|
Battery Electric Vehicles
A battery electric vehicle (BEV), pure electric vehicle, only-electric vehicle, fully electric vehicle or all-electric vehicle is a type of electric vehicle (EV) that uses electrical energy exclusively from an on-board battery pack to power one or more electric traction motors, on which the vehicle solely relies for propulsion. This definition excludes hybrid electric vehicles (HEVs; including mild, full and plug-in hybrids), which use internal combustion engines (ICEs) in adjunct to electric motors for propulsion; and fuel cell electric vehicles (FCEVs) and range-extended electric vehicles (REEVs), which consume fuel through a fuel cell or an ICE-driven generator to produce electricity needed for the electric motors. BEVs have no fuel tanks and replenish their energy storage by plugging into a charging station, electrical grid or getting a new battery at a battery swap station, and use motor controllers to modulate the output engine power and torque, thus eliminating ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nissan Leaf And Tesla Model S In Norway Cropped
is a Japanese multinational Automotive industry, automobile manufacturer headquartered in Yokohama, Kanagawa, Japan. The company sells its vehicles under the ''Nissan'' and ''Infiniti'' brands, and formerly the ''Datsun'' brand, with in-house performance tuning products (including cars) under the Nismo and Autech brands. The company traces back to the beginnings of the 20th century, with the Nissan ''zaibatsu'' or called Nissan Group. Since 1999, Nissan has been part of the Renault–Nissan–Mitsubishi Alliance (Mitsubishi joining in 2016), a partnership between Nissan and Mitsubishi Motors of Japan, with Renault of France. , Renault holds a 15% voting stake in Nissan, while Nissan holds the same stake in Renault. Since October 2016, Nissan held a 34% controlling stake in Mitsubishi Motors. In November 2024, Nissan reduced its stake in Mitsubishi Motors from 34% to 24%. Nissan planned to merge with Honda Motor Company in 2026, after an announcement in December 2024. However by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fuel Cell
A fuel cell is an electrochemical cell that converts the chemical energy of a fuel (often hydrogen fuel, hydrogen) and an oxidizing agent (often oxygen) into electricity through a pair of redox reactions. Fuel cells are different from most battery (electricity), batteries in requiring a continuous source of fuel and oxygen (usually from air) to sustain the chemical reaction, whereas in a battery the chemical energy usually comes from substances that are already present in the battery. Fuel cells can produce electricity continuously for as long as fuel and oxygen are supplied. The first fuel cells were invented by Sir William Robert Grove, William Grove in 1838. The first commercial use of fuel cells came almost a century later following the invention of the hydrogen–oxygen fuel cell by Francis Thomas Bacon in 1932. The alkaline fuel cell, also known as the Bacon fuel cell after its inventor, has been used in NASA space programs since the mid-1960s to generate power for sate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
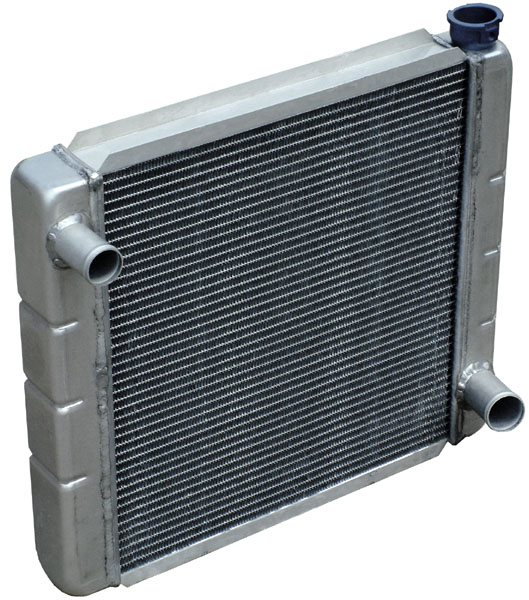
Internal Combustion Engine Cooling
Internal combustion engine cooling uses either air or liquid to remove the waste heat from an internal combustion engine. For small or special purpose engines, cooling using air from the atmosphere makes for a lightweight and relatively simple system. Watercraft can use water directly from the surrounding environment to cool their engines. For water-cooled engines on aircraft and surface vehicles, waste heat is transferred from a closed loop of water pumped through the engine to the surrounding atmosphere by a radiator. Water has a higher heat capacity than air, and can thus move heat more quickly away from the engine, but a radiator and pumping system add weight, complexity, and cost. Higher power engines can move more weight but can also generate more waste heat, meaning they are generally water-cooled. Radial engines allow air to flow around each cylinder directly, giving them an advantage for air cooling over straight engines, flat engines, and V engines. Rotary engines ha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Transmission (mechanical Device)
A transmission (also called a gearbox) is a mechanical device invented by Louis Renault (who founded Renault) which uses a gear set—two or more gears working together—to change the speed, direction of rotation, or torque multiplication/reduction in a machine. Transmissions can have a single fixed-gear ratio, multiple distinct gear ratios, or continuously variable ratios. Variable-ratio transmissions are used in all sorts of machinery, especially vehicles. Applications Early uses Early transmissions included the right-angle drives and other gearing in windmills, horse-powered devices, and steam-powered devices. Applications of these devices included pumps, mills and hoists. Bicycles Bicycles traditionally have used hub gear or Derailleur gear transmissions, but there are other more recent design innovations. Automobiles Since the torque and power output of an internal combustion engine (ICE) varies with its rpm, automobiles powered by ICEs require multi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
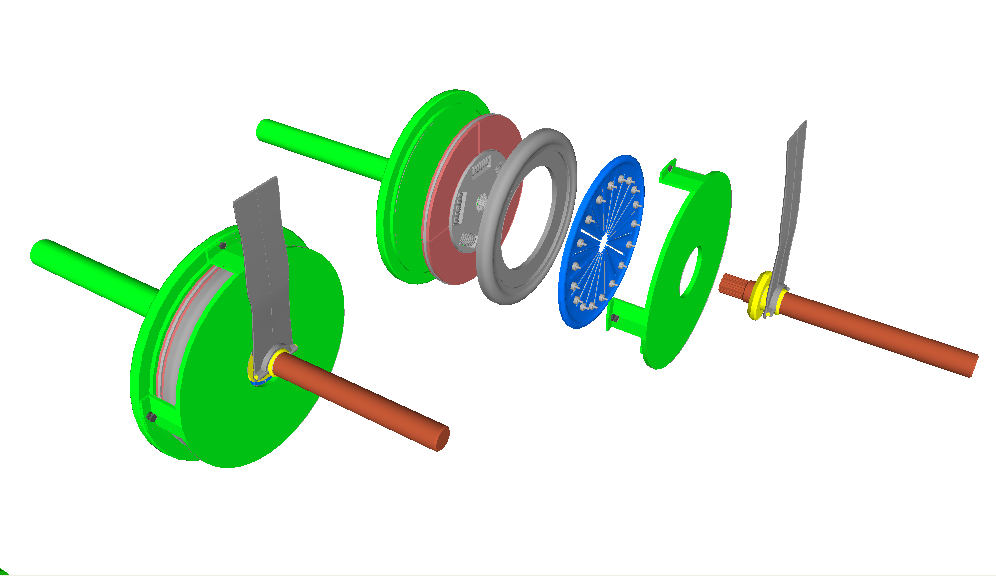
Clutch
A clutch is a mechanical device that allows an output shaft to be disconnected from a rotating input shaft. The clutch's input shaft is typically attached to a motor, while the clutch's output shaft is connected to the mechanism that does the work. In a motor vehicle, the clutch acts as a mechanical linkage between the engine and transmission. By disengaging the clutch, the engine speed (RPM) is no longer determined by the speed of the driven wheels. Another example of clutch usage is in electric drills. The clutch's input shaft is driven by a motor and the output shaft is connected to the drill bit (via several intermediate components). The clutch allows the drill bit to either spin at the same speed as the motor (clutch engaged), spin at a lower speed than the motor (clutch slipping) or remain stationary while the motor is spinning (clutch disengaged). Types Dry clutch A ''dry clutch'' uses dry friction to transfer power from the input shaft to the output shaft, f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Torque
In physics and mechanics, torque is the rotational analogue of linear force. It is also referred to as the moment of force (also abbreviated to moment). The symbol for torque is typically \boldsymbol\tau, the lowercase Greek letter ''tau''. When being referred to as moment of force, it is commonly denoted by . Just as a linear force is a push or a pull applied to a body, a torque can be thought of as a twist applied to an object with respect to a chosen point; for example, driving a screw uses torque to force it into an object, which is applied by the screwdriver rotating around its axis to the drives on the head. Historical terminology The term ''torque'' (from Latin , 'to twist') is said to have been suggested by James Thomson and appeared in print in April, 1884. Usage is attested the same year by Silvanus P. Thompson in the first edition of ''Dynamo-Electric Machinery''. Thompson describes his usage of the term as follows: Today, torque is referred to using d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Engine Power
Engine power is the power that an engine can develop. It can be expressed in power units, most commonly kilowatt, metric horsepower (often abbreviated PS), or horsepower. In terms of internal combustion engines, the engine power usually describes the ''rated power'', which is a power output that the engine can maintain over a long period of time according to a certain testing method, for example ISO 1585. In general though, an internal combustion engine has a power take-off shaft (the crankshaft), therefore, the rule for shaft power applies to internal combustion engines: Engine power is the product of the engine torque and the crankshaft's angular velocity. Definition Power is the product of torque and angular velocity:. p 233 Let: *P= Power in Watt (W) *M= Torque in Newton-metre (N·m) *n= Crankshaft speed per Second (s−1) *\omega= Angular velocity = 2\pi n Power is then: :P= M \cdot \omega In internal combustion engines, the crankshaft speed n is a more common ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Motor Controller
A motor controller is a device or group of devices that can coordinate in a predetermined manner the performance of an electric motor. A motor controller might include a manual or automatic means for starting and stopping the motor, selecting forward or reverse rotation, selecting and regulating the speed, regulating or limiting the torque, and protecting against overloads and electrical faults. Motor controllers may use electromechanical switching, or may use power electronics devices to regulate the speed and direction of a motor. Applications Motor controllers are used with both DC motors (direct current) and AC motors (alternating current). A controller includes means to connect the motor's windings to the electrical power supply, and may also include overload, over-current, and oveheating protection and wiring (i.e. magnetic starter). A motor controller may also supervise the motor's field circuit, or detect conditions such as low supply voltage, incorrect polarity or in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battery Swapping
Battery swapping or battery switching is an electric vehicle technology that allows battery electric vehicles to quickly exchange a discharged electric vehicle battery, battery pack for a fully charged one, rather than recharging the vehicle via a charging station. Battery swapping is common in electric forklift truck, forklift applications. , Taiwanese electric motorcycles and scooters, electric scooter manufacturer Gogoro operates the largest battery swap network for electric mopeds, with nearly 11,000 GoStations in Taiwan, and 250 in Mainland China. Chinese luxury carmaker Nio Inc., Nio is the only major operator of automobile battery swapping stations for the public. The company has built around 2250 battery swap stations around China and Europe, and the process takes three minutes from start to finish. Previously, Renault and Tesla Inc., Tesla attempted to make their vehicles capable of swapping batteries. History The concept of an exchangeable battery service was proposed ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electrical Grid
An electrical grid (or electricity network) is an interconnected network for electricity delivery from producers to consumers. Electrical grids consist of power stations, electrical substations to step voltage up or down, electric power transmission to carry power over long distances, and finally electric power distribution to customers. In that last step, voltage is stepped down again to the required service voltage. Power stations are typically built close to energy sources and far from densely populated areas. Electrical grids vary in size and can cover whole countries or continents. From small to large there are microgrids, wide area synchronous grids, and super grids. The combined transmission and distribution network is part of electricity delivery, known as the ''power grid''. Grids are nearly always synchronous, meaning all distribution areas operate with three phase alternating current (AC) frequencies synchronized (so that voltage swings occur at almost the same ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Charging Station
A charging station, also known as a charge point, chargepoint, or electric vehicle supply equipment (EVSE), is a power supply electrical device, device that supplies electrical power for recharging plug-in electric vehicles (including battery electric vehicles, electric trucks, electric buses, neighborhood electric vehicles, and plug-in hybrid vehicles). There are two main types of EV chargers: Alternating current (AC) charging stations and direct current (DC) charging stations. Electric vehicle batteries can only be charged by direct current electricity, while most mains electricity is delivered from the power grid as alternating current. For this reason, most electric vehicles have a built-in AC-to-DC converter commonly known as the "onboard charger" (OBC). At an AC charging station, AC power from the grid is supplied to this onboard charger, which converts it into DC power to recharge the battery. DC chargers provide higher power charging (which requires much larger AC-to- ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plug-in Electric Vehicle
A plug-in electric vehicle (PEV) is any road vehicle that can utilize an external source of electricity (such as a wall socket that connects to the power grid) via an detachable power cable to store electrical energy within its onboard rechargeable battery packs, which will in turn power an electric traction motor that propel the vehicle's drive wheels. It is a subset of electric vehicles and includes all-electric/battery electric vehicles (BEVs) and plug-in hybrid electric vehicles (PHEVs) ''See definition on pp. 2.'' both of which are capable of sustained all-electric driving within a designated range due to the ability to fully charge their batteries before a journey. Plug-in electric cars have several benefits compared to conventional internal combustion engine vehicles. All-electric vehicles have lower operating and maintenance costs, and produce little or no air pollution when under all-electric mode, thus (depending on the electricity source) reducing societal de ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |