|
Astérix (satellite)
''Astérix'' or A-1 (initially conceptualized as FR.2 or FR-2) is the first French satellite. It was launched on 26 November 1965 by a Diamant A rocket from the CIEES launch site at Hammaguir, Algeria. With ''Astérix'', France became the sixth country to have an artificial satellite and the third country to launch a satellite on its own rocket. Its main purpose was to test the Diamant launcher, though it was also designed to study the ionosphere. ''Astérix'' continues to orbit Earth as of 2023 and is expected to remain in orbit for centuries. Background The French space agencies Centre national d'études spatiales (CNES) and Centre national d'études des télécommunications (CNET) were developing ''Astérix'' concurrent with FR-1, another satellite, as early as 1963. FR-1 was the first step of an ambitious French plan to launch six FR-series satellites, each meant to study a different aspect of the Earth's atmosphere. FR-1 was generally designed to study the Earth's magnet ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Musée De L'air Et De L'espace
The Musée de l'air et de l'espace (, ) is a French aerospace museum, located at the south-eastern edge of Paris–Le Bourget Airport, north of Paris, and in the Communes of France, commune of Le Bourget. It was inaugurated in 1919 after a proposal by the celebrated aeronautics engineer Albert Caquot (1881–1976). Description Occupying over 1.5sq km of land and hangars, it is one of the oldest aviation museums in the world. The museum's collection contains more than 19,595 items, including 150 aircraft, and material from as far back as the 16th Century. Also displayed are more modern air and spacecraft, including the prototype for Concorde, and Swiss and Soviet rockets. The museum also has the only known remaining piece — the jettisoned main landing gear — of ''L'Oiseau Blanc'' (''The White Bird''), the 1927 aircraft which attempted to make the first Transatlantic flight, Transatlantic crossing from Paris to New York. On 8 May 1927 Charles Nungesser and François Coli abo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
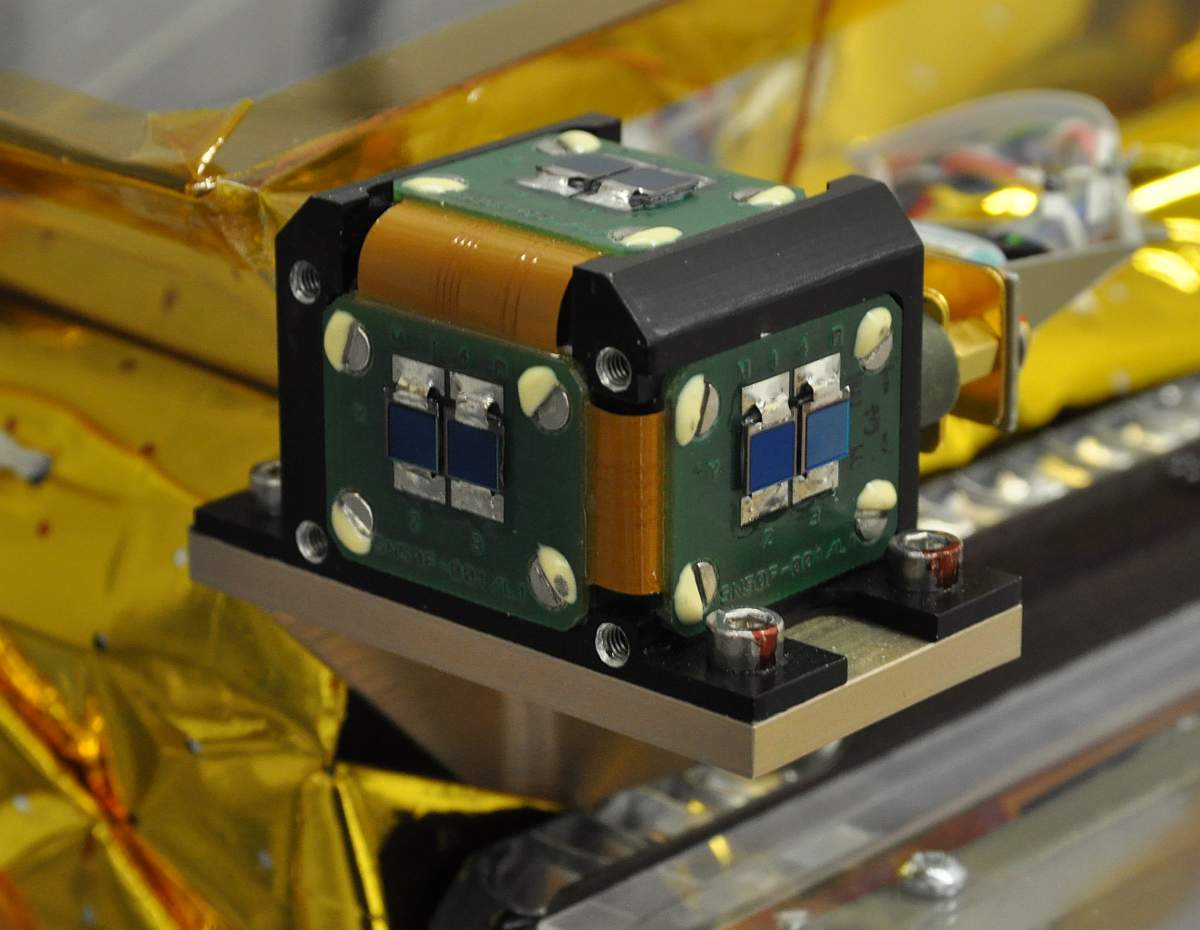
Sun Sensor
A Sun sensor is a navigational instrument used by spacecraft to detect the position of the Sun. Sun sensors are used for Spacecraft attitude control, attitude control, solar array pointing, gyroscope, gyro updating, and safe mode (spacecraft), fail-safe recovery. In addition to spacecraft, Sun sensors find use in ground-based weather stations and Sun-tracking systems, and aerial vehicles including Balloon (aeronautics), balloons and Unmanned aerial vehicle, UAVs. Mechanism There are various types of Sun sensors, which differ in their technology and performance characteristics. Sun presence sensors provide a binary number, binary output, indicating when the Sun is within the sensor's field of view. Analog electronics, Analog and digital electronics, digital Sun sensors, in contrast, indicate the angle of the Sun by continuous and discrete signal outputs, respectively. In typical Sun sensors, a thin slit at the top of a rectangular chamber allows a line of light to fall on an array ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fiberglass
Fiberglass (American English) or fibreglass (English in the Commonwealth of Nations, Commonwealth English) is a common type of fibre-reinforced plastic, fiber-reinforced plastic using glass fiber. The fibers may be randomly arranged, flattened into a sheet called a chopped strand mat, or woven into glass cloth. The plastic Matrix (composite), matrix may be a thermoset polymer matrix—most often based on thermosetting polymers such as epoxy, polyester resin, or vinyl ester resin—or a thermoplastic. Cheaper and more flexible than Carbon-fiber-reinforced polymers, carbon fiber, it is stronger than many metals by weight, non-magnetic, non-conductive, transparent to electromagnetic radiation, can be molded into complex shapes, and is chemically inert under many circumstances. Applications include aircraft, boats, automobiles, bath tubs and enclosures, swimming pools, hot tubs, septic tanks, water tanks, roofing, pipes, cladding, orthopedic casts, surfboards, and external door skins ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
European Space Research Organisation
The European Space Research Organisation (ESRO) was an international organisation founded by 10 European nations with the intention of jointly pursuing scientific research in space. It was founded in 1964. As an organisation ESRO was based on a previously existing international scientific institution, CERN. The ESRO convention, the organisations founding document outlines it as an entity exclusively devoted to scientific pursuits. This was the case for most of its lifetime but in the final years before the formation of ESA, the European Space Agency, ESRO began a programme in the field of telecommunications. Consequently, ESA is not a mainly pure science focused entity but concentrates on telecommunications, earth observation and other application motivated activities. ESRO was merged with European Launcher Development Organisation, ELDO in 1975 to form the European Space Agency. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
CERN
The European Organization for Nuclear Research, known as CERN (; ; ), is an intergovernmental organization that operates the largest particle physics laboratory in the world. Established in 1954, it is based in Meyrin, western suburb of Geneva, on the France–Switzerland border. It comprises #Member states and budget, 24 member states. Israel, admitted in 2013, is the only full member geographically out of Europe. CERN is an official United Nations General Assembly observers#Intergovernmental organizations, United Nations General Assembly observer. The acronym CERN is also used to refer to the laboratory; in 2023, it had 2,666 scientific, technical, and administrative staff members, and hosted about 12,370 users from institutions in more than 80 countries. In 2016, CERN generated 49 Byte#Multiple-byte units, petabytes of data. CERN's main function is to provide the particle accelerators and other infrastructure needed for high-energy physics research – consequently, numer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
NASA
The National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA ) is an independent agencies of the United States government, independent agency of the federal government of the United States, US federal government responsible for the United States's civil list of government space agencies, space program, aeronautics research and outer space, space research. National Aeronautics and Space Act, Established in 1958, it succeeded the National Advisory Committee for Aeronautics (NACA) to give the American space development effort a distinct civilian orientation, emphasizing peaceful applications in space science. It has since led most of America's space exploration programs, including Project Mercury, Project Gemini, the 1968–1972 Apollo program missions, the Skylab space station, and the Space Shuttle. Currently, NASA supports the International Space Station (ISS) along with the Commercial Crew Program and oversees the development of the Orion (spacecraft), Orion spacecraft and the Sp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Saphir (rocket)
VE 231 Saphir (French, meaning ''sapphire'') was a French two stage sounding rocket. It was part of the ''pierres précieuses'' (fr.: gemstones) program, that included five prototypes Agathe, Topaze, Emeraude, Rubis and Saphir, leading up to the Diamant orbital rocket. Its codename, VE 231, indicates that it is a "Véhicule Expérimental" (Experimental Vehicle) with 2 stages, using liquid and solid propellant (code 3), and guided (code 1). Saphir was used between 1965 and 1967 and had a payload capacity of . The rocket could reach a maximum altitude of and produced thrust of at launch. Saphir had a launch mass of , a diameter of and a length of . Saphir variants were designed to allow testing of radio-controlled guidance (VE231P), inertial guidance (VE231G), and warhead separation and ablative heat shielding of a re-entry vehicle (VE231R). The Diamant rocket, which carried the first French satellite, Asterix-1, into orbit, was developed from the Saphir with the additi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Intermediate-range Ballistic Missile
An intermediate-range ballistic missile (IRBM) is a ballistic missile with a range (aeronautics), range between (), categorized between a medium-range ballistic missile (MRBM) and an intercontinental ballistic missile (ICBM). Classifying ballistic missiles by range is done mostly for convenience. In principle there is little difference between a high-performance IRBM and a low-performance ICBM, because decreasing payload mass can increase the range over the ICBM threshold. The range definition used here is used within the U.S. Missile Defense Agency. History The progenitor for the IRBM was the Aggregate (rocket family)#A4b/A9, A4b rocket, winged for increased range and based on the famous V-2 rocket, V-2, Vergeltung, or "Reprisal", officially called Aggregate series, A4, rocket designed by Wernher von Braun. The V-2 was widely used by Nazi Germany at the end of World War II to bomb English and Belgian cities. The A4b was the prototype for the upper stage of the Aggregate (rock ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
V-2 Rocket
The V2 (), with the technical name ''Aggregat (rocket family), Aggregat-4'' (A4), was the world's first long-range missile guidance, guided ballistic missile. The missile, powered by a liquid-propellant rocket engine, was developed during the Second World War in Nazi Germany as a "V-weapons, vengeance weapon" and assigned to attack Allies of World War II, Allied cities as retaliation for the Strategic bombing during World War II#The British later in the war, Allied bombings of German cities. The rocket also became the first artificial object to travel into space by crossing the Kármán line (edge of space) with the vertical launch of MW 18014 on 20 June 1944. Research of military use of long-range rockets began when the graduate studies of Wernher von Braun were noticed by the German Army. A series of prototypes culminated in the A4, which went to war as the . Beginning in September 1944, more than 3,000 were launched by the Wehrmacht against Allied targets, first London and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nazi Germany
Nazi Germany, officially known as the German Reich and later the Greater German Reich, was the German Reich, German state between 1933 and 1945, when Adolf Hitler and the Nazi Party controlled the country, transforming it into a Totalitarianism, totalitarian dictatorship. The Third Reich, meaning "Third Realm" or "Third Empire", referred to the Nazi claim that Nazi Germany was the successor to the earlier Holy Roman Empire (800–1806) and German Empire (1871–1918). The Third Reich, which the Nazis referred to as the Thousand-Year Reich, ended in May 1945, after 12 years, when the Allies of World War II, Allies defeated Germany and entered the capital, Berlin, End of World War II in Europe, ending World War II in Europe. After Hitler was appointed Chancellor of Germany in 1933, the Nazi Party began to eliminate political opposition and consolidate power. A 1934 German referendum confirmed Hitler as sole ''Führer'' (leader). Power was centralised in Hitler's person, an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cold War
The Cold War was a period of global Geopolitics, geopolitical rivalry between the United States (US) and the Soviet Union (USSR) and their respective allies, the capitalist Western Bloc and communist Eastern Bloc, which lasted from 1947 until the dissolution of the Soviet Union in 1991. The term ''Cold war (term), cold war'' is used because there was no direct fighting between the two superpowers, though each supported opposing sides in regional conflicts known as proxy wars. In addition to the struggle for ideological and economic influence and an arms race in both conventional and Nuclear arms race, nuclear weapons, the Cold War was expressed through technological rivalries such as the Space Race, espionage, propaganda campaigns, Economic sanctions, embargoes, and sports diplomacy. After the end of World War II in 1945, during which the US and USSR had been allies, the USSR installed satellite state, satellite governments in its occupied territories in Eastern Europe and N ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gaullism
Gaullism ( ) is a Politics of France, French political stance based on the thought and action of World War II French Resistance leader Charles de Gaulle, who would become the founding President of France, President of the Fifth French Republic. De Gaulle French withdrawal from NATO command, withdrew French forces from the Structure of NATO, NATO Command Structure, forced the removal of allied (United States, US) military bases from France, as well as initiated Force de dissuasion, France's own independent nuclear deterrent programme. His actions were predicated on the view that France would not be subordinate to other nations. According to Serge Berstein, Gaullism is "neither a doctrine nor a political ideology" and cannot be considered either Left-wing politics, left or Right-wing politics, right. Rather, "considering its historical progression, it is a Pragmatism, pragmatic exercise of power that is neither free from contradictions nor of concessions to momentary necessity, eve ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |