters in length. Clusters of several rounded flowers each appear in the leaf axils and yield small fruits about 2 millimeters wide. Many Native American groups used this plant as a medicine and a food. Southwestern tribes ground the seeds, combining them with mesquite Mesquite is a common name for some plants in the genera ''Neltuma'' and '' Strombocarpa'', which contain over 50 species of spiny, deep-rooted leguminous shrubs ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chenopodium Foliosum
''Blitum virgatum'', ( syn. ''Chenopodium foliosum'') is a species of flowering plant in the amaranth family known by the common name leafy goosefoot. It is native to Eurasia. It can be found on other continents as an introduced species, growing as a minor weed in disturbed habitats and cultivated land. Description This is an erect annual herb growing to a maximum height just over half a meter. The leaves are 1 to 4 centimeters long and may be toothed or smooth-edged. The inflorescences are small spherical clusters of tiny reddish-green flowers wrapped around fruits which are about a millimeter wide. Uses The leaves and inflorescences are edible and resemble spinach; the plant was grown as a leaf vegetable in Europe Europe is a continent located entirely in the Northern Hemisphere and mostly in the Eastern Hemisphere. It is bordered by the Arctic Ocean to the north, the Atlantic Ocean to the west, the Mediterranean Sea to the south, and Asia to the east ... in former ti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spinacia
''Spinacia'' is a flowering plant genus in the subfamily Chenopodioideae of the family Amaranthaceae. The most common member is spinach. Description The species in genus ''Spinacia'' are annual or biennial herbs. Plants are always glabrous. Their stems grow erect and are unbranched or sparsely branched. The alternate leaves consist of a petiole and a simple blade. The basal leaves are often forming a rosette. The leaf blade is triangular-hastate to ovate, sometimes with elongated lobes, with entire or dentate margins and an acute apex. The plants are usually dioecious, (rarely monoecious). The male flowers are in glomerules forming interrupted terminal spike-like panicles. They consist of 4-5 oblong perianth segments and 4-5 stamens. Female flowers are in glomerules sitting in the leaf axils. Enclosed by 2 accrescent or united bracteoles, without perianth, they consist of an ovary with 4-5 filiform stigmas. In fruit, bracteoles become enlarged and hardened, sometimes with de ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amaranthaceae
Amaranthaceae ( ) is a family of flowering plants commonly known as the amaranth family, in reference to its type genus '' Amaranthus''. It includes the former goosefoot family Chenopodiaceae and contains about 165 genera and 2,040 species, making it the most species-rich lineage within its parent order, Caryophyllales. Description Most species in the Amaranthaceae are annual or perennial herbs or subshrubs; others are shrubs; very few species are vines or trees. Some species are succulent. Many species have stems with thickened nodes. The wood of the perennial stem has a typical "anomalous" secondary growth; only in subfamily Polycnemoideae is secondary growth normal. The leaves are simple and mostly alternate, sometimes opposite. They never possess stipules. They are flat or terete, and their shape is extremely variable, with entire or toothed margins. In some species, the leaves are reduced to minute scales. In most cases, neither basal nor terminal aggregations of leav ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rosette (botany)
In botany, a rosette is a circular arrangement of leaves or of structures resembling leaves. In flowering plants, rosettes usually sit near the soil, but they can also be at the top of an otherwise naked branch or trunk. Their structure is an example of a Aerial stem modification, modified stem in which the internode (botany), internode gaps between the leaves do not expand, so that all the leaves remain clustered tightly together and at a similar height. Some insects induce the development of Gall, galls that are leafy rosettes. In bryophytes and algae, a rosette results from the repeated branching of the thallus as the plant grows, resulting in a circular outline. Taxonomies Many plant family (taxonomy), families have varieties with rosette Morphology (biology), morphology; they are particularly common in Asteraceae (such as dandelions), Brassicaceae (such as cabbage), and Bromeliaceae. The fern ''Blechnum fluviatile'' or New Zealand Water Fern (''kiwikiwi'') is a rosette plan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pericarp
Fruits are the mature ovary or ovaries of one or more flowers. They are found in three main anatomical categories: aggregate fruits, multiple fruits, and simple fruits. Fruitlike structures may develop directly from the seed itself rather than the ovary, such as a fleshy aril or sarcotesta. The grains of grasses are single-seed simple fruits wherein the pericarp and seed coat are fused into one layer. This type of fruit is called a caryopsis. Examples include cereal grains, such as wheat, barley, oats and rice. Categories of fruits Fruits are found in three main anatomical categories: aggregate fruits, multiple fruits, and simple fruits. Aggregate fruits are formed from a single compound flower and contain many ovaries or fruitlets. Examples include raspberries and blackberries. Multiple fruits are formed from the fused ovaries of multiple flowers or inflorescence. An example of multiple fruits are the fig, mulberry, and the pineapple. Simple fruits are formed from ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stigma (botany)
The stigma (: stigmas or stigmata) is the receptive tip of a Gynoecium#Carpels, carpel, or of several fused carpels, in the gynoecium of a flower. Description The stigma, together with the Style (botany), style and ovary (botany), ovary (typically called the stigma-style-ovary system) comprises the pistil, which is part of the gynoecium or female reproductive organ of a plant. The stigma itself forms the distal portion of the style, or stylodia, and is composed of , the cells of which are receptive to pollen. These may be restricted to the apex of the style or, especially in wind pollinated species, cover a wide surface. The stigma receives pollen and it is on the stigma that the pollen grain germination, germinates. Often sticky, the stigma is adapted in various ways to catch and trap pollen with various hairs, flaps, or sculpturings. The pollen may be captured from the air (wind-borne pollen, anemophily), from visiting insects or other animals (Pollination syndrome#Biotic, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |