|
Anthracene
Anthracene is a solid polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon (PAH) of formula C14H10, consisting of three fused benzene rings. It is a component of coal tar. Anthracene is used in the production of the red dye alizarin and other dyes, as a scintillator to detect high energy particles, as production of pharmaceutical drugs. Anthracene is colorless but exhibits a blue (400–500 nm peak) fluorescence under ultraviolet radiation. History and etymology Crude anthracene (with a melting point of only 180°) was discovered in 1832 by Jean-Baptiste Dumas and Auguste Laurent who crystalized it from a fraction of coal tar later known as "anthracene oil". Since their (inaccurate) measurements showed the proportions of carbon and hydrogen of it to be the same as in naphthalene, Laurent called it ''paranaphtaline'' in his 1835 publication of the discovery, which is translated to English as paranaphthalene. Two years later, however, he decided to rename the compound to its modern name d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anthracene Singlet Oxygen Diels-Alder Reaction
Anthracene is a solid polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon (PAH) of formula C14H10, consisting of three fused benzene rings. It is a component of coal tar. Anthracene is used in the production of the red dye alizarin and other dyes, as a scintillator to detect high energy particles, as production of pharmaceutical drugs. Anthracene is colorless but exhibits a blue (400–500 nm peak) fluorescence under ultraviolet radiation. History and etymology Crude anthracene (with a melting point of only 180°) was discovered in 1832 by Jean-Baptiste Dumas and Auguste Laurent who crystalized it from a fraction of coal tar later known as "anthracene oil". Since their (inaccurate) measurements showed the proportions of carbon and hydrogen of it to be the same as in naphthalene, Laurent called it ''paranaphtaline'' in his 1835 publication of the discovery, which is translated to English as paranaphthalene. Two years later, however, he decided to rename the compound to its modern name derived fr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons
A Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon (PAH) is any member of a class of organic compounds that is composed of multiple fused aromatic rings. Most are produced by the incomplete combustion of organic matter— by engine exhaust fumes, tobacco, incinerators, in roasted meats and cereals, or when biomass burns at lower temperatures as in forest fires. The simplest representative is naphthalene, having two aromatic rings, and the three-ring compounds anthracene and phenanthrene. PAHs are uncharged, non-polar and planar. Many are colorless. Many of them are also found in fossil fuel deposits such as coal and in petroleum. Exposure to PAHs can lead to different types of cancer, to fetal development complications, and to cardiovascular issues. Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons are discussed as possible starting materials for abiotic syntheses of materials required by the earliest forms of life. Nomenclature and structure The terms polyaromatic hydrocarbon, or polynuclear aromat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbon
A Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon (PAH) is any member of a class of organic compounds that is composed of multiple fused aromatic rings. Most are produced by the incomplete combustion of organic matter— by engine exhaust fumes, tobacco, incinerators, in roasted meats and cereals, or when biomass burns at lower temperatures as in forest fires. The simplest representative is naphthalene, having two aromatic rings, and the three-ring compounds anthracene and phenanthrene. PAHs are uncharged, non-polar and planar. Many are colorless. Many of them are also found in fossil fuel deposits such as coal and in petroleum. Exposure to PAHs can lead to different types of cancer, to fetal development complications, and to cardiovascular issues. Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons are discussed as possible starting materials for abiotic syntheses of materials required by the earliest forms of life. Nomenclature and structure The terms polyaromatic hydrocarbon, or polynuclear aromatic hydro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alizarin
Alizarin (also known as 1,2-dihydroxyanthraquinone, Mordant Red 11, C.I. 58000, and Turkey Red) is an organic compound with formula that has been used throughout history as a red dye, principally for dyeing textile fabrics. Historically it was derived from the roots of plants of the madder genus.The primary madder species from which alizarin historically has been obtained is '' Rubia tinctorum''. See also In 1869, it became the first natural dye to be produced synthetically. Alizarin is the main ingredient for the manufacture of the madder lake pigments known to painters as rose madder and alizarin crimson. Alizarin in the most common usage of the term has a deep red color, but the term is also part of the name for several related non-red dyes, such as Alizarine Cyanine Green and Alizarine Brilliant Blue. A use of alizarin in modern times is as a staining agent in biological research because it stains free calcium and certain calcium compounds a red or light purple color. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
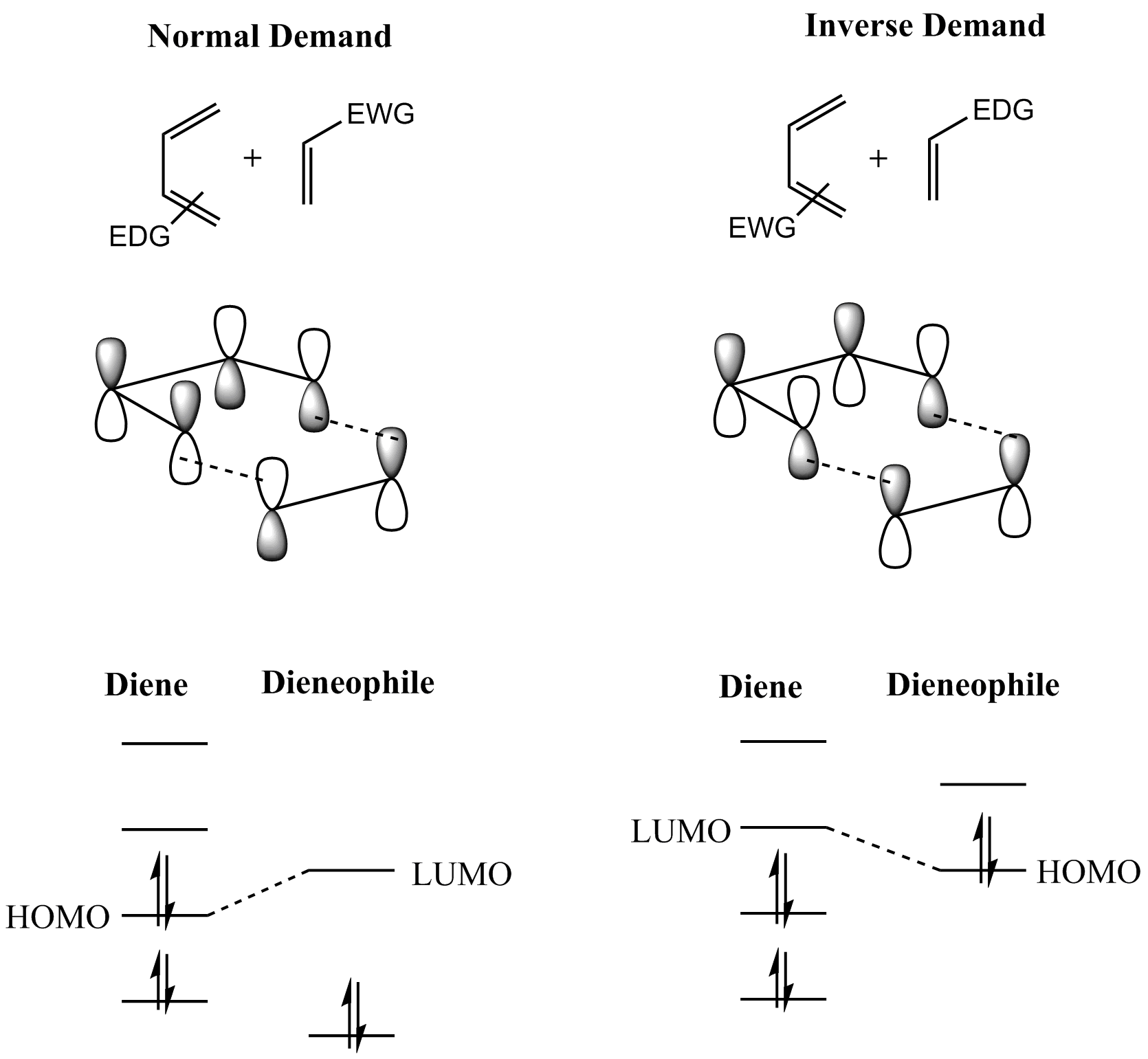
Diels–Alder Reaction
In organic chemistry, the Diels–Alder reaction is a chemical reaction between a Conjugated system, conjugated diene and a substituted alkene, commonly termed the Diels–Alder reaction#The dienophile, dienophile, to form a substituted cyclohexene derivative. It is the prototypical example of a pericyclic reaction with a concerted reaction, concerted mechanism. More specifically, it is classified as a thermally allowed [4+2] cycloaddition with Woodward–Hoffmann rules, Woodward–Hoffmann symbol [π4s + π2s]. It was first described by Otto Diels and Kurt Alder in 1928. For the discovery of this reaction, they were awarded the Nobel Prize in Chemistry in 1950. Through the simultaneous construction of two new carbon–carbon bonds, the Diels–Alder reaction provides a reliable way to form six-membered rings with good control over the regio- and stereochemical outcomes. Consequently, it has served as a powerful and widely applied tool for the introduction of chemical complexity in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dihydroanthracene
9,10-Dihydroanthracene is an organic compound that is derived from the polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon anthracene. Several isomers of dihydroanthracene are known, but the 9,10 derivative is most common. It is a colourless solid that is used as a carrier of H2 as a hydrogen-donor. Preparation Because the aromaticity is not compromised for the flanking rings, anthracene is susceptible to hydrogenation at the 9- and 10- positions. It is produced in the laboratory by dissolving metal reduction using sodium/ethanol, an application of the Bouveault–Blanc reduction. The reduction can be effected by magnesium as well. Finally, it can also be prepared by the coupling of benzyl chloride using aluminium chloride as a catalyst. The bond dissociation energy The bond-dissociation energy (BDE, ''D''0, or ''DH°'') is one measure of the strength of a chemical bond . It can be defined as the standard enthalpy change when is cleaved by homolysis to give fragments A and B, which ar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phenanthrene
Phenanthrene is a polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon (PAH) with formula C14H10, consisting of three fused benzene rings. It is a colorless, crystal-like solid, but can also appear yellow. Phenanthrene is used to make dyes, plastics, pesticides, explosives, and drugs. It has also been used to make bile acids, cholesterol and steroids. Phenanthrene occurs naturally and also is a man-made chemical. Commonly, humans are exposed to phenanthrene through inhalation of cigarette smoke, but there are many routes of exposure. Animal studies have shown that phenanthrene is a potential carcinogen. However, according to IARC, it is not identified as a probable, possible or confirmed human carcinogen. Phenanthrene's three fused rings are angled as in the phenacenes, rather than straight as in the acenes. The compounds with a phenanthrene skeleton but with nitrogen atoms in place of CH sites are known as phenanthrolines. History and etymology Phenanthrene was discovered in coal tar in 1872 inde ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fluorescence
Fluorescence is one of two kinds of photoluminescence, the emission of light by a substance that has absorbed light or other electromagnetic radiation. When exposed to ultraviolet radiation, many substances will glow (fluoresce) with colored visible light. The color of the light emitted depends on the chemical composition of the substance. Fluorescent materials generally cease to glow nearly immediately when the radiation source stops. This distinguishes them from the other type of light emission, phosphorescence. Phosphorescent materials continue to emit light for some time after the radiation stops. This difference in duration is a result of quantum spin effects. Fluorescence occurs when a photon from incoming radiation is absorbed by a molecule, exciting it to a higher energy level, followed by the emission of light as the molecule returns to a lower energy state. The emitted light may have a longer wavelength and, therefore, a lower photon energy than the absorbed radi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scintillator
A scintillator ( ) is a material that exhibits scintillation, the property of luminescence, when excited by ionizing radiation. Luminescent materials, when struck by an incoming particle, absorb its energy and scintillate (i.e. re-emit the absorbed energy in the form of light). Sometimes, the excited state is metastable, so the relaxation back down from the excited state to lower states is delayed (necessitating anywhere from a few nanoseconds to hours depending on the material). The process then corresponds to one of two phenomena: delayed fluorescence or phosphorescence. The correspondence depends on the type of transition and hence the wavelength of the emitted optical photon. Principle of operation A scintillation detector or scintillation counter is obtained when a scintillator is coupled to an electronic light sensor such as a photomultiplier tube (PMT), photodiode, or silicon photomultiplier. PMTs absorb the light emitted by the scintillator and re-emit it in the form ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Naphthalene
Naphthalene is an organic compound with formula . It is the simplest polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon, and is a white Crystal, crystalline solid with a characteristic odor that is detectable at concentrations as low as 0.08 Parts-per notation, ppm by mass. As an Aromaticity, aromatic hydrocarbon, naphthalene's structure consists of a fused pair of benzene rings. It is the main ingredient of traditional mothballs. History In the early 1820s, two separate reports described a white solid with a pungent odor derived from the distillation of coal tar. In 1821, John Kidd (chemist), John Kidd cited these two disclosures and then described many of this substance's properties and the means of its production. He proposed the name ''naphthaline'', as it had been derived from a kind of naphtha (a broad term encompassing any volatile, flammable liquid hydrocarbon mixture, including coal tar). Naphthalene's chemical formula was determined by Michael Faraday in 1826. The structure of two f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Economic Production
Production is the process of combining various inputs, both material (such as metal, wood, glass, or plastics) and immaterial (such as plans, or knowledge) in order to create output. Ideally this output will be a good or service which has value and contributes to the utility of individuals. The area of economics that focuses on production is called production theory, and it is closely related to the consumption (or consumer) theory of economics. The production process and output directly result from productively utilising the original inputs (or factors of production). Known as primary producer goods or services, land, labour, and capital are deemed the three fundamental factors of production. These primary inputs are not significantly altered in the output process, nor do they become a whole component in the product. Under classical economics, materials and energy are categorised as secondary factors as they are byproducts of land, labour and capital. Delving further, primary fa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |