|
Anansi
Anansi or Ananse ( ; literally translates to ''spider'') is a character in Akan religion and folklore associated with stories, wisdom, knowledge, and trickery, most commonly depicted as a spider. Anansi is a character who reflects the culture that he originates from. The Akan people are a close-knit people from present-day southern Ghana who rely on social order, which translates through the stories that come out of their culture. In many ways, Anansi is a paradoxical character whose actions defy this social order, but in incorporating rebellion and doubt into faith, his folkloric presence strengthens it. Taking the role of a trickster, he is also one of the most important characters of West African mythology, West African, African-American folktales, African American and West Indian folklore. These spider tales were spread to the Americas via the Atlantic slave trade. Anansi is best known for his ability to outsmart and triumph over more powerful opponents through his use ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
House Of Anansi Press
House of Anansi Press is a Canadian publishing company, founded in 1967 by writers Dennis Lee and Dave Godfrey. The company specializes in finding and developing new Canadian writers of literary fiction, poetry, and non-fiction. History Anansi started as a small press with only one full-time employee, writer George Fetherling. It quickly gained attention for publishing significant authors such as Margaret Atwood, Matt Cohen, Michael Ondaatje, Marian Engel, Erín Moure, Paulette Jiles, George Grant and Northrop Frye. The company also published many translations of French language works by authors such as Roch Carrier, Anne Hébert, Lise Bissonnette and Marie-Claire Blais. Anansi publishes the transcripts for many of the Massey Lectures. House of Anansi Press was purchased in 1989 by General Publishing, parent of Stoddart Publishing. In June 2002 it was acquired by Scott Griffin, founder of the Griffin Poetry Prize. Select bibliography *'' Survival: A Thematic Guide to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
African-American Folktales
African-American folktales refer to the storytelling and oral history practices of Slavery in the United States, enslaved African Americans from the 1700s through the 1900s. Common themes in African-American folktales include tricksters, life lessons, heartwarming tales, and slavery. African Americans created folktales that spoke about the hardships of slavery, telling stories of folk spirits who could outwit their slaveholders and defeat their enemies. These folk stories gave hope to enslaved people that folk spirits would liberate them from slavery. Folktales have been misused to perpetuate negative stereotypes about the African American community, from minstrel shows to academic journals. One of these figures is John the Conqueror, High John de Conqueror. He often symbolized empowerment for newly freed slaves, saying that if they needed him, his spirit was said to reside in a local root. Other common figures in African American folktales include Anansi, Br'er Rabbit, and Uncle ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trickster
In mythology and the study of folklore and religion, a trickster is a character in a story (god, goddess, spirit, human or anthropomorphisation) who exhibits a great degree of intellect or secret knowledge and uses it to play tricks or otherwise disobey normal rules and defy conventional behavior. Mythology Tricksters, as archetypal characters, appear in the myths of many different cultures. Lewis Hyde describes the trickster as a "boundary-crosser".Hyde, Lewis. ''Trickster Makes This World: Mischief, Myth, and Art''. New York: Farrar, Straus and Giroux, 1998. The trickster crosses and often breaks both physical and societal rules: Tricksters "violate principles of social and natural order, playfully disrupting normal life and then re-establishing it on a new basis." Often, this bending and breaking of rules takes the form of tricks and thievery. Tricksters can be cunning or foolish or both. The trickster openly questions, disrupts and mocks authority. Many cultures have ta ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Akan Religion
Akan religion comprises the traditional beliefs and religious practices of the Akan people of Ghana and eastern Ivory Coast. Akan religion is referred to as Akom. Although most Akan people have identified as Christians since the early 20th century, Akan religion remains practiced by some and is often syncretized with Christianity. The Akan have many subgroups (including the Fanti, Ashanti, the Akuapem, the Wassa, the Abron, the Anyi, and the Baoulé, among others), so the religion varies greatly by region and subgroup. Similar to other traditional religions of West and Central Africa such as West African Vodun, Yoruba religion, or Odinani, Akan cosmology consists of a senior god who generally does not interact with humans and many gods who assist humans. Anansi the spider is a folk hero who is prominent in Ashanti folktales where he is depicted as a wise trickster. In other aspects of Akan spirituality, Anansi is also sometimes considered both a trickster and a deity ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Owuo
Owuo is the abosom of Death in the Asante and Akan mythology of West Ghana and the Ewe, specifically the Krachi tribe of East Ghana and Togo. He is represented with the Adinkra symbol of a ladder. It is said that he was created by Odomankoma (could also be spelt Odomankama) just so he could kill humans (although, specifically for the Asante and Akan retelling, this attribute comes later during an altercation with Ta Kora, hinting that he might've been created before humans) and possibly other deities, such as Odomankoma himself. He signifies the termination of the creative process in the world, a reference to him killing Odomankoma, the Great Creator. Names Owuo is also known as Odomakama Owuo', or the Destroyer (or the Death of Creation), due to his destructive nature of killing mortal life and the fact that he killed Odomankoma, causing Odomankoma to then get resurrected and then live through Nyankapon:''Onyankopon onye Odumankoma sunsum ' (literally 'Nyankopon is Odumanko ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
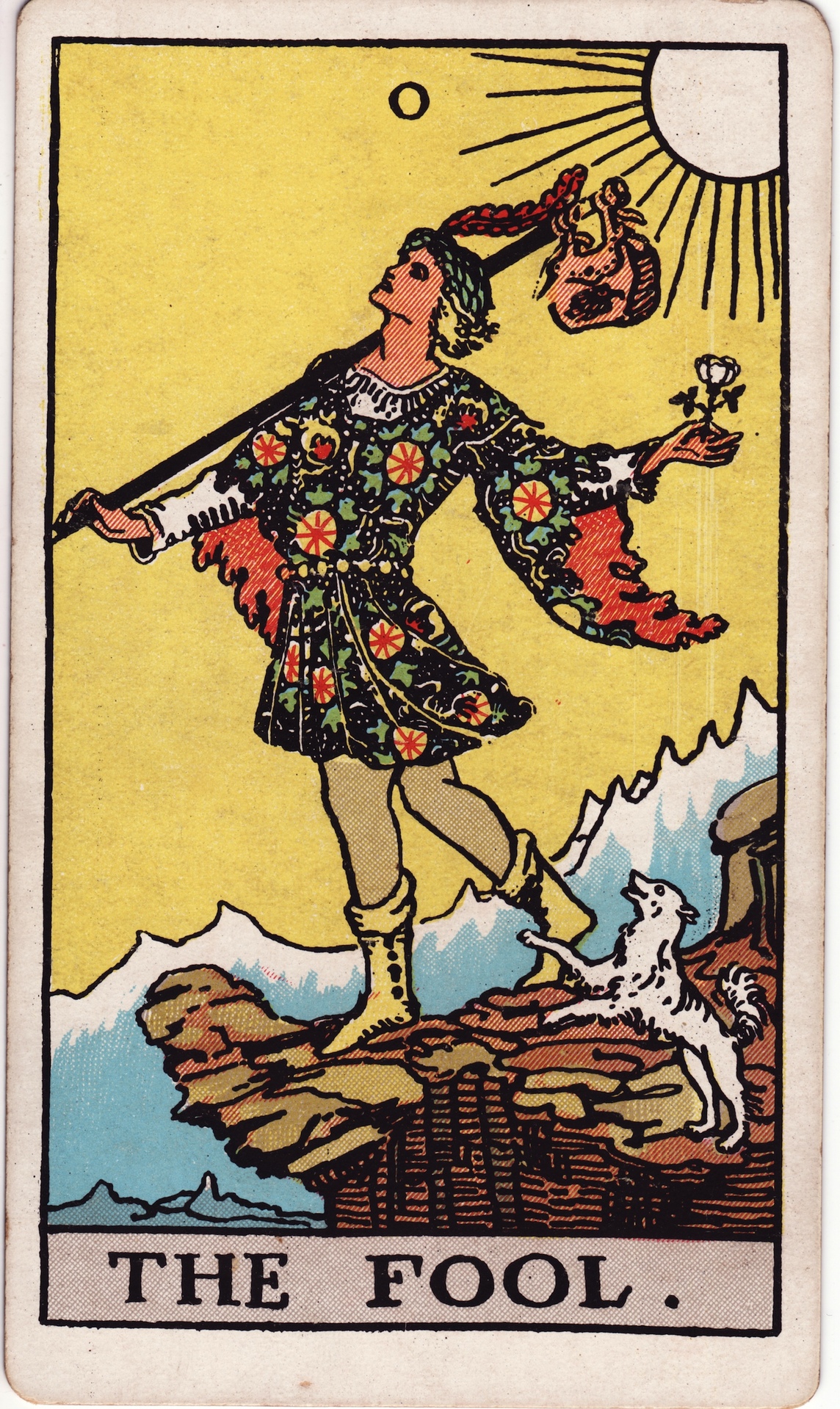
Pamela Colman Smith
Pamela Colman Smith (16 February 1878 – 16 September 1951), nicknamed "Pixie", was a British artist, illustrator, writer, publisher, and occultist. She is best-known for illustrating the Rider–Waite Tarot (also known as the Rider–Waite–Smith or Waite–Smith Tarot) for Arthur Edward Waite. This Tarot, tarot deck became the standard among tarot card reading, tarot card readers, and remains the most widely used today. Smith also illustrated over 20 books, wrote two collections of Caribbean folklore, Jamaican folklore, edited two magazines, and ran the Green Sheaf Press, a small press focused on women writers. Biography Smith was born at 28 Belgrave Road in Pimlico, part of central London. She was the only child of a merchant from Brooklyn, New York (state), New York (before it was part of New York City), Charles Edward Smith (son of Brooklyn mayor Cyrus P. Smith, Cyrus Porter Smith), and his wife Corinne Colman (sister of the painter Samuel Colman). The family was based i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Akan People
The Akan () people are a kwa languages, Kwa group living primarily in present-day Ghana and in parts of Ivory Coast and Togo in West Africa. The Akan speak languages within the Central Tano languages, Central Tano branch of the Potou–Tano languages, Potou–Tano subfamily of the Niger–Congo languages, Niger–Congo family.''Languages of the Akan Area: Papers in Western Kwa Linguistics and on the Linguistic Geography of the Area of Ancient''. Isaac K. Chinebuah, H. Max J. Trutenau, Linguistic Circle of Accra, Basler Afrika Bibliographien, 1976, pp. 168. Subgroups of the Akan people include: the Adansi, Agona, Akuapem people, Akuapem, Akwamu, Akyem, Anyi people, Anyi, Ashanti people, Asante, Baoulé people, Baoulé, Bono people, Bono, Chakosi people, Chakosi, Fante people, Fante, Kwahu, Sefwi people, Sefwi, Wassa, Ahanta people, Ahanta, Denkyira and Nzema people, Nzema, among others. The Akan subgroups all have cultural attributes in common; most notably the tracing of royal m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ashanti People
The Asante, also known as Ashanti in English (), are part of the Akan people, Akan ethnic group and are native to the Ashanti Region of modern-day Ghana. Asantes are the last group to emerge out of the various Akan civilisations. Twi is spoken by over nine million Asante people as their native language. The Asante people developed the Ashanti Empire, along the Lake Volta and Gulf of Guinea. The empire was founded in 1670, and the capital Kumasi, Kumase was founded in 1680 by Asantehene Osei Kofi Tutu I on the advice of Okomfo Anokye, his premier. Sited at the crossroads of the Trans-Saharan trade, Kumase's strategic location contributed significantly to its growth. Over time a number of peculiar factors have combined to transform the Kumase metropolis into a financial centre and political capital. The main causal factors included the unquestioning loyalty to the List of rulers of Asante, Asante rulers and the Kumase metropolis' growing wealth, derived in part from the capital's lu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oral Tradition
Oral tradition, or oral lore, is a form of human communication in which knowledge, art, ideas and culture are received, preserved, and transmitted orally from one generation to another.Jan Vansina, Vansina, Jan: ''Oral Tradition as History'' (1985), reported statements from present generation which "specifies that the message must be oral statements spoken, sung or called out on musical instruments only"; "There must be transmission by word of mouth over at least a generation". He points out, "Our definition is a working definition for the use of historians. Sociologists, linguists or scholars of the verbal arts propose their own, which in, e.g., sociology, stresses common knowledge. In linguistics, features that distinguish the language from common dialogue (linguists), and in the verbal arts features of form and content that define art (folklorists)."Ki-Zerbo, Joseph: "Methodology and African Pre-history", 1990, ''UNESCO International Scientific Committee for the Drafting of a G ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Curaçao
Curaçao, officially the Country of Curaçao, is a constituent island country within the Kingdom of the Netherlands, located in the southern Caribbean Sea (specifically the Dutch Caribbean region), about north of Venezuela. Curaçao includes the main island of Curaçao and the much smaller, uninhabited island of Klein Curaçao ("Little Curaçao"). Curaçao has a population of 158,665 (January 2019 estimate), with an area of ; its capital is Willemstad. Together with Aruba and Bonaire, Curaçao forms the ABC islands (Leeward Antilles), ABC islands. Collectively, Curaçao, Aruba, and other Dutch islands in the Caribbean are often called the Dutch Caribbean. It is the largest of the ABC islands in terms of area, as well as in terms of population, and is the largest in the Dutch Caribbean. The island's name "Curaçao" may originate from the indigenous autonym of its people; this idea is supported by early Spanish accounts referring to the inhabitants as Indios Curaçaos. Curaç ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tano (Tano Akora)
Tano (Tanoɛ), whose true name is Ta Kora (abbreviated from Tano Kora/Akora, not to be confused with Tano Akora) and is known as Tando to the Fante is the Abosom of war and strife in Akan mythology and Abosom of Thunder and Lightning in the Asante mythology of Ghana as well as the Agni mythology of the Ivory Coast. He represents the Tano River, which is located in Ghana. He is regarded as the highest and king of all Obosom. The Tano abosom are his sons in Akan mythology. Names and epithets Tano is commonly as ''Kora'', ''Ta Akora'', ''Tano Kora'' and/or ''Tano Akora'' in the Techiman-Bono area. The name ''Ta Kora'' most likely means the “immense father' as “kora” means "the immense" and “ta” may be derived from a word meaning "father", stemming from how he is the father of a majority of the abosom. "Kora" can also mean "to mend", which means the name can also translate to "Tano The Mender” or "Tano The Healer”, referencing his healing abilities. Another name for th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Akan Language
Akan (), or Twi-Fante, is the most populous language of Ghana, and the principal native language of the Akan people, spoken over much of the southern half of Ghana. About 80% of Ghana's population speak Akan as a first or second language, and about 44% of Ghanaians are native speakers. The Bono dialect is also spoken across the border in Ivory Coast. Three dialects were developed as literary standards with distinct orthographies: Asante and Akuapem, collectively known as Twi, and Fante. Despite being mutually intelligible, they were inaccessible in written form to speakers of the other standards until the Akan Orthography Committee (AOC)'s development of a common Akan orthography in 1978, based mainly on Akuapem dialect. As the first Akan variety to be used for Bible translation, Akuapem had become the prestige dialect. With the Atlantic slave trade, Akan languages were introduced to the Caribbean and South America, notably in Suriname, spoken by the Ndyuka, and i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |