|
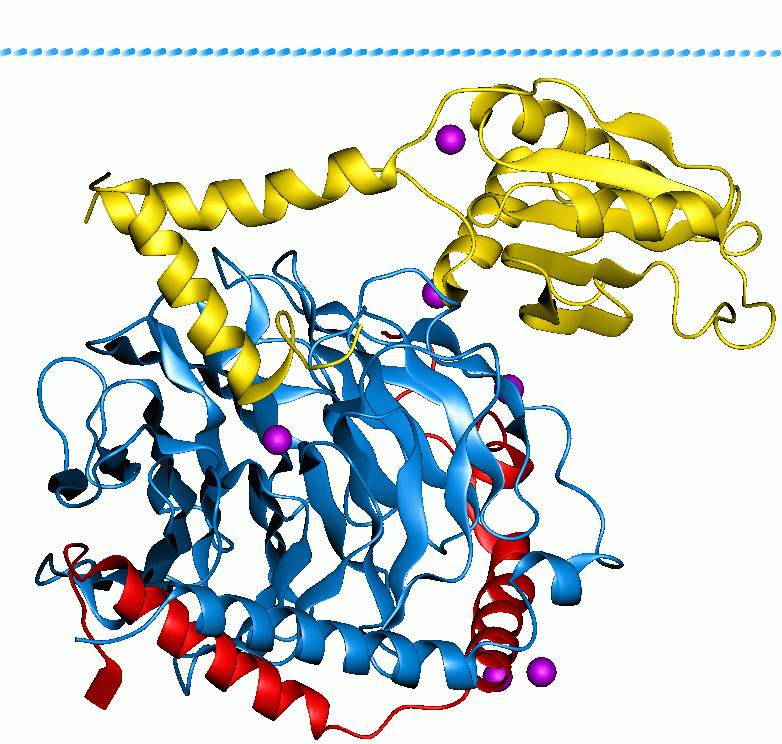
Arrestin
Arrestins (abbreviated Arr) are a small family of proteins important for regulating signal transduction at G protein-coupled receptors. Arrestins were first discovered in the late '80s as a part of a conserved two-step mechanism for regulating the activity of G protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs) in the visual rhodopsin system by Hermann Kühn, Scott Hall, and Ursula Wilden and in the β-adrenergic system by Martin J. Lohse and co-workers. Function In response to a stimulus, GPCRs activate heterotrimeric G proteins. In order to turn off this response, or adapt to a persistent stimulus, active receptors need to be desensitized. The first step in desensitization is phosphorylation of the receptor by a class of serine/threonine kinases called G protein coupled receptor kinases (GRKs). GRK phosphorylation specifically prepares the activated receptor for arrestin binding. Arrestin binding to the receptor blocks further G protein-mediated signaling and targets receptors for int ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arrestin Beta 2
Beta-arrestin-2, or β-arrestin2, also known as arrestin beta-2, is an intracellular protein that in humans is encoded by the ''ARRB2'' gene. Members of arrestin/beta-arrestin protein family are thought to participate in agonist-mediated desensitization of G protein-coupled receptors and cause specific dampening of cellular responses to stimuli such as hormones, neurotransmitters, or sensory signals, as well as having signalling roles in their own right. Arrestin beta 2, like arrestin beta 1, was shown to inhibit beta-adrenergic receptor function in vitro. It is expressed at high levels in the central nervous system and may play a role in the regulation of synaptic receptors. Besides the brain, a cDNA for arrestin beta 2 was isolated from thyroid gland, and thus it may also be involved in hormone-specific desensitization of TSH receptors. Multiple alternatively spliced transcript variants have been found for this gene, but the full-length nature of some variants has not been de ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arrestin Beta 1
Arrestin, beta 1, also known as ARRB1, is a protein which in humans is encoded by the ''ARRB1'' gene. Function Members of arrestin/beta-arrestin protein family are thought to participate in agonist-mediated desensitization of G protein-coupled receptors and cause specific dampening of cellular responses to stimuli such as hormones, neurotransmitters, or sensory signals. Arrestin beta 1 is a cytosolic protein and acts as a cofactor in the beta-adrenergic receptor kinase (BARK) mediated desensitization of beta-adrenergic receptors. Besides the central nervous system, it is expressed at high levels in peripheral blood leukocytes, and thus the BARK/beta-arrestin system is believed to play a major role in regulating receptor-mediated immune functions. Alternatively spliced transcripts encoding different isoforms of arrestin beta 1 have been described, however, their exact functions are not known. Beta-arrestin has been shown to play a role as a scaffold that binds intermediates a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
G Protein–coupled Receptor
G protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs), also known as seven-(pass)-transmembrane domain receptors, 7TM receptors, heptahelical receptors, serpentine receptors, and G protein-linked receptors (GPLR), form a large group of evolutionarily related proteins that are cell surface receptors that detect molecules outside the cell and activate cellular responses. They are coupled with G proteins. They pass through the cell membrane seven times in the form of six loops (three extracellular loops interacting with ligand molecules, three intracellular loops interacting with G proteins, an N-terminal extracellular region and a C-terminal intracellular region) of amino acid residues, which is why they are sometimes referred to as seven-transmembrane receptors. Text was copied from this source, which is available under Attribution 2.5 Generic (CC BY 2.5) licence/ref> Ligands can bind either to the extracellular N-terminus and loops (e.g. glutamate receptors) or to the binding site wit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
SAG (gene)
S-arrestin is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''SAG'' gene. Members of arrestin/beta-arrestin protein family are thought to participate in agonist-mediated desensitization of G-protein-coupled receptors and cause specific dampening of cellular responses to stimuli such as hormones, neurotransmitters, or sensory signals. S-arrestin, also known as S-antigen, is a major soluble protein in photoreceptor cells that is involved in desensitization of the photoactivated transduction cascade. It is expressed in the retina and the pineal gland and inhibits coupling of rhodopsin to transducin in vitro. Additionally, S-arrestin is highly antigenic, and is capable of inducing experimental autoimmune uveoretinitis. Mutations in this gene have been associated with Oguchi disease, a rare autosomal recessive In genetics, dominance is the phenomenon of one variant (allele) of a gene on a chromosome masking or overriding the Phenotype, effect of a different variant of the same gen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ARR3
Arrestin-C, also known as retinal cone arrestin-3, is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''ARR3'' gene. See also * Arrestin Arrestins (abbreviated Arr) are a small family of proteins important for regulating signal transduction at G protein-coupled receptors. Arrestins were first discovered in the late '80s as a part of a conserved two-step mechanism for regulatin ... References Further reading * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * External links * {{gene-X-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
G-protein Coupled Receptor Kinases
G protein-coupled receptor kinases (GPCRKs, GRKs) are a protein family, family of protein kinases within the protein kinase#Protein kinase groups, AGC (protein kinase A, protein kinase G, protein kinase C) group of kinases. Like all AGC kinases, GRKs use ATP to add phosphate to Serine and Threonine residues in specific locations of target proteins. In particular, GRKs phosphorylation, phosphorylate intracellular domains of G protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs). GRKs function in tandem with arrestin proteins to regulate the sensitivity of GPCRs for stimulating downstream heterotrimeric G protein and G protein-coupled receptor#G-protein-independent signaling, G protein-independent signaling pathways. Types of GRKs GRK activity and regulation GRKs reside normally in an inactive state, but their kinase activity is stimulated by binding to a ligand-activated GPCR (rather than by regulatory phosphorylation as is common in other AGC kinases). Because there are only seven GRKs (only ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rhodopsin
Rhodopsin, also known as visual purple, is a protein encoded by the ''RHO'' gene and a G-protein-coupled receptor (GPCR). It is a light-sensitive receptor protein that triggers visual phototransduction in rod cells. Rhodopsin mediates dim light vision and thus is extremely sensitive to light. When rhodopsin is exposed to light, it immediately photobleaches. In humans, it is fully regenerated in about 30 minutes, after which the rods are more sensitive. Defects in the rhodopsin gene cause eye diseases such as retinitis pigmentosa and congenital stationary night blindness. History Rhodopsin was discovered by Franz Christian Boll in 1876. The name rhodopsin derives from Ancient Greek () for "rose", due to its pinkish color, and () for "sight". It was coined in 1878 by the German physiologist Wilhelm Friedrich Kühne (1837–1900). When George Wald discovered that rhodopsin is a holoprotein, consisting of retinal and an apoprotein, he called it opsin, which tod ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Signal Transduction
Signal transduction is the process by which a chemical or physical signal is transmitted through a cell as a biochemical cascade, series of molecular events. Proteins responsible for detecting stimuli are generally termed receptor (biology), receptors, although in some cases the term sensor is used. The changes elicited by ligand (biochemistry), ligand binding (or signal sensing) in a receptor give rise to a biochemical cascade, which is a chain of biochemical events known as a Cell signaling#Signaling pathways, signaling pathway. When signaling pathways interact with one another they form networks, which allow cellular responses to be coordinated, often by combinatorial signaling events. At the molecular level, such responses include changes in the transcription (biology), transcription or translation (biology), translation of genes, and post-translational modification, post-translational and conformational changes in proteins, as well as changes in their location. These molecula ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
G Protein
G proteins, also known as guanine nucleotide-binding proteins, are a Protein family, family of proteins that act as molecular switches inside cells, and are involved in transmitting signals from a variety of stimuli outside a cell (biology), cell to its interior. Their activity is regulated by factors that control their ability to bind to and hydrolyze guanosine triphosphate (GTP) to guanosine diphosphate (GDP). When they are bound to GTP, they are 'on', and, when they are bound to GDP, they are 'off'. G proteins belong to the larger group of enzymes called GTPases. There are two classes of G proteins. The first function as monomeric small GTPases (small G-proteins), while the second function as heterotrimeric G protein protein complex, complexes. The latter class of complexes is made up of ''G alpha subunit, alpha'' (Gα), ''beta'' (Gβ) and ''gamma'' (Gγ) protein subunit, subunits. In addition, the beta and gamma subunits can form a stable Protein dimer, dimeric complex re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |